AP Psychology
... 5. Using figure 2.3 on page 49, explain how neurons communicate. Be sure to include synapse and neurotransmitters in your response. 6. Describe each of the following neurotransmitters: a. dopamine b. serotonin c. norepinephrine d. (GABA) Gamma-amniobutyric acid e. acetylcholine (Ach) 7. What are the ...
... 5. Using figure 2.3 on page 49, explain how neurons communicate. Be sure to include synapse and neurotransmitters in your response. 6. Describe each of the following neurotransmitters: a. dopamine b. serotonin c. norepinephrine d. (GABA) Gamma-amniobutyric acid e. acetylcholine (Ach) 7. What are the ...
• Main Function: It releases hormones into the blood to It releases
... Axons branching out to muscle fibers ...
... Axons branching out to muscle fibers ...
The Nervous System
... The AXON carries impulses away from the cell body. The axon is covered in a membrane called the MYELIN SHEATH. There are gaps in the myelin sheath, called NODES. The signal can jump from node to node, increasing the speed of the impulse. ...
... The AXON carries impulses away from the cell body. The axon is covered in a membrane called the MYELIN SHEATH. There are gaps in the myelin sheath, called NODES. The signal can jump from node to node, increasing the speed of the impulse. ...
Neuroscience and Behavior
... Electroencephalogram (EEG) An amplified recording of the electrical waves sweeping across the brain’s surface, measured by electrodes placed on the scalp. ...
... Electroencephalogram (EEG) An amplified recording of the electrical waves sweeping across the brain’s surface, measured by electrodes placed on the scalp. ...
Using Breakthroughs in Visual Neuroscience to
... human medical applications. Studies using an array of electrodes implanted in the brain show that monkeys can use their visual system to control an artificial limb remotely, by mental control alone.1 If this ability holds true in humans, it could dramatically improve sensory substitution treatments ...
... human medical applications. Studies using an array of electrodes implanted in the brain show that monkeys can use their visual system to control an artificial limb remotely, by mental control alone.1 If this ability holds true in humans, it could dramatically improve sensory substitution treatments ...
Basic Brain Facts - The Practice of Parenting
... through electrical and chemical signals. • Strong connections between neurons are made when we do things again and again, and when we have big feelings while we experience something. • Our brains are shaped by our biology (genes), our environment, and our experiences. • The way we are with each othe ...
... through electrical and chemical signals. • Strong connections between neurons are made when we do things again and again, and when we have big feelings while we experience something. • Our brains are shaped by our biology (genes), our environment, and our experiences. • The way we are with each othe ...
Test 5 Study Guide
... The sympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system (thoracolumbar division) functions during “fight or flight.” During sympathetic activation, elevated heart rate, elevated blood pressure, sweating, elevated blood glucose , dilation of the pupils, increased blood flow to skeletal muscles. Post ...
... The sympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system (thoracolumbar division) functions during “fight or flight.” During sympathetic activation, elevated heart rate, elevated blood pressure, sweating, elevated blood glucose , dilation of the pupils, increased blood flow to skeletal muscles. Post ...
Spastic cerebral palsy (spasticity) This is caused by impairment in
... leading to a decreased range of movement in the joints. The effects may increase with anxiety or increased effort, leading to excessive fatigue. Athetoid or dystonic, also known as dyskinetic cerebral palsy (athetosis) This is caused by impairment in the basal ganglia area of the brain. It is charac ...
... leading to a decreased range of movement in the joints. The effects may increase with anxiety or increased effort, leading to excessive fatigue. Athetoid or dystonic, also known as dyskinetic cerebral palsy (athetosis) This is caused by impairment in the basal ganglia area of the brain. It is charac ...
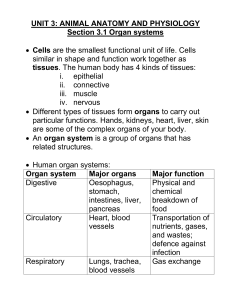
unit 3: animal anatomy and physiology
... Cells are the smallest functional unit of life. Cells similar in shape and function work together as tissues. The human body has 4 kinds of tissues: i. epithelial ii. connective iii. muscle iv. nervous Different types of tissues form organs to carry out particular functions. Hands, kidneys, hear ...
... Cells are the smallest functional unit of life. Cells similar in shape and function work together as tissues. The human body has 4 kinds of tissues: i. epithelial ii. connective iii. muscle iv. nervous Different types of tissues form organs to carry out particular functions. Hands, kidneys, hear ...
Basic Neuroscience Series: Introduction and Series Overview
... How the knowledge of some esoteric anatomic, cellular or signaling process may help you treat a patient ...
