Chapter 1 Structure and Bonding
... c) These are the same p bonds that Y must use as it approaches to bond ...
... c) These are the same p bonds that Y must use as it approaches to bond ...
The Synthesis of trans-Dichlorobis(ethylenediamine)cobalt(III
... This synthesis involves oxidation of the Cobalt from Co+2 to Co+3 by hydrogen peroxide: 2 Co2+ + H2O2 + 2 H+ 2 Co3+ + 2 H2O (Eq. 2) (Here, H2O2 acts as an Oxidizing Agent and is reduced from O-1 to O2-.) However, Co3+ is unstable in an aqueous environment, being readily reduced back to Co2+. To pre ...
... This synthesis involves oxidation of the Cobalt from Co+2 to Co+3 by hydrogen peroxide: 2 Co2+ + H2O2 + 2 H+ 2 Co3+ + 2 H2O (Eq. 2) (Here, H2O2 acts as an Oxidizing Agent and is reduced from O-1 to O2-.) However, Co3+ is unstable in an aqueous environment, being readily reduced back to Co2+. To pre ...
Week #10: The Synthesis of a Compound using a Limiting Reagent
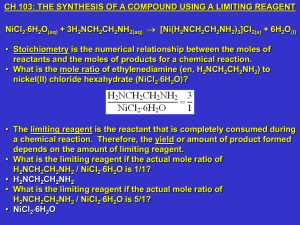
... • The limiting reagent is the reactant that is completely consumed during a chemical reaction. Therefore, the yield or amount of product formed depends on the amount of limiting reagent. • What is the limiting reagent if the actual mole ratio of H2NCH2CH2NH2 / NiCl26H2O is 1/1? • H2NCH2CH2NH2 • Wha ...
... • The limiting reagent is the reactant that is completely consumed during a chemical reaction. Therefore, the yield or amount of product formed depends on the amount of limiting reagent. • What is the limiting reagent if the actual mole ratio of H2NCH2CH2NH2 / NiCl26H2O is 1/1? • H2NCH2CH2NH2 • Wha ...
Document
... • The limiting reagent is the reactant that is completely consumed during a chemical reaction. Therefore, the yield or amount of product formed depends on the amount of limiting reagent. • What is the limiting reagent if the actual mole ratio of H2NCH2CH2NH2 / NiCl26H2O is 1/1? • H2NCH2CH2NH2 • Wha ...
... • The limiting reagent is the reactant that is completely consumed during a chemical reaction. Therefore, the yield or amount of product formed depends on the amount of limiting reagent. • What is the limiting reagent if the actual mole ratio of H2NCH2CH2NH2 / NiCl26H2O is 1/1? • H2NCH2CH2NH2 • Wha ...
Ligand Design_revised
... HSAB Theory in Donor Atoms • HSAB theory can be used to manipulate discreet differences in different metal ions ...
... HSAB Theory in Donor Atoms • HSAB theory can be used to manipulate discreet differences in different metal ions ...
A Summary of Organometallic Chemistry
... Exceptions to the 18-electrons rule - Early transition metal complexes and/or complexes with bulky ligands are stable with less than 18 v.e. mainly for steric reasons. - Complexes with many π-donor ligands (see below) are stable even with less than 18 v.e. because the πdonation adds electron densit ...
... Exceptions to the 18-electrons rule - Early transition metal complexes and/or complexes with bulky ligands are stable with less than 18 v.e. mainly for steric reasons. - Complexes with many π-donor ligands (see below) are stable even with less than 18 v.e. because the πdonation adds electron densit ...
Lecture 3
... access dissolved Fe from the FeL1 complex, resulting in excess L1 between dissolved Fe and L1 ligand concentrations in samples with intermediate dissolved Fe, and this is a seemingly ubiquitous feature of dissolved Fe cycling in the marine environment.” ...
... access dissolved Fe from the FeL1 complex, resulting in excess L1 between dissolved Fe and L1 ligand concentrations in samples with intermediate dissolved Fe, and this is a seemingly ubiquitous feature of dissolved Fe cycling in the marine environment.” ...
InorgCh425
... Conditions for High and Low Oxidation States 1) Hard ligand select for high oxidation states: MnO4- (Mn+7), PtF6 (Pt+6) 2) Soft ligands select for low oxidation states: V(CO)6 (V0) ...
... Conditions for High and Low Oxidation States 1) Hard ligand select for high oxidation states: MnO4- (Mn+7), PtF6 (Pt+6) 2) Soft ligands select for low oxidation states: V(CO)6 (V0) ...
CH2ch24_2
... ii. Fe3+—NCS = isothiocyanate complex b) NO2- Linkage isomers i. M—ONO = nitrito complex ii. M—NO2 = nitro complex ...
... ii. Fe3+—NCS = isothiocyanate complex b) NO2- Linkage isomers i. M—ONO = nitrito complex ii. M—NO2 = nitro complex ...
