LT5ActivityPacket
... It is a giant volcanic crater called a collapsed caldera. It formed when ground above the magma chamber sank down as it was emptied in the last eruption. ...
... It is a giant volcanic crater called a collapsed caldera. It formed when ground above the magma chamber sank down as it was emptied in the last eruption. ...
Formation of Sedimentary Rocks
... During lithification, parts of an organism can be replaced by minerals and turned into rock, such as shells that have been mineralized. ...
... During lithification, parts of an organism can be replaced by minerals and turned into rock, such as shells that have been mineralized. ...
Rock Cycle homework
... Igneous rock is any rock that forms from magma or lava. The name “igneous” comes from the Latin word ignis, meaning “fire.” Igneous rocks are classified according to their origin, texture, and mineral composition. Extrusive rock is igneous rock formed from lava that erupted onto Earth’s surface. Bas ...
... Igneous rock is any rock that forms from magma or lava. The name “igneous” comes from the Latin word ignis, meaning “fire.” Igneous rocks are classified according to their origin, texture, and mineral composition. Extrusive rock is igneous rock formed from lava that erupted onto Earth’s surface. Bas ...
Rocks and Minerals - Georgia Standards
... Minerals can be identified by their physical properties. Igneous rocks are dominated by silicate minerals. Rocks are composed of minerals. Minerals are the building blocks of rocks. The rock cycle explains how one rock type can be transformed into another. This process is continuing today. Magma coo ...
... Minerals can be identified by their physical properties. Igneous rocks are dominated by silicate minerals. Rocks are composed of minerals. Minerals are the building blocks of rocks. The rock cycle explains how one rock type can be transformed into another. This process is continuing today. Magma coo ...
Igneous Rocks
... small or no crystals formed • An igneous rock that forms within Earth’s crust is called an intrusive rock, magma pushes into surrounding rock below the Earth’s surface Which rocks are more likely to have large crystals? ...
... small or no crystals formed • An igneous rock that forms within Earth’s crust is called an intrusive rock, magma pushes into surrounding rock below the Earth’s surface Which rocks are more likely to have large crystals? ...
Sedimentary Rocks and the Rock Cycle
... precipitated minerals causes the grains to cement together. Cementation can occur in combination with the presence of other minerals, rock fragments, or organic constituents such as fossilized organisms. Lithification occurs when unconsolidated sediments are cohesively bound to form a solid sediment ...
... precipitated minerals causes the grains to cement together. Cementation can occur in combination with the presence of other minerals, rock fragments, or organic constituents such as fossilized organisms. Lithification occurs when unconsolidated sediments are cohesively bound to form a solid sediment ...
geotime1
... • CROSS-CUTTING: a body of igneous rock is younger than rock it has intruded (cut across). – Intrusion - magma flow – Extrusion – lava flow ...
... • CROSS-CUTTING: a body of igneous rock is younger than rock it has intruded (cut across). – Intrusion - magma flow – Extrusion – lava flow ...
STEINWAY INTERMEDIATE SCHOOL 141Q A NASA Explorer
... Rock: A solid material made up of minerals, fossils, and/or organic material. Rock Cycle: A natural process constantly being forming, wearing down, and reforming rock. Metamorphic Rock: Rocks formed because of changes to high temperature and/or pressure, and form in foliated layers. Sediment ...
... Rock: A solid material made up of minerals, fossils, and/or organic material. Rock Cycle: A natural process constantly being forming, wearing down, and reforming rock. Metamorphic Rock: Rocks formed because of changes to high temperature and/or pressure, and form in foliated layers. Sediment ...
Primary Rock Structures
... Flute Casts: current-formed erosion structure, bulbous cast formed by scouring of sediment interface, bulbous end generally points up-current. ...
... Flute Casts: current-formed erosion structure, bulbous cast formed by scouring of sediment interface, bulbous end generally points up-current. ...
Rocks
... bottom become compacted together by the heavy weight from above. Water is often involved in forming sedimentary rocks, as sediments fall to the bottom of seas, rivers and lakes. ...
... bottom become compacted together by the heavy weight from above. Water is often involved in forming sedimentary rocks, as sediments fall to the bottom of seas, rivers and lakes. ...
Study Guide Exam #4
... Mountain ranges; volcanic arcs; ocean trenches; strike-slip faults; Mid-ocean ridges What type of geologic features are associated with: Convergent Boundary, Divergent Boundaries; Hot Spots What boundary or other geologic feature formed: Himalayas, Yellowstone, Hawaii, & Mid-Ocean Ridges Sedimentary ...
... Mountain ranges; volcanic arcs; ocean trenches; strike-slip faults; Mid-ocean ridges What type of geologic features are associated with: Convergent Boundary, Divergent Boundaries; Hot Spots What boundary or other geologic feature formed: Himalayas, Yellowstone, Hawaii, & Mid-Ocean Ridges Sedimentary ...
chapter 6 Metamorphic Rks.pptx
... – Very hard and dense (indurated); if fractured or broken, could break across pebbles as easily as around them ...
... – Very hard and dense (indurated); if fractured or broken, could break across pebbles as easily as around them ...
Meta = change Morph = shape Metamorphic Rock are rocks in
... More intense the closer the rock is to the magma Near igneous intrusions Some minerals can change into other minerals because of the heat ...
