Physical Chemistry
... • (1) Is not stable relative to collapse of electron into nucleus • (2) Does not yield discrete emission lines, • (3) Does not explain the Rydberg formula ...
... • (1) Is not stable relative to collapse of electron into nucleus • (2) Does not yield discrete emission lines, • (3) Does not explain the Rydberg formula ...
Chapter 14 Extra Credit Test Review
... 13. Write the name for the formula Na2O. ______Sodium Oxide___ 14. Write the name for the formula NO. _____Nitrogen Monoxide________ 15. Preservatives are considered to be __inhibitors___ because they are added to foods to slow down the rate at which the food spoils. 16. Four factors that affect the ...
... 13. Write the name for the formula Na2O. ______Sodium Oxide___ 14. Write the name for the formula NO. _____Nitrogen Monoxide________ 15. Preservatives are considered to be __inhibitors___ because they are added to foods to slow down the rate at which the food spoils. 16. Four factors that affect the ...
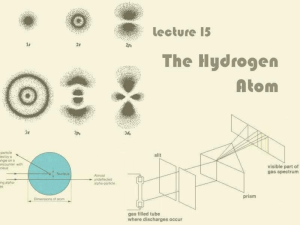
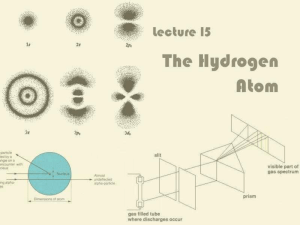
Lecture 15: The Hydrogen Atom
... It is known that accelerating charges emit radiation Thus, electron should emit radiation, lose energy and eventually fall into the nucleus! Why doesn’t this happen? Shows that something was wrong with this model of the hydrogen atom ...
... It is known that accelerating charges emit radiation Thus, electron should emit radiation, lose energy and eventually fall into the nucleus! Why doesn’t this happen? Shows that something was wrong with this model of the hydrogen atom ...
ELECTRONIC STRUCTURE OF ATOMS
... Using Plancks hypothesis Einstein explained the photoelectric effect. Experiments had shown that light shining on a metal surface caused it to emit electrons. For each metal there is a minimum frequency below which no electrons are emitted. Einstein assumed light travels in packets(photons) that ...
... Using Plancks hypothesis Einstein explained the photoelectric effect. Experiments had shown that light shining on a metal surface caused it to emit electrons. For each metal there is a minimum frequency below which no electrons are emitted. Einstein assumed light travels in packets(photons) that ...
Lecture 15: The Hydrogen Atom
... It only absorbs or emits photons with precisely the right energies dictated by energy conservation ...
... It only absorbs or emits photons with precisely the right energies dictated by energy conservation ...
Chapter2. Elements of quantum mechanics
... a. What is the work function of the photocathode surface, in eV? b. If a UV radiation of wavelength 300 nm is incident upon the photocathode surface, what will be the maximum kinetic energy of the photoemitted electrons, in eV? c. Given that the UV light of wavelength 300 nm has an intensity of 20 m ...
... a. What is the work function of the photocathode surface, in eV? b. If a UV radiation of wavelength 300 nm is incident upon the photocathode surface, what will be the maximum kinetic energy of the photoemitted electrons, in eV? c. Given that the UV light of wavelength 300 nm has an intensity of 20 m ...
Historical Introduction to the Elementary Particles
... • The discovery of the neutron put the final touch on what we might call the classical period in elementary particle physics. Never before has physics offered so simple and satisfying an answer to the question, “What is matter made of?” In 1932 ...
... • The discovery of the neutron put the final touch on what we might call the classical period in elementary particle physics. Never before has physics offered so simple and satisfying an answer to the question, “What is matter made of?” In 1932 ...
Atomic (proton) number = is the number of protons found in the
... Characteristic radiation = ionizing radiation with a discrete energy spectrum, emitted in a nuclear transition from a high-energy electron shell to a lower on. X radiation = ionizing radiation consisting of photons, originating in the extranuclear part of the atom, comprising bremsstrahlung and char ...
... Characteristic radiation = ionizing radiation with a discrete energy spectrum, emitted in a nuclear transition from a high-energy electron shell to a lower on. X radiation = ionizing radiation consisting of photons, originating in the extranuclear part of the atom, comprising bremsstrahlung and char ...
Tutorial 1 - NUS Physics Department
... 2. The Gell-Mann/Okubo mass formula relates the masses of members of the baryon octet (ignoring small differences between p and n ; , 0 , and ; and 0 and ...
... 2. The Gell-Mann/Okubo mass formula relates the masses of members of the baryon octet (ignoring small differences between p and n ; , 0 , and ; and 0 and ...