Transition Metals
... • The transition metals can form a variety of ions by losing one or more electrons. • For the first five metals the maximum possible oxidation state corresponds to the loss of all the 4s and 3d electrons. • Toward the right end of the period, maximum oxidation state are not observed, in fact 2+ ions ...
... • The transition metals can form a variety of ions by losing one or more electrons. • For the first five metals the maximum possible oxidation state corresponds to the loss of all the 4s and 3d electrons. • Toward the right end of the period, maximum oxidation state are not observed, in fact 2+ ions ...
Nugget
... In the field of homogenous catalysis, few reports have appeared offering general, chemically mild methods for the introduction of nitrogen- or oxygen-containing functional groups into simple hydrocarbon substrates. The combination of small-molecule activation with C—H bond functionalization represen ...
... In the field of homogenous catalysis, few reports have appeared offering general, chemically mild methods for the introduction of nitrogen- or oxygen-containing functional groups into simple hydrocarbon substrates. The combination of small-molecule activation with C—H bond functionalization represen ...
Chapter 1 Structure and Bonding
... Linkage Isomers = depends on which atom of the ligand is attached to metal 1) SCN- = thiocyanato a) Pb2+—SCN = soft/soft interaction b) Fe3+--NCS = hard/hard interaction 2) NO2- = nitrito M—ONO vs. M—NO2 ...
... Linkage Isomers = depends on which atom of the ligand is attached to metal 1) SCN- = thiocyanato a) Pb2+—SCN = soft/soft interaction b) Fe3+--NCS = hard/hard interaction 2) NO2- = nitrito M—ONO vs. M—NO2 ...
Coordination Number 2
... Transition metal complexes with the coordination number 1 are rare. In the case of main group elements this coordination number is more common, e.g. in HF, IF. It can be also observed in the gas phase. In the following reference (this journal is in the library) a compound had been reported which is ...
... Transition metal complexes with the coordination number 1 are rare. In the case of main group elements this coordination number is more common, e.g. in HF, IF. It can be also observed in the gas phase. In the following reference (this journal is in the library) a compound had been reported which is ...
Chapter 1 Structure and Bonding
... iv. PtA2B2 only has two isomers. It must be square planar rather than tetrahedral, which would only have 1 isomer. v. ...
... iv. PtA2B2 only has two isomers. It must be square planar rather than tetrahedral, which would only have 1 isomer. v. ...
model answers
... corresponding distances in [(η5-C5H5)Co(PEt3)2]+ are 223 pm and 182.9 pm. Account for the changes in these distances as the former complex is oxidised. The oxidised complex is less able to donate electron density into σ* PEt3 antibonding orbitals, so P-C bonds become shorter. Weakening of π-back bon ...
... corresponding distances in [(η5-C5H5)Co(PEt3)2]+ are 223 pm and 182.9 pm. Account for the changes in these distances as the former complex is oxidised. The oxidised complex is less able to donate electron density into σ* PEt3 antibonding orbitals, so P-C bonds become shorter. Weakening of π-back bon ...
Chapter 1 Structure and Bonding
... Antiprimatic should give 3 isomers. Octahedral only has two possible isomers. Thus the structure must be Oh. iv. PtA2B2 only has two isomers. It must be square planar rather than tetrahedral, which would only have 1 isomer. v. ...
... Antiprimatic should give 3 isomers. Octahedral only has two possible isomers. Thus the structure must be Oh. iv. PtA2B2 only has two isomers. It must be square planar rather than tetrahedral, which would only have 1 isomer. v. ...
Coordination compounds :
... The central atoms of coordination complexes are most often cations (positive ions), but may in some cases be neutral atoms, as in nickel carbonyl Ni(CO)4. Ligands composed of ions such as F– or small molecules such as H2O or CN– possess more than one set of lone pair electrons, but only one of thes ...
... The central atoms of coordination complexes are most often cations (positive ions), but may in some cases be neutral atoms, as in nickel carbonyl Ni(CO)4. Ligands composed of ions such as F– or small molecules such as H2O or CN– possess more than one set of lone pair electrons, but only one of thes ...
An introduction to the virtual issue on Coordination
... solid-state structures of coordination compounds consisting of conceptually infinite one-dimensional chains, two-dimensional nets and three-dimensional frameworks. The obvious common feature shared by these different types of compounds is that they all consist of metal-containing nodes that are ‘inf ...
... solid-state structures of coordination compounds consisting of conceptually infinite one-dimensional chains, two-dimensional nets and three-dimensional frameworks. The obvious common feature shared by these different types of compounds is that they all consist of metal-containing nodes that are ‘inf ...
Coordination complex

In chemistry, a coordination complex or metal complex consists of a central atom or ion, which is usually metallic and is called the coordination centre, and a surrounding array of bound molecules or ions, that are in turn known as ligands or complexing agents. Many metal-containing compounds, especially those of transition metals, are coordination complexes.