Biological populations and communities
... Ecosystems and the organisms within them are constantly changing. These changes occur because living organisms within the ecosystem face varying stresses from both living and non-living factors in the environment. Living things must respond to those stresses and their response changes not only the a ...
... Ecosystems and the organisms within them are constantly changing. These changes occur because living organisms within the ecosystem face varying stresses from both living and non-living factors in the environment. Living things must respond to those stresses and their response changes not only the a ...
Barlow`s Brain Busters 5
... 9. Summarise the meaning of an organisms niche by reference to the physical, chemical, biological, spatial (space) and temporal (time) factors that the organism needs to survive. ...
... 9. Summarise the meaning of an organisms niche by reference to the physical, chemical, biological, spatial (space) and temporal (time) factors that the organism needs to survive. ...
BIO100 KEY CONCEPTS and TIDEPOOLS-
... Nutrient Cycling: an example showing interactions between physical environment and living things • nutrients pass from one organism to the next through feeding and are then cycled back through the ecosystem ...
... Nutrient Cycling: an example showing interactions between physical environment and living things • nutrients pass from one organism to the next through feeding and are then cycled back through the ecosystem ...
Chapter 5 (Populations) Test A
... ____ 9. If a population grows larger than the carrying capacity of the environment, the a. death rate may rise. c. death rate must fall. b. birthrate may rise. d. birthrate must fall. ____10. Which would be least likely to be affected by a densitydependent limiting factor? a. a small, scattered popu ...
... ____ 9. If a population grows larger than the carrying capacity of the environment, the a. death rate may rise. c. death rate must fall. b. birthrate may rise. d. birthrate must fall. ____10. Which would be least likely to be affected by a densitydependent limiting factor? a. a small, scattered popu ...
A is for Abundance:
... exclusion of one species from the habitat by another, or to a joint population where the competing species manage to coexist. A strong interspecific competitor will invariably out-compete a weak interspecific competitor. Without competitors a species may occupy its “fundamental niche.” In the presen ...
... exclusion of one species from the habitat by another, or to a joint population where the competing species manage to coexist. A strong interspecific competitor will invariably out-compete a weak interspecific competitor. Without competitors a species may occupy its “fundamental niche.” In the presen ...
Chapter 5 - Mr. Carlson`s Science 8
... parasite can contribute to biodiversity by controlling the size of specific species populations. 2. Mutualism is a relationship that benefits both species; these benefits can be in dispersing pollen and seeds for reproduction, in receiving food, or in receiving protection. a. Mutualism is not cooper ...
... parasite can contribute to biodiversity by controlling the size of specific species populations. 2. Mutualism is a relationship that benefits both species; these benefits can be in dispersing pollen and seeds for reproduction, in receiving food, or in receiving protection. a. Mutualism is not cooper ...
Chapter 13
... affect them. Between them, these factors place an upper limit on the size of the population that can be sustained. This upper limit is known as the carrying capacity of that particular area. You could imagine what might happen if some thrushes were introduced into a suitable area where there had pre ...
... affect them. Between them, these factors place an upper limit on the size of the population that can be sustained. This upper limit is known as the carrying capacity of that particular area. You could imagine what might happen if some thrushes were introduced into a suitable area where there had pre ...
Community Structure Symbiosis Succession
... May not provide useful information about ecology of a community (e.g., abundance or physical structure may have more significance than richness). ...
... May not provide useful information about ecology of a community (e.g., abundance or physical structure may have more significance than richness). ...
species richness - Green Resistance
... -- review -• Every population exists within a web of interactions • with other populations • across several trophic levels ...
... -- review -• Every population exists within a web of interactions • with other populations • across several trophic levels ...
ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING
... It consists of the following stages: Installing ___________________ or nets in the populated region Counting the ____________________ animals and __________________ them with ________________, _________________, __________________ or ___________________ _______________________ the marked anima ...
... It consists of the following stages: Installing ___________________ or nets in the populated region Counting the ____________________ animals and __________________ them with ________________, _________________, __________________ or ___________________ _______________________ the marked anima ...
Evaluating condition-specific and asymmetric competition in a
... resulting in the competitive exclusion of a subordinate species when it occurs in the presence of a dominant species (Morin 1999). A few researchers have invoked conditionspecific competition as an explanation for parapatric (largely allopatric but slightly overlapping) distributions of closely rela ...
... resulting in the competitive exclusion of a subordinate species when it occurs in the presence of a dominant species (Morin 1999). A few researchers have invoked conditionspecific competition as an explanation for parapatric (largely allopatric but slightly overlapping) distributions of closely rela ...
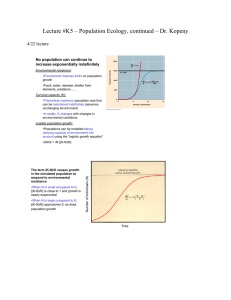
Lecture #K5 – Population Ecology, continued – Dr
... likely to be found in variable environments in which population densities fluctuate, or in “open” habitats where individuals likely to face little competition •“K-selected populations” likely to be living at a density near the limit imposed by their resources •Life history traits do often vary in wa ...
... likely to be found in variable environments in which population densities fluctuate, or in “open” habitats where individuals likely to face little competition •“K-selected populations” likely to be living at a density near the limit imposed by their resources •Life history traits do often vary in wa ...
