Geologic History Notes
... An unstable radioactive isotope, called the parent, will decay and form daughter products. The length of time for one-half of the nuclei of a radioactive isotope to decay is called the half-life of the isotope. If the half-life of the isotope is known, and the parent/daughter ratio can be measured, ...
... An unstable radioactive isotope, called the parent, will decay and form daughter products. The length of time for one-half of the nuclei of a radioactive isotope to decay is called the half-life of the isotope. If the half-life of the isotope is known, and the parent/daughter ratio can be measured, ...
Shales sandstones and associated rocks
... calcite - soluble, crystalline intergrowths dolomite – soluble but less than calcite gypsum – extremely soluble halite – extremely soluble clay - (not true cement) can be leached by ground water ...
... calcite - soluble, crystalline intergrowths dolomite – soluble but less than calcite gypsum – extremely soluble halite – extremely soluble clay - (not true cement) can be leached by ground water ...
magma
... 1. Igneous Rocks (Fact: Igneous means “fiery”) a. How they form: When magma reaches the surface, it becomes lava. b. This hot, molten rock cools and hardens to form igneous rock. c. Characteristics: Igneous rocks vary in size, shape, color, and texture. Examples: basalt, pumice, obsidian ...
... 1. Igneous Rocks (Fact: Igneous means “fiery”) a. How they form: When magma reaches the surface, it becomes lava. b. This hot, molten rock cools and hardens to form igneous rock. c. Characteristics: Igneous rocks vary in size, shape, color, and texture. Examples: basalt, pumice, obsidian ...
Semester 1 Unit 2 Review
... (Ch.10) Rocks and Minerals 1. Describe the Rock Cycle: i. Name the three major rock types. ...
... (Ch.10) Rocks and Minerals 1. Describe the Rock Cycle: i. Name the three major rock types. ...
Geology
... • Series of natural changes that cause one type of rock to become another type of rock • Heat and pressure change rock into various forms • Compacting and cementation will create sedimentary rock • Weathering and erosion, breaking apart of rock, will make sediments ...
... • Series of natural changes that cause one type of rock to become another type of rock • Heat and pressure change rock into various forms • Compacting and cementation will create sedimentary rock • Weathering and erosion, breaking apart of rock, will make sediments ...
Rocks - Warnick
... – A sill is a sheet of igneous rock that lies parallel to the layers it intrudes. – A sill is formed when magma is forced between, not across, rock layers. – A sill can be hundreds of meters thick, and ...
... – A sill is a sheet of igneous rock that lies parallel to the layers it intrudes. – A sill is formed when magma is forced between, not across, rock layers. – A sill can be hundreds of meters thick, and ...
1 Rocks and weathering new
... granite. It is also a course-grained rock. is a coursegrained rock with large, shiny crystals. This is pumice. This rock This is a conglomerate. It absorbs water very consists of rounded pebbles set in a mixture of finer grains easily. ...
... granite. It is also a course-grained rock. is a coursegrained rock with large, shiny crystals. This is pumice. This rock This is a conglomerate. It absorbs water very consists of rounded pebbles set in a mixture of finer grains easily. ...
Igneous Rock Classification Lab
... Extrusive – magma solidifies above the Earth’s surface •magma cools very fast •minerals can not be seen with un-aided eye •very fine-grained texture (no visible minerals •referred to as Volcanic rocks ...
... Extrusive – magma solidifies above the Earth’s surface •magma cools very fast •minerals can not be seen with un-aided eye •very fine-grained texture (no visible minerals •referred to as Volcanic rocks ...
“Igneous and Metamorphic Rocks” Newcomer Academy
... Igneous rocks are identified by their composition (mineral content) and texture (size of crystals). Rocks that cool slowly have large crystals (e.g. pegmatites are intrusive, igneous rocks that form in d ...
... Igneous rocks are identified by their composition (mineral content) and texture (size of crystals). Rocks that cool slowly have large crystals (e.g. pegmatites are intrusive, igneous rocks that form in d ...
The Rock Cycle - Valhalla High School
... Clams, oysters, sea snails) • When these organisms die, their shells pile up and are broken down into fragments, and can form organic limestone ...
... Clams, oysters, sea snails) • When these organisms die, their shells pile up and are broken down into fragments, and can form organic limestone ...
Powerpoint Presentation Physical Geology, 10/e
... • examples: glacial valleys, alluvial fans, river channels, floodplains, lakes, deltas, beaches, dunes, shallow marine, reefs, deep marine ...
... • examples: glacial valleys, alluvial fans, river channels, floodplains, lakes, deltas, beaches, dunes, shallow marine, reefs, deep marine ...
Unit 3 Earth Science..
... B. Plutonic igneous rocks are the result of the slow cooling of molten rock far beneath the surface. 2. Sedimentary Rocks: Formed in layers as the result of moderate pressure on accumulated sediments. 3. Metamorphic Rocks: Formed from older "parent" rock (either igneous or sedimentary) under intense ...
... B. Plutonic igneous rocks are the result of the slow cooling of molten rock far beneath the surface. 2. Sedimentary Rocks: Formed in layers as the result of moderate pressure on accumulated sediments. 3. Metamorphic Rocks: Formed from older "parent" rock (either igneous or sedimentary) under intense ...
Determining the Age of Rocks
... Types of Rock Sedimentary rock forms from sediment (sediment- solid particles of rock produced by weathering and erosion by water and wind) * Igneous rock forms from volcanic lava flows * Metamorphic rock- forms from intense heat and pressure ...
... Types of Rock Sedimentary rock forms from sediment (sediment- solid particles of rock produced by weathering and erosion by water and wind) * Igneous rock forms from volcanic lava flows * Metamorphic rock- forms from intense heat and pressure ...
