Lecture #5
... Molecularity: The number of molecules in the activated complex. Thermodynamics tells only that Ea > H. III D. KINETIC THEORY OF GASES When molecules in the gas phase collide they sometimes rearrange their chemical bonds to form new molecules. The rate of formation of the new molecules is determined ...
... Molecularity: The number of molecules in the activated complex. Thermodynamics tells only that Ea > H. III D. KINETIC THEORY OF GASES When molecules in the gas phase collide they sometimes rearrange their chemical bonds to form new molecules. The rate of formation of the new molecules is determined ...
Enthalpy
... The additional energy required by the system gets absorbed from the rest of the system as heat causing the molecules to move slower (less kinetic energy) and the temperature to decrease. ...
... The additional energy required by the system gets absorbed from the rest of the system as heat causing the molecules to move slower (less kinetic energy) and the temperature to decrease. ...
enthalpy of reaction
... The additional energy required by the system gets absorbed from the rest of the system as heat causing the molecules to move slower (less kinetic energy) and the temperature to decrease. ...
... The additional energy required by the system gets absorbed from the rest of the system as heat causing the molecules to move slower (less kinetic energy) and the temperature to decrease. ...
Reactants Products
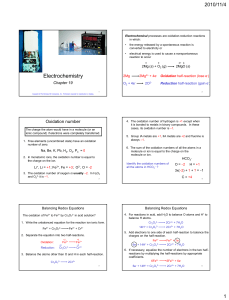
... Reaction Rate and Stoichiometry • In most reactions, the coefficients of the balanced equation are not all the same. H2 (g) + I2 (g) 2 HI(g) • For these reactions, the change in the number of molecules of one substance is a multiple of the change in the number of molecules of another. – For the ab ...
... Reaction Rate and Stoichiometry • In most reactions, the coefficients of the balanced equation are not all the same. H2 (g) + I2 (g) 2 HI(g) • For these reactions, the change in the number of molecules of one substance is a multiple of the change in the number of molecules of another. – For the ab ...
Physical Chemistry (SCQF level 7)
... within the contexts of chemical equilibrium, feasibility of chemical reactions and reaction kinetics. The Unit should develop the candidate’s knowledge and understanding of some of the major concepts used to explain chemical behaviour. The Unit also seeks to develop the candidate’s problem solving a ...
... within the contexts of chemical equilibrium, feasibility of chemical reactions and reaction kinetics. The Unit should develop the candidate’s knowledge and understanding of some of the major concepts used to explain chemical behaviour. The Unit also seeks to develop the candidate’s problem solving a ...
Slajd 1
... forth between states along the same path. When 1 mol of water is frozen at 1 atm at 0 °C to form 1 mol of ice, q = ∆Hvap of heat is removed. To reverse the process, q = ∆Hvap must be added to the 1 mol of ice at 0°C and 1 atm to form 1 mol of water at 0 °C ...
... forth between states along the same path. When 1 mol of water is frozen at 1 atm at 0 °C to form 1 mol of ice, q = ∆Hvap of heat is removed. To reverse the process, q = ∆Hvap must be added to the 1 mol of ice at 0°C and 1 atm to form 1 mol of water at 0 °C ...
E 0
... Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. ...
... Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. ...