Chapter 12 Communities and Populations Worksheets
... Exponential and Logistic Growth. Curve A shows exponential growth. Curve B shows logistic growth. (Image courtesy of CK-12 Foundation and under the Creative Commons license CC-BY-NC-SA 3.0.) Logistic Growth Most populations do not live under ideal conditions. Therefore, most do not grow exponentiall ...
... Exponential and Logistic Growth. Curve A shows exponential growth. Curve B shows logistic growth. (Image courtesy of CK-12 Foundation and under the Creative Commons license CC-BY-NC-SA 3.0.) Logistic Growth Most populations do not live under ideal conditions. Therefore, most do not grow exponentiall ...
Population Dynamics Populations Organisms do not generally live
... Epiphytes (perching plants) gain access to a better position in the forest canopy, with more light for photosynthesis, but do no harm to the host tree. Commensal anemone shrimps (Periclimenes spp.) live within the tentacles of host sea anemones. The shrimp gains protection from predators, but the an ...
... Epiphytes (perching plants) gain access to a better position in the forest canopy, with more light for photosynthesis, but do no harm to the host tree. Commensal anemone shrimps (Periclimenes spp.) live within the tentacles of host sea anemones. The shrimp gains protection from predators, but the an ...
“Trade-offs” and Life Histories
... Some populations overshoot K before settling down to a relatively stable density Some populations fluctuate greatly and make it difficult to define K Some populations show an Allele effect, in which individuals have a more difficult time surviving or reproducing if the population size is too small. ...
... Some populations overshoot K before settling down to a relatively stable density Some populations fluctuate greatly and make it difficult to define K Some populations show an Allele effect, in which individuals have a more difficult time surviving or reproducing if the population size is too small. ...
Text 2 How Species Interact
... get as many resources as they can but do not fight over resources or get in each other’s way. In this type of scramble competition, the winner is the individual or species that gets the most resources the fastest. Some examples of scramble competition are fish feeding on plankton or sea turtles and ...
... get as many resources as they can but do not fight over resources or get in each other’s way. In this type of scramble competition, the winner is the individual or species that gets the most resources the fastest. Some examples of scramble competition are fish feeding on plankton or sea turtles and ...
Appendix S1. Details of Species Distribution Modeling and
... patches). This leads to a carrying capacity estimate of 1,173 per ha for age 60+ shrubs. While these values may underestimate the actual but theoretical ceiling possible, they provide a consistent upper bound that can be used across all scenarios for ranking and comparison of outcomes. Density depen ...
... patches). This leads to a carrying capacity estimate of 1,173 per ha for age 60+ shrubs. While these values may underestimate the actual but theoretical ceiling possible, they provide a consistent upper bound that can be used across all scenarios for ranking and comparison of outcomes. Density depen ...
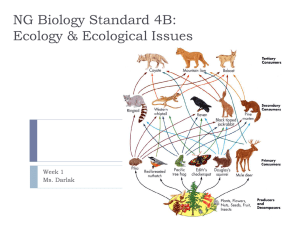
BioB4Symbiosis - Darlak4Science
... Northern pike (it’s a fish) feed on another fish, the yellow perch. An increase in the yellow perch population causes an increase in the northern pike population. The BP oil spill in the Gulf of Mexico has harmed many aquatic organisms that live in the Gulf region. A new strain of influenza (the flu ...
... Northern pike (it’s a fish) feed on another fish, the yellow perch. An increase in the yellow perch population causes an increase in the northern pike population. The BP oil spill in the Gulf of Mexico has harmed many aquatic organisms that live in the Gulf region. A new strain of influenza (the flu ...
Chapter 1 - Garland Science
... species. Other data might include distributions of ages, stages, sex, locations, etc. Though we might think of the picture, and/or the data behind it, as being stable, even permanent, over our time of observation, it is quite likely still changing – evolving naturally with some species on their way ...
... species. Other data might include distributions of ages, stages, sex, locations, etc. Though we might think of the picture, and/or the data behind it, as being stable, even permanent, over our time of observation, it is quite likely still changing – evolving naturally with some species on their way ...
Unit04: Evolution and Biodiversity
... 3. If environment is changeable, the generalist will survive better than the specialist. C. Some species have narrow ecological roles and are termed specialist species. 1. Specialist species can live only in very specific environments. 2. This makes them more prone to extinction when environmental c ...
... 3. If environment is changeable, the generalist will survive better than the specialist. C. Some species have narrow ecological roles and are termed specialist species. 1. Specialist species can live only in very specific environments. 2. This makes them more prone to extinction when environmental c ...
Chesson, P., Pacala, S., Neuhauser, C. 2001. Environmental niches
... resources, such as changes in individual growth rates due to changes in temperature or variation in rainfall, or simply development time independent of the external environment as seen most strikingly in periodical cicadas. The full temporal niche also includes temporal variation in mortality rates ...
... resources, such as changes in individual growth rates due to changes in temperature or variation in rainfall, or simply development time independent of the external environment as seen most strikingly in periodical cicadas. The full temporal niche also includes temporal variation in mortality rates ...
