The Classification of Stellar Spectra
... spectrum in 1814 and found some 600 dark lines, and he specifically measured the wavelength of 324 of them. Many of the Fraunhofer lines in the solar spectrum retain the notations he created to designate them. In 1864, Sir William Huggins matched some of these dark lines in spectra from other stars ...
... spectrum in 1814 and found some 600 dark lines, and he specifically measured the wavelength of 324 of them. Many of the Fraunhofer lines in the solar spectrum retain the notations he created to designate them. In 1864, Sir William Huggins matched some of these dark lines in spectra from other stars ...
1 pracovni list HR diagram I EN
... distance is in parsecs (pc). Parallax π is given in arc seconds in column Plx. Note: value of the parallax in the catalogue is in arc milliseconds. Mark the new column as r. Absolute magnitude M can be calculated using the formula M = m + 5 ⋅ [1 − log(r )], where apparent magnitude m is in column Vm ...
... distance is in parsecs (pc). Parallax π is given in arc seconds in column Plx. Note: value of the parallax in the catalogue is in arc milliseconds. Mark the new column as r. Absolute magnitude M can be calculated using the formula M = m + 5 ⋅ [1 − log(r )], where apparent magnitude m is in column Vm ...
*Studying Complex Star-Forming Fields: Rosette Nebula and Monoceros Loop by Chris Hathaway and Anthony Kuchera
... The stars in our sample are dominated by the Mon OB2 association. This association has been extensively studied by a number of authors and is considered to cover a large area of the sky toward the Rosette Nebula and Monoceros Loop. This area also contains a large number of young open clusters. The e ...
... The stars in our sample are dominated by the Mon OB2 association. This association has been extensively studied by a number of authors and is considered to cover a large area of the sky toward the Rosette Nebula and Monoceros Loop. This area also contains a large number of young open clusters. The e ...
star - Cloudfront.net
... 1d. Students know the evidence indicating that the planets are much closer to Earth than the stars are. 2a. Students know why the solar system is located in an outer edge of the disc-shaped Milky Way galaxy, which spans 100,000 light years. 2b. Students know galaxies are made of billions of stars an ...
... 1d. Students know the evidence indicating that the planets are much closer to Earth than the stars are. 2a. Students know why the solar system is located in an outer edge of the disc-shaped Milky Way galaxy, which spans 100,000 light years. 2b. Students know galaxies are made of billions of stars an ...
Stars and Galaxies
... dozens to thousands of stars young stars! only a few million years old may still be surrounded by nebula from which they formed located in the spiral arms of a galaxy example: Pleiades Image at http://hubblesite.org/newscenter/archive/releases/star%20cluster/open/2004/20/image/a/results/50/ ...
... dozens to thousands of stars young stars! only a few million years old may still be surrounded by nebula from which they formed located in the spiral arms of a galaxy example: Pleiades Image at http://hubblesite.org/newscenter/archive/releases/star%20cluster/open/2004/20/image/a/results/50/ ...
Stellar Populations of Galaxies- 2 Lectures H
... The limit of the Balmer series and the blending of the high-order Balmer lines produces a discontinuity of the spectrum blueward of 3650°A. (the Balmer break) –more important in young populations, The break amplitude and position is a proxy for the age of the stellar population The UV continuum flux ...
... The limit of the Balmer series and the blending of the high-order Balmer lines produces a discontinuity of the spectrum blueward of 3650°A. (the Balmer break) –more important in young populations, The break amplitude and position is a proxy for the age of the stellar population The UV continuum flux ...
PPT - ALFALFA survey
... Luminosity - Color Diagram. The ADBS galaxies display a weak relationship between MB and color, in the sense that dwarfier galaxies tend to be bluer. There are many outliers, however. ...
... Luminosity - Color Diagram. The ADBS galaxies display a weak relationship between MB and color, in the sense that dwarfier galaxies tend to be bluer. There are many outliers, however. ...
Ursa Minor
... Constellations visible in the November sky Click on constellations to learn more about them ...
... Constellations visible in the November sky Click on constellations to learn more about them ...
Visual Double Star Measurements with Equatorial - Alt
... telescope is moved so that the primary star accurately drifts through the central division mark. In practice, the primary is situated about 5-8 division marks away from the central mark and allowed to drift. If the star drifts through the central mark, the drift sequence is allowed to continue until ...
... telescope is moved so that the primary star accurately drifts through the central division mark. In practice, the primary is situated about 5-8 division marks away from the central mark and allowed to drift. If the star drifts through the central mark, the drift sequence is allowed to continue until ...