... How the knowledge of some esoteric anatomic, cellular or signaling process may help you treat a patient ...
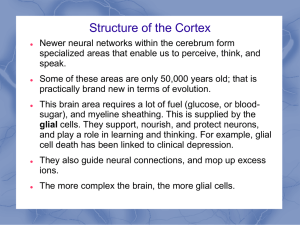
Module 6 The Cerebral Cortex and Our Divided Brain
... This brain area requires a lot of fuel (glucose, or bloodsugar), and myeline sheathing. This is supplied by the glial cells. They support, nourish, and protect neurons, and play a role in learning and thinking. For example, glial cell death has been linked to clinical depression. They also guide neu ...
... This brain area requires a lot of fuel (glucose, or bloodsugar), and myeline sheathing. This is supplied by the glial cells. They support, nourish, and protect neurons, and play a role in learning and thinking. For example, glial cell death has been linked to clinical depression. They also guide neu ...
Chapter Two
... • Uses the detection of radio frequency signals produced by displaced radio waves in a magnetic field • Creates a detailed anatomical image of the brain ...
... • Uses the detection of radio frequency signals produced by displaced radio waves in a magnetic field • Creates a detailed anatomical image of the brain ...
xpx tampa bay
... XPX TAMPA BAY The Self Aware Advisor: The Key to Seeing and influencing Others September 11, 2013 ...
... XPX TAMPA BAY The Self Aware Advisor: The Key to Seeing and influencing Others September 11, 2013 ...
BSC1005 400 – Assignment I
... 3. Explain the structure of the plasma membrane. Include descriptions of the proteins present and the reason some substances pass through while others do not. 4. Give the relationship between the endoplasmic reticulum, the golgi apparatus and lysosomes. Detail the function of each one. 5. Describe t ...
... 3. Explain the structure of the plasma membrane. Include descriptions of the proteins present and the reason some substances pass through while others do not. 4. Give the relationship between the endoplasmic reticulum, the golgi apparatus and lysosomes. Detail the function of each one. 5. Describe t ...
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE CONTACT: Name Institution Telephone
... This new noninvasive approach uses a unique radiopharmaceutical imaging agent in combination with Siemens' Biograph mCT PET•CT family of scanners and proprietary neurology quantification software.* The radiopharmaceutical helps physicians visualize protein deposits in the brain called amyloid plaque ...
... This new noninvasive approach uses a unique radiopharmaceutical imaging agent in combination with Siemens' Biograph mCT PET•CT family of scanners and proprietary neurology quantification software.* The radiopharmaceutical helps physicians visualize protein deposits in the brain called amyloid plaque ...
Chapter 2 Notes
... • Structures are part of Limbic System: System within forebrain closely linked to ...
... • Structures are part of Limbic System: System within forebrain closely linked to ...
Ms. Setzer-The Brain!
... The functional MRI scan shows the auditory cortex is active in patients who hallucinate. ...
... The functional MRI scan shows the auditory cortex is active in patients who hallucinate. ...
Quiz - psychm5
... Scott was challenged to catch a dollar bill as fast as he could with his thumb and index finger as it fell between the. Scott was successful one time out of five trials. Which statement best explains why Scott failed to catch the dollar bill? a. Scott’s injury to the temporal lobe has caused him to ...
... Scott was challenged to catch a dollar bill as fast as he could with his thumb and index finger as it fell between the. Scott was successful one time out of five trials. Which statement best explains why Scott failed to catch the dollar bill? a. Scott’s injury to the temporal lobe has caused him to ...
The Brain & Cerebral Hemispheres
... The maps show that regions of the body with many sensory (or _______) neurons have corresponding large areas of the _______ linked to them. ...
... The maps show that regions of the body with many sensory (or _______) neurons have corresponding large areas of the _______ linked to them. ...
Developmental plasticity: Pruning
... They regulate the number of neurons at early developmental stages by dynamically influencing neural precursor divisions, and at later stages by promoting neuronal cell death through engulfment. Glia also participate in the fine sculpting of neuronal connections by pruning excess axonal projections, ...
... They regulate the number of neurons at early developmental stages by dynamically influencing neural precursor divisions, and at later stages by promoting neuronal cell death through engulfment. Glia also participate in the fine sculpting of neuronal connections by pruning excess axonal projections, ...
Haemodynamic response
In haemodynamics, the body must respond to physical activities, external temperature, and other factors by homeostatically adjusting its blood flow to deliver nutrients such as oxygen and glucose to stressed tissues and allow them to function. Haemodynamic response (HR) allows the rapid delivery of blood to active neuronal tissues. Since higher processes in the brain occur almost constantly, cerebral blood flow is essential for the maintenance of neurons, astrocytes, and other cells of the brain.