The Nervous System
... Understand common conditions that may affect the Nervous System. Identify nursing care specific to each condition. ...
... Understand common conditions that may affect the Nervous System. Identify nursing care specific to each condition. ...
Step back and look at the Science
... See what disabilities result from specific physical damage In humans wait for accident In animals do damage deliberately ...
... See what disabilities result from specific physical damage In humans wait for accident In animals do damage deliberately ...
Unit 3A Notes
... return to the original neuron and are ready again. 4. How neurotransmitters influence us 1. Neurotransmitters affect people in many ways such as: depression, happiness, hunger, thinking, addictions, and therapy. 2. An example is acetylcholine (ACh). ACh tells muscles to contract. When it’s blocked ( ...
... return to the original neuron and are ready again. 4. How neurotransmitters influence us 1. Neurotransmitters affect people in many ways such as: depression, happiness, hunger, thinking, addictions, and therapy. 2. An example is acetylcholine (ACh). ACh tells muscles to contract. When it’s blocked ( ...
Systems and Balance in Organisms PAP Biology Test
... biconvex shape to move freely through blood vessels; they contain hemoglobin which carries oxygen molecules to cells d. Muscle cell – these cells form bundles and contain proteins (actin and myosin) that overlap to allow for contraction of cell e. Cells of small intestine – cells have structures cal ...
... biconvex shape to move freely through blood vessels; they contain hemoglobin which carries oxygen molecules to cells d. Muscle cell – these cells form bundles and contain proteins (actin and myosin) that overlap to allow for contraction of cell e. Cells of small intestine – cells have structures cal ...
Flight Physiology
... • The link between the heart, lungs, brain, and other parts (blood vessels) • Function: To maintain blood supply to all tissues of the body ...
... • The link between the heart, lungs, brain, and other parts (blood vessels) • Function: To maintain blood supply to all tissues of the body ...
File - Mrs. Walston Science
... a complex collection of nerves and specialized cells known as neurons that transmit signals between different parts of the body. It is essentially the body’s electrical wiring. ...
... a complex collection of nerves and specialized cells known as neurons that transmit signals between different parts of the body. It is essentially the body’s electrical wiring. ...
Nervous System
... Ecstasy essentially takes these upkeep transporters and reverses their roles. This causes a massive flood of serotonin from the brain cells into the synapse. ...
... Ecstasy essentially takes these upkeep transporters and reverses their roles. This causes a massive flood of serotonin from the brain cells into the synapse. ...
File
... Receptors are special nerve endings found within our skin and include: touch, pain, pressure and temperature receptors. It is their job to detect changes in the environment. These changes, known as stimuli may include temperature changes, pain or pressure, are carried in the form of electrical impul ...
... Receptors are special nerve endings found within our skin and include: touch, pain, pressure and temperature receptors. It is their job to detect changes in the environment. These changes, known as stimuli may include temperature changes, pain or pressure, are carried in the form of electrical impul ...
C48 Nervous System
... Synaptic terminals – specialized endings of the axons which relay signals to other cells by releasing neurotransmitters (chemical messengers). Synapse – junction between neurons or to a muscle or gland cell. Membrane potential – voltage measured across the plasma membrane from differences in ion ...
... Synaptic terminals – specialized endings of the axons which relay signals to other cells by releasing neurotransmitters (chemical messengers). Synapse – junction between neurons or to a muscle or gland cell. Membrane potential – voltage measured across the plasma membrane from differences in ion ...
Older Adulthood Physical And Cognitive Development
... lipofusein, accumulate in blood and muscle cells. Eventually, these substances take up space and slow down normal cell processes. ...
... lipofusein, accumulate in blood and muscle cells. Eventually, these substances take up space and slow down normal cell processes. ...
Chapter 3
... environment 2. motor neurons – send information from brain to parts of body 3. interneurons – intermediaries between motor and sensory neurons; receive and send information b. parts of the neuron (diagram p. 48) c. glial cells – hold neurons in place; care and feeding of neurons ...
... environment 2. motor neurons – send information from brain to parts of body 3. interneurons – intermediaries between motor and sensory neurons; receive and send information b. parts of the neuron (diagram p. 48) c. glial cells – hold neurons in place; care and feeding of neurons ...
The Brain, Biology, and Behavior Neuron
... A highly magnified view of the synapse. Neurotransmitters are stored in tiny sacs called synaptic vesicles. When a nerve impulse arrives at an axon terminal, the vesicles move to the surface and release neurotransmitters. These transmitter molecules cross the synaptic gap to affect the next neuron. ...
... A highly magnified view of the synapse. Neurotransmitters are stored in tiny sacs called synaptic vesicles. When a nerve impulse arrives at an axon terminal, the vesicles move to the surface and release neurotransmitters. These transmitter molecules cross the synaptic gap to affect the next neuron. ...
An Integrative Approach to Psychopathology - Home
... Frontal – Thinking and reasoning abilities, memory ...
