Examination of Physiology Class_____ Name_____________
... 4.SystoIic Pressure:: The highest value of aortic blood pressure in systole. 1.The smooth muscle membrane automatically and slowly, depolarizes and repolarizes in a cyclic fashion, these electric activity is called the basic electric rhythm 2.The hormones which are secreted at nerve endings of pepti ...
... 4.SystoIic Pressure:: The highest value of aortic blood pressure in systole. 1.The smooth muscle membrane automatically and slowly, depolarizes and repolarizes in a cyclic fashion, these electric activity is called the basic electric rhythm 2.The hormones which are secreted at nerve endings of pepti ...
Animal form and function
... Basal metabolic rate: at rest Endotherm: 1,600 – 2,000Kcal/day Maximum rate: can not sustain for long Use: ATP that’s already present Then make some anaerobically by glycolysis Start to break down glycogen in liver and muscle cells ...
... Basal metabolic rate: at rest Endotherm: 1,600 – 2,000Kcal/day Maximum rate: can not sustain for long Use: ATP that’s already present Then make some anaerobically by glycolysis Start to break down glycogen in liver and muscle cells ...
Chapter 4 Outline
... (2) Abnormal GABA levels associated with sleep and eating disorders and convulsive disorders (3) Loss of cells that produce acetylcholine associated with Alzheimer’s disease e. Each neurotransmitter plays many roles and functions overlap f. Cause and effect between neurotransmitters and behavior unc ...
... (2) Abnormal GABA levels associated with sleep and eating disorders and convulsive disorders (3) Loss of cells that produce acetylcholine associated with Alzheimer’s disease e. Each neurotransmitter plays many roles and functions overlap f. Cause and effect between neurotransmitters and behavior unc ...
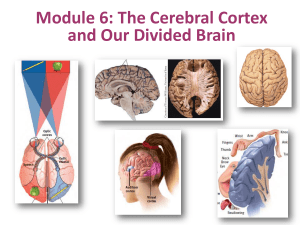
Frontal Lobes
... that opposite side. Without the corpus callosum, the halves of the body and the halves of the visual field do ...
... that opposite side. Without the corpus callosum, the halves of the body and the halves of the visual field do ...
Brain PowerPoint
... “learn,” by growing more synaptic connections and increasing dendritic branching - INCREMENTAL NOT FIXED! ...
... “learn,” by growing more synaptic connections and increasing dendritic branching - INCREMENTAL NOT FIXED! ...
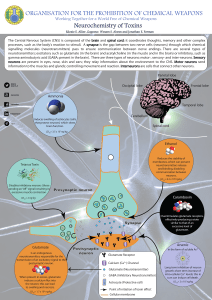
Working Together for a World Free of Chemical Weapons
... Is an endogenous neurotransmitter, responsible for the transmission of an excitatory signal to the postsynaptic neuron. ...
... Is an endogenous neurotransmitter, responsible for the transmission of an excitatory signal to the postsynaptic neuron. ...
Biological and Psychology Why are psychologists concerned about
... Neurotransmitters – chemicals that transmit information from one neuron to another. Stored in small sacs within the terminal buttons Nerve impulse triggers their release Over 50 have been identified Major ones are described in the text Drugs and Neurotransmitters Agonist – mimics or enhanc ...
... Neurotransmitters – chemicals that transmit information from one neuron to another. Stored in small sacs within the terminal buttons Nerve impulse triggers their release Over 50 have been identified Major ones are described in the text Drugs and Neurotransmitters Agonist – mimics or enhanc ...
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM
... Electrical impulse transmission Gap between neuron and a muscle or between two neurons ...
... Electrical impulse transmission Gap between neuron and a muscle or between two neurons ...
Biology of the Mind
... gyrus leaves the person able to speak and understand but unable to read. Research indicates that neural tissue can reorganize in response to injury or damage. When one brain area is damaged, others may in time take over some of its function. For example, if neurons are destroyed as the result of a ...
... gyrus leaves the person able to speak and understand but unable to read. Research indicates that neural tissue can reorganize in response to injury or damage. When one brain area is damaged, others may in time take over some of its function. For example, if neurons are destroyed as the result of a ...
Topic: Nervous system Reading: Chapter 38 Main concepts
... • Nerve signals involve the concentration of potassium and sodium ions on either side of the cell membrane. The signal is conducted when ion channels open briefly in a “wave” down the cell, allowing sodium and potassium to switch sides. • The synapse is a small gap between two neurons, and is bridge ...
... • Nerve signals involve the concentration of potassium and sodium ions on either side of the cell membrane. The signal is conducted when ion channels open briefly in a “wave” down the cell, allowing sodium and potassium to switch sides. • The synapse is a small gap between two neurons, and is bridge ...
The Structures of the Brain
... activities like eating, drinking, body temperature, and control of emotions. - It helps govern the endocrine system via the pituitary gland. - Monitors reward activities - Eating, Drinking, and Sex -Emotion, Stress, and Reward ...