... More intense the closer the rock is to the magma Near igneous intrusions Some minerals can change into other minerals because of the heat ...
Name Date Class The Rock Cycle Review Worksheet Answer the
... grains (the sides of the small blocks seen on the cube’s faces) are large, and their shape is ...
... grains (the sides of the small blocks seen on the cube’s faces) are large, and their shape is ...
Igneous Rock PPT notes
... rock cools above ground. Usually they are formed after the material has been erupted by a volcano. 1. This molten material cools quickly. 2. No crystals are visible to the eye. ...
... rock cools above ground. Usually they are formed after the material has been erupted by a volcano. 1. This molten material cools quickly. 2. No crystals are visible to the eye. ...
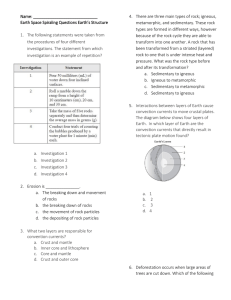
Name: Earth Space Spiraling Questions Earth`s Structure 1. The
... Name: _____________________________ Earth Space Spiraling Questions Earth’s Structure 1. The following statements were taken from the procedures of four different investigations. The statement from which investigation is an example of repetition? ...
... Name: _____________________________ Earth Space Spiraling Questions Earth’s Structure 1. The following statements were taken from the procedures of four different investigations. The statement from which investigation is an example of repetition? ...
Outstanding geologic feature of Pennsylvania—Sentinel
... vertical, northeast-oriented joint from a blocky outcrop of Brunswick Formation, which is composed of brownish-red shale, mudstone, and siltstone. Very close to the northwest and beneath the spillway, the overlying rock unit is the Lockatong Formation—a dark-gray argillite with some black shale. The ...
... vertical, northeast-oriented joint from a blocky outcrop of Brunswick Formation, which is composed of brownish-red shale, mudstone, and siltstone. Very close to the northwest and beneath the spillway, the overlying rock unit is the Lockatong Formation—a dark-gray argillite with some black shale. The ...
Sediment and Sedimentary Rocks
... Sediment Maturity refers to the length of time that the sediment has been in the sedimentary cycle. Texturally mature sediment is sediment that is well rounded, (as rounding increases with transport distance and time) and well sorted (as sorting gets better as larger clasts are left behind and small ...
... Sediment Maturity refers to the length of time that the sediment has been in the sedimentary cycle. Texturally mature sediment is sediment that is well rounded, (as rounding increases with transport distance and time) and well sorted (as sorting gets better as larger clasts are left behind and small ...
UNIT 2, CHAPTER 5:
... Topic 1: The Geologic Column Pages 156-161 As rocks are weathered, eroded, and deposited their sediments form layers that eventually become compacted and cemented into solid rock called sedimentary rock. These rocks play an important role in helping geologists and paleontologists (scientists who stu ...
... Topic 1: The Geologic Column Pages 156-161 As rocks are weathered, eroded, and deposited their sediments form layers that eventually become compacted and cemented into solid rock called sedimentary rock. These rocks play an important role in helping geologists and paleontologists (scientists who stu ...
Rocks - Faculty Server Contact
... varies from very fine to coarse foliation (mica flakes clearly visible) to gneissic textures in which the minerals are segregated into layers (Fig. 4). Foliated metamorphic rocks are indicative of regional metamorphism rocks over a broad area have been subjected to elevated pressures and temperature ...
... varies from very fine to coarse foliation (mica flakes clearly visible) to gneissic textures in which the minerals are segregated into layers (Fig. 4). Foliated metamorphic rocks are indicative of regional metamorphism rocks over a broad area have been subjected to elevated pressures and temperature ...
Midterm Review 1
... Hydrothermal alteration involves alteration of minerals through percolation of hot, mineral-rich fluids through the rock The ‘Parent’ rock is an important control on the type of metamorphic rock formed Index minerals form at specific temperatures and pressures and thus record the T and P ‘experience ...
... Hydrothermal alteration involves alteration of minerals through percolation of hot, mineral-rich fluids through the rock The ‘Parent’ rock is an important control on the type of metamorphic rock formed Index minerals form at specific temperatures and pressures and thus record the T and P ‘experience ...
Mineral
... A supercontinent containing all of Earth’s land existing about 225 million years ago. ...
... A supercontinent containing all of Earth’s land existing about 225 million years ago. ...
Can you begin by explaining why there Temperature-time-Deformation histories
... mass spectrometry, the team has utilised electron backscatter and cathodoluminesence (CL) imaging. The latter has proved to be a particularly important tool for this project. Previous studies have determined that the CL intensity of quartz in the blue wavelengths is strongly indicative of the titani ...
... mass spectrometry, the team has utilised electron backscatter and cathodoluminesence (CL) imaging. The latter has proved to be a particularly important tool for this project. Previous studies have determined that the CL intensity of quartz in the blue wavelengths is strongly indicative of the titani ...
Clastic rock

Clastic rocks are composed of fragments, or clasts, of pre-existing minerals and rock. A clast is a fragment of geological detritus, chunks and smaller grains of rock broken off other rocks by physical weathering. Geologists use the term clastic with reference to sedimentary rocks as well as to particles in sediment transport whether in suspension or as bed load, and in sediment deposits.