P2_5 The Apparent Magnitude of α Orionis Supernova
... It has been found that when α Orionis becomes a supernova, it will be visible during the day. However, it will appear as a bright star rather than illuminating the Earth in the same way as the sun or moon. The moon has a mean apparent magnitude of -12.74 [6], and gives just enough light to help see ...
... It has been found that when α Orionis becomes a supernova, it will be visible during the day. However, it will appear as a bright star rather than illuminating the Earth in the same way as the sun or moon. The moon has a mean apparent magnitude of -12.74 [6], and gives just enough light to help see ...
AST1100 Lecture Notes
... standard rulers. For instance a special kind of galaxy which has been shown to always have the same dimensions could be used as a standard ruler. ...
... standard rulers. For instance a special kind of galaxy which has been shown to always have the same dimensions could be used as a standard ruler. ...
Guidestar: February, 2015 - Houston Astronomical Society
... February 6th meeting to get your 2015 code. We will soon be putting the site orientation program on the website. In doing so we are going to ask everyone who already has taken the course to take a refresher course. When you complete the course and pass the 10 or so question quiz the data base will a ...
... February 6th meeting to get your 2015 code. We will soon be putting the site orientation program on the website. In doing so we are going to ask everyone who already has taken the course to take a refresher course. When you complete the course and pass the 10 or so question quiz the data base will a ...
The Milky Way Model - University of Chicago
... observation wavelength, galactic coordinates and distance, to place them appropriately in your model. Only two angular coordinates are needed to specify the location of any object on the sky, for instance common coordinates used in astronomy are: 1. Azimuth (az) - the angle the object can be found a ...
... observation wavelength, galactic coordinates and distance, to place them appropriately in your model. Only two angular coordinates are needed to specify the location of any object on the sky, for instance common coordinates used in astronomy are: 1. Azimuth (az) - the angle the object can be found a ...
Stars - WhatisOutThere
... helium. These are the two lightest elements. They shine by burning the hydrogen into helium in their cores, then later in life they create heavier elements. Most stars have heavy elements, like carbon, nitrogen, oxygen and iron but only small amounts. These elements came from the stars that existed ...
... helium. These are the two lightest elements. They shine by burning the hydrogen into helium in their cores, then later in life they create heavier elements. Most stars have heavy elements, like carbon, nitrogen, oxygen and iron but only small amounts. These elements came from the stars that existed ...
HST Key Project to Measure the Hubble Constant from
... – Supernova from massive stars, fainter and show wider variation in luminosity than IaSN – Baade-Wesselink technique: follow spectral fits of color T, flux and radial vel of envelope over time to det dist. – Applied independent of local calibration of extragalactic distance scale but verified with g ...
... – Supernova from massive stars, fainter and show wider variation in luminosity than IaSN – Baade-Wesselink technique: follow spectral fits of color T, flux and radial vel of envelope over time to det dist. – Applied independent of local calibration of extragalactic distance scale but verified with g ...
Death of the Stars
... if the rocket can overcome this force it can escape from Earth. If shoot the rocket up with a speed greater than 11km/s, it can leave the Earth. To leave the surface of the Sun, you need a speed of 620km/s. When the Sun becomes a white dwarf, you will need 6400km/s. If the Sun became a neutron star, ...
... if the rocket can overcome this force it can escape from Earth. If shoot the rocket up with a speed greater than 11km/s, it can leave the Earth. To leave the surface of the Sun, you need a speed of 620km/s. When the Sun becomes a white dwarf, you will need 6400km/s. If the Sun became a neutron star, ...
Lesson 3: Calculating distances to stars
... the star is very far away, then the brightness of the star can be used to estimate the distance to the star. It is a rather simple principle; if a star is close by then it will appear bright, and if the star is far away it will appear dim. This method was first proposed by the Dutch astronomer, Chri ...
... the star is very far away, then the brightness of the star can be used to estimate the distance to the star. It is a rather simple principle; if a star is close by then it will appear bright, and if the star is far away it will appear dim. This method was first proposed by the Dutch astronomer, Chri ...
Lecture 12
... • Most binaries are too far away to see both stars separately. • But, you can detect their orbital motions by the periodic Doppler shifts of their spectral lines. – Determine the orbit period & size from velocities. ...
... • Most binaries are too far away to see both stars separately. • But, you can detect their orbital motions by the periodic Doppler shifts of their spectral lines. – Determine the orbit period & size from velocities. ...