... activities like eating, drinking, body temperature, and control of emotions. - It helps govern the endocrine system via the pituitary gland. - Monitors reward activities - Eating, Drinking, and Sex -Emotion, Stress, and Reward ...
The Brain
... = the brain’s sensory switchboard, located on top of the brainstem; it directs messages to the sensory receiving areas in the cortex and transmits replies to the cerebellum and medulla. ...
... = the brain’s sensory switchboard, located on top of the brainstem; it directs messages to the sensory receiving areas in the cortex and transmits replies to the cerebellum and medulla. ...
Seminar Slides
... Synapse - point where the axon of one neuron connects to a dendrite of another Electrical synapse - two cells touch and are connected by tiny holes, which lets the nerve impulse pass directly from one neuron to the other Chemical synapse - two cells do not touch and the nerve impulse needs par ...
... Synapse - point where the axon of one neuron connects to a dendrite of another Electrical synapse - two cells touch and are connected by tiny holes, which lets the nerve impulse pass directly from one neuron to the other Chemical synapse - two cells do not touch and the nerve impulse needs par ...
Neuron and Brain Review Handout
... Lesions: Destruction of brain tissue (Phineas Gage) EEG (electroencephalogram): amplified recordings of brain wave activity. CT (computerized tomography) scan: X-ray photos of slices of the brain. CT (or CAT) scans show structures within the brain but not functions of the brain. PET (positron emissi ...
... Lesions: Destruction of brain tissue (Phineas Gage) EEG (electroencephalogram): amplified recordings of brain wave activity. CT (computerized tomography) scan: X-ray photos of slices of the brain. CT (or CAT) scans show structures within the brain but not functions of the brain. PET (positron emissi ...
HW CH 5 PSY 2513 Submit your answers on canvas
... In a highly plastic cerebral cortex, a. the areas of the brain are strongly committed to specific functions, and there is a high capacity for learning. b. if a part of the cortex is damaged, other parts can take over the tasks it would have handled. c. spatial skills develop more rapidly than langua ...
... In a highly plastic cerebral cortex, a. the areas of the brain are strongly committed to specific functions, and there is a high capacity for learning. b. if a part of the cortex is damaged, other parts can take over the tasks it would have handled. c. spatial skills develop more rapidly than langua ...
Unit N Notes #1 – The Central Nervous System - Mr. Lesiuk
... Bones including the skull and vertebrae primarily protect the CNS from trauma. The brain and spine are also wrapped in three layers of protective membranes, which form the Meninges, in between these layers cerebro-spinal fluid is present to further cushion the CNS. A) Spinal Cord: i) Function1. To r ...
... Bones including the skull and vertebrae primarily protect the CNS from trauma. The brain and spine are also wrapped in three layers of protective membranes, which form the Meninges, in between these layers cerebro-spinal fluid is present to further cushion the CNS. A) Spinal Cord: i) Function1. To r ...
Neuroscience, Genetics and Behavior
... Vogel and Bogen performed surgery on a patient with epilepsy Patient acted normal afterward personality and intellect hardly affected Sperry and Gazzaniga noticed patients who had surgery developed changes in perception and speech ...
... Vogel and Bogen performed surgery on a patient with epilepsy Patient acted normal afterward personality and intellect hardly affected Sperry and Gazzaniga noticed patients who had surgery developed changes in perception and speech ...
Nervous System Notes PP
... Example: receptors throughout the body are constantly sensing temperature, if the temperature deviates away from the average 98.6º F, neurons take the information to the hypothalamus in the brain and the information is interpreted, then a response in sent to parts of the body to react in a specific ...
... Example: receptors throughout the body are constantly sensing temperature, if the temperature deviates away from the average 98.6º F, neurons take the information to the hypothalamus in the brain and the information is interpreted, then a response in sent to parts of the body to react in a specific ...
International Baccalaureate Biology Option
... Controls speech. Damage to this area results in the person knowing what they want to say but they can only make sounds and are unable to make meaningful words and sentences. ...
... Controls speech. Damage to this area results in the person knowing what they want to say but they can only make sounds and are unable to make meaningful words and sentences. ...
Function of plasma proteins
... 3-Blood coagulation :- is a complex process in the blood is converted in to a thicken gall . Blood coagulation involves three basic stages :stage 1 :- Formation of prothrombin activator . This stage is initiated by one of two mechanisms :a. Extrinsic pathway of blood clotting . b. Intrinsic pathway ...
... 3-Blood coagulation :- is a complex process in the blood is converted in to a thicken gall . Blood coagulation involves three basic stages :stage 1 :- Formation of prothrombin activator . This stage is initiated by one of two mechanisms :a. Extrinsic pathway of blood clotting . b. Intrinsic pathway ...
Haemodynamic response
In haemodynamics, the body must respond to physical activities, external temperature, and other factors by homeostatically adjusting its blood flow to deliver nutrients such as oxygen and glucose to stressed tissues and allow them to function. Haemodynamic response (HR) allows the rapid delivery of blood to active neuronal tissues. Since higher processes in the brain occur almost constantly, cerebral blood flow is essential for the maintenance of neurons, astrocytes, and other cells of the brain.