AP Project (Final)highbaugh
... 6. Only 10% of energy is transferred through trophic levels 7.Primary succession occurs in a lifeless area; Secondary succession occurs when an existing community has been cleared 8. Closer islands have lower extinction rates and higher immigration rates ...
... 6. Only 10% of energy is transferred through trophic levels 7.Primary succession occurs in a lifeless area; Secondary succession occurs when an existing community has been cleared 8. Closer islands have lower extinction rates and higher immigration rates ...
06_3eIG - ThilowAPES
... 2. Many parasites live in close contact with their hosts, such as disease pathogens, tapeworms, ticks, and lamprey. 3. Other types of parasites are free-living and come into contact with their hosts only infrequently (e.g., nest parasites such as cuckoos and cowbirds). 4. Some parasites cause little ...
... 2. Many parasites live in close contact with their hosts, such as disease pathogens, tapeworms, ticks, and lamprey. 3. Other types of parasites are free-living and come into contact with their hosts only infrequently (e.g., nest parasites such as cuckoos and cowbirds). 4. Some parasites cause little ...
IJEE SOAPBOX: PRINCE KROPOTKIN MEETS THE
... In this essay, I reflect on how community ecology seems to be going through a comparable intellectual transformation, also involving the interplay of competition and (in a sense) “cooperation” among species. To place this transformation into context, it is important to go back to the basics of the c ...
... In this essay, I reflect on how community ecology seems to be going through a comparable intellectual transformation, also involving the interplay of competition and (in a sense) “cooperation” among species. To place this transformation into context, it is important to go back to the basics of the c ...
6 - White River High School
... 2. Many parasites live in close contact with their hosts, such as disease pathogens, tapeworms, ticks, and lamprey. 3. Other types of parasites are free-living and come into contact with their hosts only infrequently (e.g., nest parasites such as cuckoos and cowbirds). 4. Some parasites cause little ...
... 2. Many parasites live in close contact with their hosts, such as disease pathogens, tapeworms, ticks, and lamprey. 3. Other types of parasites are free-living and come into contact with their hosts only infrequently (e.g., nest parasites such as cuckoos and cowbirds). 4. Some parasites cause little ...
Experimental evolution of protozoan traits in response to
... cysts, which are associated with a decline in food resources (Yamaoka et al., 2004; Foissner et al., 2009). These cysts are resistant to desiccation and may allow populations to survive transient aquatic environments (Ekelund et al., 2002). The peak in density (# per 0.1 mL) was used as a proxy meas ...
... cysts, which are associated with a decline in food resources (Yamaoka et al., 2004; Foissner et al., 2009). These cysts are resistant to desiccation and may allow populations to survive transient aquatic environments (Ekelund et al., 2002). The peak in density (# per 0.1 mL) was used as a proxy meas ...
Prey is a term used to describe animals that are hunted and killed by
... Many of the subjects on midterm II relate to Coevolution – Symbiosis, predation strategies, prey survival strategies. Natural selection not only refers to genetic traits and physical appearance or abilities, but it also refers to behaviors. If the behavior is beneficial for that species, it is highl ...
... Many of the subjects on midterm II relate to Coevolution – Symbiosis, predation strategies, prey survival strategies. Natural selection not only refers to genetic traits and physical appearance or abilities, but it also refers to behaviors. If the behavior is beneficial for that species, it is highl ...
Ecology13
... • Abiotic factors: low precipitation; variable temperatures; soils rich in minerals but poor in organic material • Plants: cacti and other succulents; ...
... • Abiotic factors: low precipitation; variable temperatures; soils rich in minerals but poor in organic material • Plants: cacti and other succulents; ...
the species pool
... ability to migrate in post-glacial period (but includes also biotic factors, as competition on migration pathways) – note, this is very wide definition – for some: Species pool excludes species not able to withstand given abiotic environment, and sometimes it is defined in even more restrictive way ...
... ability to migrate in post-glacial period (but includes also biotic factors, as competition on migration pathways) – note, this is very wide definition – for some: Species pool excludes species not able to withstand given abiotic environment, and sometimes it is defined in even more restrictive way ...
Ch. 8 Sec. 2 power point
... • Competition is the relationship between two species (or individuals) in which both species (or individuals) attempt to use the same limited resource such that both are negatively affected by the relationship. • Members of the same species must compete with each other because they require the same ...
... • Competition is the relationship between two species (or individuals) in which both species (or individuals) attempt to use the same limited resource such that both are negatively affected by the relationship. • Members of the same species must compete with each other because they require the same ...
Revista de Biologia Tropical
... not occur in al1 females. Thus, in August only 40% of the females carry oviductal eggs which are oviposited later in the same month. Maximum reproductive activity in males and females takes place during the spring. Thus, differences in reproductive cycles cause the hatchlings of each species to be b ...
... not occur in al1 females. Thus, in August only 40% of the females carry oviductal eggs which are oviposited later in the same month. Maximum reproductive activity in males and females takes place during the spring. Thus, differences in reproductive cycles cause the hatchlings of each species to be b ...
P_9.pulation - A group of organisms of the same species that live in
... N= Estimate of total population ’size M= Total # of animals marked on the first capture C= Total # of animals (marked and tmmarked) caught during the second capture R= # of marked animals caught during the second capture (recapture) After the first capture and before the second capture, the marked a ...
... N= Estimate of total population ’size M= Total # of animals marked on the first capture C= Total # of animals (marked and tmmarked) caught during the second capture R= # of marked animals caught during the second capture (recapture) After the first capture and before the second capture, the marked a ...