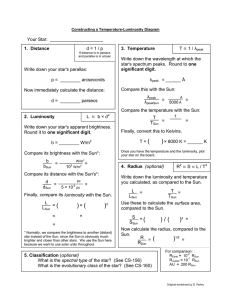
Your Star: _____________________ d = 1 / p
... of some of the well-known stars to calculate, using the formulas and methods discussed in class, their intrinsic properties (temperature, luminosity, and radius.) We will then look for patterns in these properties by way of the H-R (temperature-luminosity) diagram. Your group will be in charge of a ...
... of some of the well-known stars to calculate, using the formulas and methods discussed in class, their intrinsic properties (temperature, luminosity, and radius.) We will then look for patterns in these properties by way of the H-R (temperature-luminosity) diagram. Your group will be in charge of a ...
Galaxy Formation and Evolution
... density field evolve. In a universe dominated by non-relativistic matter, perturbations grow with time. A region whose initial density is higher than the mean will attract its surroundings more strongly than average. On the other hand, underdense regions become even more rarefied as matter flows awa ...
... density field evolve. In a universe dominated by non-relativistic matter, perturbations grow with time. A region whose initial density is higher than the mean will attract its surroundings more strongly than average. On the other hand, underdense regions become even more rarefied as matter flows awa ...
Astronomy Report Southern Cross Authors Maria Constanza Pavez
... This circumpolar constellation (always situated above the horizon) of the South Hemisphere, is located between the Centauri and the Fly constellations, just above the Polar Antarctic Circle and it is crossed by the Milky Way. The Crux is visible the whole year between 25 N and 90 S degrees of latitu ...
... This circumpolar constellation (always situated above the horizon) of the South Hemisphere, is located between the Centauri and the Fly constellations, just above the Polar Antarctic Circle and it is crossed by the Milky Way. The Crux is visible the whole year between 25 N and 90 S degrees of latitu ...
Stars part 1
... Detecting two or more lines of that element in the star’s spectrum indicates that element is present in that star. The brighter the spectral line, the greater amount of that element in the star. ...
... Detecting two or more lines of that element in the star’s spectrum indicates that element is present in that star. The brighter the spectral line, the greater amount of that element in the star. ...
Analemma - Stony Brook University
... Sun at civil noon (standard time). This demonstrates: •The inclination of the ecliptic •The equation of time •The non-circularity of Earth’s orbit ...
... Sun at civil noon (standard time). This demonstrates: •The inclination of the ecliptic •The equation of time •The non-circularity of Earth’s orbit ...
Proficiency Step #5--
... The summer triangle is an easily found asterism in the summer sky and is made up of three of the brightest stars in the sky—each of which is actually in three separate constellation areas (Vega in Lyra, Deneb in Cygnus, and Altair in Aquilla). The Coathanger asterism (officially called Brocchi’s clu ...
... The summer triangle is an easily found asterism in the summer sky and is made up of three of the brightest stars in the sky—each of which is actually in three separate constellation areas (Vega in Lyra, Deneb in Cygnus, and Altair in Aquilla). The Coathanger asterism (officially called Brocchi’s clu ...
Serpens

Serpens (""the Serpent"", Greek Ὄφις) is a constellation of the northern hemisphere. One of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, it remains one of the 88 modern constellations defined by the International Astronomical Union. It is unique among the modern constellations in being split into two non-contiguous parts, Serpens Caput (Serpent's Head) to the west and Serpens Cauda (Serpent's Tail) to the east. Between these two halves lies the constellation of Ophiuchus, the ""Serpent-Bearer"". In figurative representations, the body of the serpent is represented as passing behind Ophiuchus between Mu Serpentis in Serpens Caput and Nu Serpentis in Serpens Cauda.The brightest star in Serpens is the red giant star Alpha Serpentis, or Unukalhai, in Serpens Caput, with an apparent magnitude of 2.63. Also located in Serpens Caput are the naked-eye globular cluster Messier 5 and the naked-eye variables R Serpentis and Tau4 Serpentis. Notable extragalactic objects include Seyfert's Sextet, one of the densest galaxy clusters known; Arp 220, the prototypical ultraluminous infrared galaxy; and Hoag's Object, the most famous of the very rare class of galaxies known as ring galaxies.Part of the Milky Way's galactic plane passes through Serpens Cauda, which is therefore rich in galactic deep-sky objects, such as the Eagle Nebula (IC 4703) and its associated star cluster Messier 16. The nebula measures 70 light-years by 50 light-years and contains the Pillars of Creation, three dust clouds that became famous for the image taken by the Hubble Space Telescope. Other striking objects include the Red Square Nebula, one of the few objects in astronomy to take on a square shape; and Westerhout 40, a massive nearby star-forming region consisting of a molecular cloud and an H II region.