... Frontal – Thinking and reasoning abilities, memory ...
History and Methods
... EEG: Scalp electrodes. Very small potentials when neurons are active. But because there are a lot of neurons and because neighboring neurons frequently are active close together in time we can pick up signal. ERP: time-locking the recording of the EEG to the onset of events (such as a person reading ...
... EEG: Scalp electrodes. Very small potentials when neurons are active. But because there are a lot of neurons and because neighboring neurons frequently are active close together in time we can pick up signal. ERP: time-locking the recording of the EEG to the onset of events (such as a person reading ...
The Human Brain - Peoria Public Schools
... The anterior part of the neural tube expands to form the brain. • Define cephalizationa. The development of the head region. • State the number of neurons in the human brain. a. 86 Billion • Describe the advantage of having a brain. a. Communication between the billions of neurons is more rapid tha ...
... The anterior part of the neural tube expands to form the brain. • Define cephalizationa. The development of the head region. • State the number of neurons in the human brain. a. 86 Billion • Describe the advantage of having a brain. a. Communication between the billions of neurons is more rapid tha ...
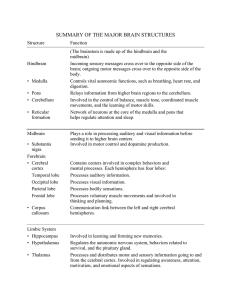
SUMMARY OF THE MAJOR BRAIN STRUCTURES
... Incoming sensory messages cross over to the opposite side of the brain; outgoing motor messages cross over to the opposite side of the body. Controls vital autonomic functions, such as breathing, heart rate, and digestion. Relays information from higher brain regions to the cerebellum. Involved in t ...
... Incoming sensory messages cross over to the opposite side of the brain; outgoing motor messages cross over to the opposite side of the body. Controls vital autonomic functions, such as breathing, heart rate, and digestion. Relays information from higher brain regions to the cerebellum. Involved in t ...
Introduction to Psychology
... a nerve network in the brainstem plays an important role in controlling arousal ...
... a nerve network in the brainstem plays an important role in controlling arousal ...
A1984SR69800001
... substances. By more precise electrophysiological techniques, it became possible to release minute amounts of various substances from microelectrodes inserted into the brain and spinal cord and thus examine their effects on individual nerve cells. Numerous such ‘iontophoretic’ studies revealed widesp ...
... substances. By more precise electrophysiological techniques, it became possible to release minute amounts of various substances from microelectrodes inserted into the brain and spinal cord and thus examine their effects on individual nerve cells. Numerous such ‘iontophoretic’ studies revealed widesp ...
The Great Brain Drain Review
... Schizophrenia and Parkinson’s disease are both caused by an imbalance of the chemical, dopamine in the brain. When we experience extreme pain, the body releases endorphins. acetylcholine is the chemical found at neuromuscular junctions. The poison of a black widow spider affects it by mimicking it. ...
... Schizophrenia and Parkinson’s disease are both caused by an imbalance of the chemical, dopamine in the brain. When we experience extreme pain, the body releases endorphins. acetylcholine is the chemical found at neuromuscular junctions. The poison of a black widow spider affects it by mimicking it. ...
Neuron encyclopaedia fires up to reveal brain secrets
... or the tens of billions in the human one. “There are too many neurons in the brain, and we have only sampled a very, very small set,” says the Allen Institute’s Hanchuan Peng, who is leading the BigNeuron project. A major bottleneck in cataloguing more neurons has been extracting the three-dimension ...
... or the tens of billions in the human one. “There are too many neurons in the brain, and we have only sampled a very, very small set,” says the Allen Institute’s Hanchuan Peng, who is leading the BigNeuron project. A major bottleneck in cataloguing more neurons has been extracting the three-dimension ...
Nervous and Endocrine Systems
... Midbrain and Pons = pathways connecting various parts of the brain with each other Medulla = controls involuntary actions ...
... Midbrain and Pons = pathways connecting various parts of the brain with each other Medulla = controls involuntary actions ...
Biopsychology The Nervous System
... AP students in psychology should be able to do the following: • Identify basic processes and systems in the biological bases of behavior, including parts of the neuron and the process of transmission of a signal between neurons (pp. 5556). • Discuss the influence of drugs on neurotransmitters ( ...
... AP students in psychology should be able to do the following: • Identify basic processes and systems in the biological bases of behavior, including parts of the neuron and the process of transmission of a signal between neurons (pp. 5556). • Discuss the influence of drugs on neurotransmitters ( ...
Haemodynamic response
In haemodynamics, the body must respond to physical activities, external temperature, and other factors by homeostatically adjusting its blood flow to deliver nutrients such as oxygen and glucose to stressed tissues and allow them to function. Haemodynamic response (HR) allows the rapid delivery of blood to active neuronal tissues. Since higher processes in the brain occur almost constantly, cerebral blood flow is essential for the maintenance of neurons, astrocytes, and other cells of the brain.