Quiz 1 Key
... White light has all of the colors and therefore wavelengths present. The emission spectrum of hydrogen had only certain colors and thus certain wavelengths present. Because wavelength is related to energy, this indicated that there were only certain energies of light emitted. This indicated that the ...
... White light has all of the colors and therefore wavelengths present. The emission spectrum of hydrogen had only certain colors and thus certain wavelengths present. Because wavelength is related to energy, this indicated that there were only certain energies of light emitted. This indicated that the ...
study guide first semester chemistry
... 1. Write the balanced equation for the following: (include the state of each reactant and product) a. magnesium reacts with nitrogen to produce magnesium nitride. b. silver nitrate reacts with copper to form copper(II) nitrate and silver. c. ammonia reacts with hydrochloric acid to form ammonium ch ...
... 1. Write the balanced equation for the following: (include the state of each reactant and product) a. magnesium reacts with nitrogen to produce magnesium nitride. b. silver nitrate reacts with copper to form copper(II) nitrate and silver. c. ammonia reacts with hydrochloric acid to form ammonium ch ...
107 chem Assement Q
... c. Avogadro’s number d. 4.184 2. The energy of a photon of electromagnetic energy divided by its frequency equals: a. c, the speed of light b. h, Planck’s constant c. Avogadro’s number d. 4.184 3. Light that contains colors of all wavelengths is called: a. b. c. d. ...
... c. Avogadro’s number d. 4.184 2. The energy of a photon of electromagnetic energy divided by its frequency equals: a. c, the speed of light b. h, Planck’s constant c. Avogadro’s number d. 4.184 3. Light that contains colors of all wavelengths is called: a. b. c. d. ...
Thermal Bremsstrahlung - Ira-Inaf
... Bremsstrahlung real plasma The real case: a cloud with ion number density nZ and free electron number density ne In a unit time, each electron experiences a number of collisions with an impact parameter between b and b + db is 2 ...
... Bremsstrahlung real plasma The real case: a cloud with ion number density nZ and free electron number density ne In a unit time, each electron experiences a number of collisions with an impact parameter between b and b + db is 2 ...
High-Energy Astrophysics
... Figure 2. This figure shows the results of fitting all four models to the SED of PKS0227. Whilst all four models can fit the observations reasonably well only model 4 can fit to the data with an equipartition jet. The fits for models 1, 2 and 3 require a jet out of equipartition by a factor of 10 an ...
... Figure 2. This figure shows the results of fitting all four models to the SED of PKS0227. Whilst all four models can fit the observations reasonably well only model 4 can fit to the data with an equipartition jet. The fits for models 1, 2 and 3 require a jet out of equipartition by a factor of 10 an ...
PPTX
... on bg • The same energy loss in gas (or liquid gas, e.g. in a bubble chamber) for 10 GeV muon and 100 GeV proton ...
... on bg • The same energy loss in gas (or liquid gas, e.g. in a bubble chamber) for 10 GeV muon and 100 GeV proton ...
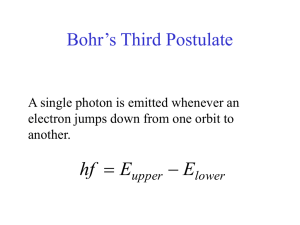
Bohr´s Third Postulate
... 4. What property of the emitted electrons depends on the intensity of incident light?What property of the emitted photoelectrons depends on the frequency of incident light? ...
... 4. What property of the emitted electrons depends on the intensity of incident light?What property of the emitted photoelectrons depends on the frequency of incident light? ...
Bremsstrahlung
Bremsstrahlung (German pronunciation: [ˈbʁɛmsˌʃtʁaːlʊŋ], from bremsen ""to brake"" and Strahlung ""radiation"", i.e. ""braking radiation"" or ""deceleration radiation"") is electromagnetic radiation produced by the deceleration of a charged particle when deflected by another charged particle, typically an electron by an atomic nucleus. The moving particle loses kinetic energy, which is converted into a photon, thus satisfying the law of conservation of energy. The term is also used to refer to the process of producing the radiation. Bremsstrahlung has a continuous spectrum, which becomes more intense and whose peak intensity shifts toward higher frequencies as the change of the energy of the accelerated particles increases.Strictly speaking, braking radiation is any radiation due to the acceleration of a charged particle, which includes synchrotron radiation, cyclotron radiation, and the emission of electrons and positrons during beta decay. However, the term is frequently used in the more narrow sense of radiation from electrons (from whatever source) slowing in matter.Bremsstrahlung emitted from plasma is sometimes referred to as free/free radiation. This refers to the fact that the radiation in this case is created by charged particles that are free both before and after the deflection (acceleration) that caused the emission.