Key for Chapter 4, Section 4 Metamorphic Rock Directed Reading A
... 4. The heat and pressure at which some metamorphic rocks originally form allow them to sometimes remain solid at pressures and temperatures that would melt other rock. 5. Pressure caused by large movements within the crust sometimes cause the mineral grains in metamorphic rocks to align themselves i ...
... 4. The heat and pressure at which some metamorphic rocks originally form allow them to sometimes remain solid at pressures and temperatures that would melt other rock. 5. Pressure caused by large movements within the crust sometimes cause the mineral grains in metamorphic rocks to align themselves i ...
Determining the Age of Rocks
... Types of Rock Sedimentary rock forms from sediment (sediment- solid particles of rock produced by weathering and erosion by water and wind) * Igneous rock forms from volcanic lava flows * Metamorphic rock- forms from intense heat and pressure ...
... Types of Rock Sedimentary rock forms from sediment (sediment- solid particles of rock produced by weathering and erosion by water and wind) * Igneous rock forms from volcanic lava flows * Metamorphic rock- forms from intense heat and pressure ...
Ch 3 Earth Science PPT
... by which rocks are physically and chemically broken down into small pieces called sediments) sediments are compacted and cemented together, ...
... by which rocks are physically and chemically broken down into small pieces called sediments) sediments are compacted and cemented together, ...
Geology Log File - Learn District 196
... 7. A missing layer of rock that forms a gap in the Earth’s geologic history is called ___________________. 8. The law of ___________________ (p.98) states that a fault or an intrusion is younger than any layer of rock that the fault or rock body cuts through. 1. ____________ ________________ are use ...
... 7. A missing layer of rock that forms a gap in the Earth’s geologic history is called ___________________. 8. The law of ___________________ (p.98) states that a fault or an intrusion is younger than any layer of rock that the fault or rock body cuts through. 1. ____________ ________________ are use ...
Physical Geology Practice Midterm Exam 1. Which of the following
... 58. Which igneous rock is the most abundant igneous rock of the crust and underlies virtually all of the floors of the ocean? A) andesite B) basalt C) granite D) peridotite ...
... 58. Which igneous rock is the most abundant igneous rock of the crust and underlies virtually all of the floors of the ocean? A) andesite B) basalt C) granite D) peridotite ...
Angular unconformity
... • Relative ages – placing rocks and geologic events in their proper sequence, oldest to youngest. • Absolute dates – define the actual numerical age of a particular geologic event. For example, large dinosaurs died out 65 mya. The Lavas along Rt 22 and Rt 78 were deposited about 205 mya. ...
... • Relative ages – placing rocks and geologic events in their proper sequence, oldest to youngest. • Absolute dates – define the actual numerical age of a particular geologic event. For example, large dinosaurs died out 65 mya. The Lavas along Rt 22 and Rt 78 were deposited about 205 mya. ...
SEDIMENTARY ROCKS
... Classification of Sedimentary Rocks Three main categories of sedimentary rocks are recognized. -Sediment has two principal sources: First, it may be an accumulation of material that originates and is transported as solid particles derived from both mechanical and chemical weathering. These deposits ...
... Classification of Sedimentary Rocks Three main categories of sedimentary rocks are recognized. -Sediment has two principal sources: First, it may be an accumulation of material that originates and is transported as solid particles derived from both mechanical and chemical weathering. These deposits ...
Geology of the New Jersey Highlands and Valley and Ridge Provinces
... underlies 50% of Highlands medium to coarse grained, massive textured Composed mainly of minerals quartz and feldspar ...
... underlies 50% of Highlands medium to coarse grained, massive textured Composed mainly of minerals quartz and feldspar ...
PC Minerals
... Many chemical changes continue to occur to a sedimentary rock even long after the rock is formed. Changes in temperature, pressure and chemistry of ground water permeating the rock formation produce new minerals. Minerals formed earlier may be replaced chemically. New minerals may also form in the i ...
... Many chemical changes continue to occur to a sedimentary rock even long after the rock is formed. Changes in temperature, pressure and chemistry of ground water permeating the rock formation produce new minerals. Minerals formed earlier may be replaced chemically. New minerals may also form in the i ...
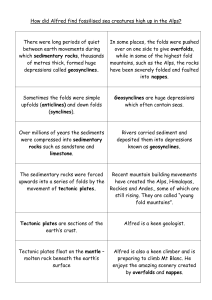
How did Alfred find fossilised sea animals high up in the Alps
... Fold mountains occur where two tectonic plates are moving towards each other. ...
... Fold mountains occur where two tectonic plates are moving towards each other. ...
First Exam, Spring 2013 Geology 1- Gavilan College
... 11. Which is NOT a characteristic of a mineral? a. naturally occurring inorganic substance b. have a definite chemical composition c. have a unique chemical structure. d. may be composed of a mixture. e. none of the above. 12. Which is a characteristic of a rock? a. they may have organic residue com ...
... 11. Which is NOT a characteristic of a mineral? a. naturally occurring inorganic substance b. have a definite chemical composition c. have a unique chemical structure. d. may be composed of a mixture. e. none of the above. 12. Which is a characteristic of a rock? a. they may have organic residue com ...
Clastic rock

Clastic rocks are composed of fragments, or clasts, of pre-existing minerals and rock. A clast is a fragment of geological detritus, chunks and smaller grains of rock broken off other rocks by physical weathering. Geologists use the term clastic with reference to sedimentary rocks as well as to particles in sediment transport whether in suspension or as bed load, and in sediment deposits.