Population Biology – an Introduction
... degree from others of its species, whether geographically or in terms of behavioral or anatomical differences, but its boundaries may be vague – for example, the fish in a lake may also interbreed with the fish of interconnecting waterways. – a population is a useful, if occasionally artificial, uni ...
... degree from others of its species, whether geographically or in terms of behavioral or anatomical differences, but its boundaries may be vague – for example, the fish in a lake may also interbreed with the fish of interconnecting waterways. – a population is a useful, if occasionally artificial, uni ...
Adaptation
... the earth since the beginning of the Cambrian period 600 million years ago. Where did they all come from? By the time Darwin published On the Origin 01 Species in 1859 it was widely (if not uni versally) held that species had evolved from one another, but no plausible mechanism for such evolution h ...
... the earth since the beginning of the Cambrian period 600 million years ago. Where did they all come from? By the time Darwin published On the Origin 01 Species in 1859 it was widely (if not uni versally) held that species had evolved from one another, but no plausible mechanism for such evolution h ...
Resource pulses, species interactions, and diversity maintenance in
... Differences in timing of resource consumption alone are not sufficient for coexistence, however: two other factors are involved in the storage effect. First, species must have high levels of persistence through times when they are not favored. Such times include not only interpulses, where no growth ...
... Differences in timing of resource consumption alone are not sufficient for coexistence, however: two other factors are involved in the storage effect. First, species must have high levels of persistence through times when they are not favored. Such times include not only interpulses, where no growth ...
... germination (12, 30, 31). This pattern of lifehistory variation is consistent with the theory that dormancy and large seed size are partially substitutable bet-hedging strategies (32). Predictive germination allows smaller-seeded species to have greater germination in years of higher reproductive su ...
Chapter 11. Diversification of the Eukaryotes: Animals
... increases, a population reaches the carrying capacity of its environment, and limited resources put a ceiling on growth. • It can also be reduced by densityindependent factors such as natural or human-caused environmental calamities. ...
... increases, a population reaches the carrying capacity of its environment, and limited resources put a ceiling on growth. • It can also be reduced by densityindependent factors such as natural or human-caused environmental calamities. ...
Hamsher - York College of Pennsylvania
... fragmentation. Fragmentation separates populations of organisms from food sources, water and other con-specifics (Gaines 1997). However, while fragmentation detrimentally effects some species, it may allow others to exploit new resources (Gehring 2003). The organisms that can exploit a fragmented la ...
... fragmentation. Fragmentation separates populations of organisms from food sources, water and other con-specifics (Gaines 1997). However, while fragmentation detrimentally effects some species, it may allow others to exploit new resources (Gehring 2003). The organisms that can exploit a fragmented la ...
Environmental Biology
... to the higher trophic levels is rarely sufficient to support large numbers of consumers (for example, 1000 tonnes of primary producer can support only 0.1 tonne of a trophic level 5 (T5) consumer). Elton (1927) introduced the concept of the pyramid of numbers (Figure 1.2.3) to demonstrate this princ ...
... to the higher trophic levels is rarely sufficient to support large numbers of consumers (for example, 1000 tonnes of primary producer can support only 0.1 tonne of a trophic level 5 (T5) consumer). Elton (1927) introduced the concept of the pyramid of numbers (Figure 1.2.3) to demonstrate this princ ...
Biodiversity and ecosystem functioning: A mechanistic model
... Abiotic nutrient flux parameters have the same qualitative effect on maximum species richness, SM, in the two cases. The inflowing nutrient concentration, R0, and the throughflow rate, q, both contribute to an increase in maximum species richness, because they contribute to increasing the amount of ...
... Abiotic nutrient flux parameters have the same qualitative effect on maximum species richness, SM, in the two cases. The inflowing nutrient concentration, R0, and the throughflow rate, q, both contribute to an increase in maximum species richness, because they contribute to increasing the amount of ...
Biology Chapter 5 Section 2 Review
... Density-dependent limiting factors become limiting only when population density—the number of organisms in a given area—reaches a certain level. These factors include competition, predation, parasitism, and disease. Density-independent limiting factors affect all populations in similar ways, regardl ...
... Density-dependent limiting factors become limiting only when population density—the number of organisms in a given area—reaches a certain level. These factors include competition, predation, parasitism, and disease. Density-independent limiting factors affect all populations in similar ways, regardl ...
The Effect of Recycling on Plant Competitive Hierarchies
... limiting. Correlation between species traits and N availability does not prove that plants are actually controlling the availability of N, however (Hobbie 1992). Mathematical models have been used to establish when recycling litter changes N availability. DeAngelis (1992) showed that increased level ...
... limiting. Correlation between species traits and N availability does not prove that plants are actually controlling the availability of N, however (Hobbie 1992). Mathematical models have been used to establish when recycling litter changes N availability. DeAngelis (1992) showed that increased level ...
Population Biology - Ocean County Vocational Technical School
... Factors that can affect population size • Birthrate • Death rate • Rate at which individuals enter or leave the population ...
... Factors that can affect population size • Birthrate • Death rate • Rate at which individuals enter or leave the population ...