E04 Atomic, Nuclear, and Particle Physics Chapter 7. Atomic
... Ionization: occurs when the electrons are completely removed from an atom, leaving a charged atom called an ion. This can happen if the atom absorbs a high energy photon or the electron could be ‘knocked off ’ by a fast moving particle like an alpha. Quantum explanation of atomic spectra • Atomic el ...
... Ionization: occurs when the electrons are completely removed from an atom, leaving a charged atom called an ion. This can happen if the atom absorbs a high energy photon or the electron could be ‘knocked off ’ by a fast moving particle like an alpha. Quantum explanation of atomic spectra • Atomic el ...
e - Purdue Physics - Purdue University
... The Bohr Model for the electronic energies in atomic Hydrogen To better understand the origin of Balmer’s empirical formula, Bohr formulated a theory of the hydrogen atom in 1911. ...
... The Bohr Model for the electronic energies in atomic Hydrogen To better understand the origin of Balmer’s empirical formula, Bohr formulated a theory of the hydrogen atom in 1911. ...
Honors Midterm Review – 2015-16
... (with any great degree of certainty) both the location and velocity of an electron) _________ responsible for the planetary model of the atom, where electrons traveled in distinct paths around the nucleus _________ responsible for the equation which determines the exact amount of energy needed for e ...
... (with any great degree of certainty) both the location and velocity of an electron) _________ responsible for the planetary model of the atom, where electrons traveled in distinct paths around the nucleus _________ responsible for the equation which determines the exact amount of energy needed for e ...
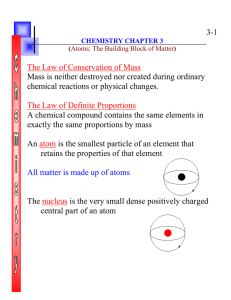
Chapter 3 Atoms: The Building Blocks
... A chemical compound contains the same elements in exactly the same proportions by mass An atom is the smallest particle of an element that retains the properties of that element All matter is made up of atoms ...
... A chemical compound contains the same elements in exactly the same proportions by mass An atom is the smallest particle of an element that retains the properties of that element All matter is made up of atoms ...
1. Define the vocabulary on page 88. Section 1
... End of Section Review – Short Answers: Page 103: # 1, 2, 3, 4, 6a Section 1 Review – Short Answers ...
... End of Section Review – Short Answers: Page 103: # 1, 2, 3, 4, 6a Section 1 Review – Short Answers ...
Quantum Mechanics
... Orbiting electrons contradicted e-m theory Niels Bohr (1913) proposed model of atom with electron orbits based on quantized energy states Difference between energy states always some multiple of Planck’s constant ...
... Orbiting electrons contradicted e-m theory Niels Bohr (1913) proposed model of atom with electron orbits based on quantized energy states Difference between energy states always some multiple of Planck’s constant ...
This `practice exam`
... NOTE: This ‘practice exam’ contains more than questions than the real final. 1. The wavelength of light emitted from a green laser pointer is 5.32 × 102 nm. What is the wavelength in meters? 5.32 × 10-7 m 2. What is the correct answer, with correct significant figures, to the following expression: ( ...
... NOTE: This ‘practice exam’ contains more than questions than the real final. 1. The wavelength of light emitted from a green laser pointer is 5.32 × 102 nm. What is the wavelength in meters? 5.32 × 10-7 m 2. What is the correct answer, with correct significant figures, to the following expression: ( ...
Chapter 4 - Rothschild Science
... energy and because of this cannot lose energy and fall into the nucleus Energy Level of an electron is the region around the nucleus where the electron is likely to be moving ...
... energy and because of this cannot lose energy and fall into the nucleus Energy Level of an electron is the region around the nucleus where the electron is likely to be moving ...
Radiation Equilibrium (in Everything Including Direct Semiconductors)
... Schrödinger equation because we already know that photons are waves described by some exp (ik·r – ωt) with ω = 2πν With that, we also know that the boundary conditions imposed by the finite crystal will only allow wave vectors that fit into the crystal and form standing waves. All we have to do then ...
... Schrödinger equation because we already know that photons are waves described by some exp (ik·r – ωt) with ω = 2πν With that, we also know that the boundary conditions imposed by the finite crystal will only allow wave vectors that fit into the crystal and form standing waves. All we have to do then ...
2.00 C = 5.99 H = 1.00 O
... molecular formula. To get the true formula we need some additional information. To find the true formula we need the true molar mass. By finding the ratio between the ratio between the true molar mass and the empirical formula’s molar mass we can find the ratio between the empirical formula and the ...
... molecular formula. To get the true formula we need some additional information. To find the true formula we need the true molar mass. By finding the ratio between the ratio between the true molar mass and the empirical formula’s molar mass we can find the ratio between the empirical formula and the ...
Chapter 4: Electrons in Atoms I. Properties of Light A
... 2. EM radiation are forms of energy which move through space as waves a. Move at speed of light (c) (1). c= 3.00 x 10^8 m/s b. Speed is equal to the frequency times the wavelength c = νλ (1). Freqency (ν) is the number of waves passing a given point in one second, measured in Hz or s^-1 (2). Wavelen ...
... 2. EM radiation are forms of energy which move through space as waves a. Move at speed of light (c) (1). c= 3.00 x 10^8 m/s b. Speed is equal to the frequency times the wavelength c = νλ (1). Freqency (ν) is the number of waves passing a given point in one second, measured in Hz or s^-1 (2). Wavelen ...
Set 3
... 8) The light falling on sodium source causes photoelectric effect. The stopping potential equals to 5 eV and the work function W = 2.2 eV. What is the wavelength of falling electromagnetic radiation? 9) In the experiment with metallic sodium source the stopping potential for photoelectric effect was ...
... 8) The light falling on sodium source causes photoelectric effect. The stopping potential equals to 5 eV and the work function W = 2.2 eV. What is the wavelength of falling electromagnetic radiation? 9) In the experiment with metallic sodium source the stopping potential for photoelectric effect was ...
Particle accelerators
... Particle accelerators A particle accelerator is a piece of apparatus used by physicists to accelerate sub atomic particles to very high speeds and then use these rapidly moving particles to investigate the structure of matter by letting these beams of high energy particles collide with a target. Ele ...
... Particle accelerators A particle accelerator is a piece of apparatus used by physicists to accelerate sub atomic particles to very high speeds and then use these rapidly moving particles to investigate the structure of matter by letting these beams of high energy particles collide with a target. Ele ...
Ideas of Modern Physics
... are coming out. To eject electrons, she should change the light by… a. decreasing the frequency b. increasing the frequency c. increasing the intensity d. increasing the wavelength e. asking Einstein 2. A beta particle, gamma ray, and alpha particle all have the same momentum. Which has the longest ...
... are coming out. To eject electrons, she should change the light by… a. decreasing the frequency b. increasing the frequency c. increasing the intensity d. increasing the wavelength e. asking Einstein 2. A beta particle, gamma ray, and alpha particle all have the same momentum. Which has the longest ...
Bremsstrahlung
Bremsstrahlung (German pronunciation: [ˈbʁɛmsˌʃtʁaːlʊŋ], from bremsen ""to brake"" and Strahlung ""radiation"", i.e. ""braking radiation"" or ""deceleration radiation"") is electromagnetic radiation produced by the deceleration of a charged particle when deflected by another charged particle, typically an electron by an atomic nucleus. The moving particle loses kinetic energy, which is converted into a photon, thus satisfying the law of conservation of energy. The term is also used to refer to the process of producing the radiation. Bremsstrahlung has a continuous spectrum, which becomes more intense and whose peak intensity shifts toward higher frequencies as the change of the energy of the accelerated particles increases.Strictly speaking, braking radiation is any radiation due to the acceleration of a charged particle, which includes synchrotron radiation, cyclotron radiation, and the emission of electrons and positrons during beta decay. However, the term is frequently used in the more narrow sense of radiation from electrons (from whatever source) slowing in matter.Bremsstrahlung emitted from plasma is sometimes referred to as free/free radiation. This refers to the fact that the radiation in this case is created by charged particles that are free both before and after the deflection (acceleration) that caused the emission.