PowerPoint
... b) appears to twinkle. c) is Doppler shifted. d) turns bluish in color. e) ionizes the dust and creates emission lines. ...
... b) appears to twinkle. c) is Doppler shifted. d) turns bluish in color. e) ionizes the dust and creates emission lines. ...
Chapter 17
... The discovery of At the turn of the 20th century astronomers believed the Milky Way other galaxies galaxy was the entire universe. As telescopes got better, though, some “smudges” that were thought to be nebulae in the Milky Way were recognized to be whole galaxies far outside our own. The discovery ...
... The discovery of At the turn of the 20th century astronomers believed the Milky Way other galaxies galaxy was the entire universe. As telescopes got better, though, some “smudges” that were thought to be nebulae in the Milky Way were recognized to be whole galaxies far outside our own. The discovery ...
The Magnitude System
... The magnitude system is invented by Hipparchus in 120 BC, and is still used today, although the magnitude scale itself is not a meaningful “physical quantity” (it is just a scale). Initially this system was arbitrary because Hipparchus decided that all the brightest and most beautiful stars had a ma ...
... The magnitude system is invented by Hipparchus in 120 BC, and is still used today, although the magnitude scale itself is not a meaningful “physical quantity” (it is just a scale). Initially this system was arbitrary because Hipparchus decided that all the brightest and most beautiful stars had a ma ...
Publisher: Emily Barrosse Acquisitions Editor: Kelley Tyner
... Stars that are more than 10 times as massive as the Sun whip through their mainsequence lifetimes at a rapid pace. These prodigal stars use up their store of hydrogen very quickly. A star containing 15 times as much mass as the Sun may take only 10 million years from the time it reaches the main seq ...
... Stars that are more than 10 times as massive as the Sun whip through their mainsequence lifetimes at a rapid pace. These prodigal stars use up their store of hydrogen very quickly. A star containing 15 times as much mass as the Sun may take only 10 million years from the time it reaches the main seq ...
Stellar Evolution
... reactions to start that are very slow at the ~15 million K temperature maintained by hydrogen fusion Star leaves the main sequence, becomes a red giant! ASTR 1120: Fall 2005 ...
... reactions to start that are very slow at the ~15 million K temperature maintained by hydrogen fusion Star leaves the main sequence, becomes a red giant! ASTR 1120: Fall 2005 ...
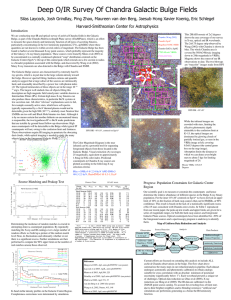
Deep O/IR Survey Of Chandra Galactic Bulge Fields
... We are conducting near-IR and optical survey of archival Chandra fields in the Galactic Bulge, as part of the Chandra Multiwavelength Plane survey (ChaMPlane), which is an effort to measure the space density and luminosity function of all types of accreting binaries, particularly concentrating on th ...
... We are conducting near-IR and optical survey of archival Chandra fields in the Galactic Bulge, as part of the Chandra Multiwavelength Plane survey (ChaMPlane), which is an effort to measure the space density and luminosity function of all types of accreting binaries, particularly concentrating on th ...
Celebrating the centennial of a celestial yardstick
... offered was an indoor position as a computer. “I should be willing to pay thirty cents an hour in view of the quality of your work,” Pickering wrote, “although our usual price, in such cases, is twenty five cents an hour.” Leavitt, in accepting the position, referred to Pickering’s offer as “very li ...
... offered was an indoor position as a computer. “I should be willing to pay thirty cents an hour in view of the quality of your work,” Pickering wrote, “although our usual price, in such cases, is twenty five cents an hour.” Leavitt, in accepting the position, referred to Pickering’s offer as “very li ...
Picture: Alnitak is the left-hand star in Orion`s Belt. Image: NASA
... to C9). A red giant whose spectrum is dominated by strong absorption bands of carbon-containing molecules; the Swan bands of C2 are especially prominent, with absorption by CN, CH, C3, SiC2, and CaII present to varying degrees, with often a strong sodium D line. Carbon stars, also known as C stars, ...
... to C9). A red giant whose spectrum is dominated by strong absorption bands of carbon-containing molecules; the Swan bands of C2 are especially prominent, with absorption by CN, CH, C3, SiC2, and CaII present to varying degrees, with often a strong sodium D line. Carbon stars, also known as C stars, ...
Estudio de Cúmulos de Galaxias en el Sloan Digital Sky Survey
... – Median stellar mass of the descendants is 4 x 1010h-1M⊙ (of bright z=3 LBGs) and 1011h-1M⊙ (of bright z=6 LBGs), – Median stellar mass of the descendants is 8 x 109h-1M⊙ (of both faint z=3 LBGs and faint z=6 LBGs), – One every 10 and one every 50 Milky Way mass galaxy is predicted to be descendant ...
... – Median stellar mass of the descendants is 4 x 1010h-1M⊙ (of bright z=3 LBGs) and 1011h-1M⊙ (of bright z=6 LBGs), – Median stellar mass of the descendants is 8 x 109h-1M⊙ (of both faint z=3 LBGs and faint z=6 LBGs), – One every 10 and one every 50 Milky Way mass galaxy is predicted to be descendant ...
two dozen compact sources and a massive disk
... • Sub-arcsecond SMA + VLA observations reveal a prolific protocluster with 25 members: NGC 6334 I(N) • We perform the first dynamical mass measurement using hot core line emission (410 ± 260 M), compatible with dust estimates • We analyze its structure using tools developed for infrared clusters (Q ...
... • Sub-arcsecond SMA + VLA observations reveal a prolific protocluster with 25 members: NGC 6334 I(N) • We perform the first dynamical mass measurement using hot core line emission (410 ± 260 M), compatible with dust estimates • We analyze its structure using tools developed for infrared clusters (Q ...
Staring Back to Cosmic Dawn - UC-HiPACC
... and filaments known as the “cosmic web,” and then into denser blobs of gas and dark matter at the intersections of dark matter filaments. These structures later collapsed to form the seeds of galaxies. More cold gas flowed along the dark matter filaments into galactic disks, where it became gravitat ...
... and filaments known as the “cosmic web,” and then into denser blobs of gas and dark matter at the intersections of dark matter filaments. These structures later collapsed to form the seeds of galaxies. More cold gas flowed along the dark matter filaments into galactic disks, where it became gravitat ...
ASTROPHYSICS UNIVERSE - Physics
... Eclipsing binaries – some binaries are too far away from us to be resolved visually as two separate stars. At big distances two stars may seem to be one. But if the plane of the orbit of the two stars is suitably oriented relative to that of the Earth, the light of one of the stars in the binary ...
... Eclipsing binaries – some binaries are too far away from us to be resolved visually as two separate stars. At big distances two stars may seem to be one. But if the plane of the orbit of the two stars is suitably oriented relative to that of the Earth, the light of one of the stars in the binary ...
star
... Stars live for a very long time, up to 100 million years or more No humans can possibly observe a star this long! How can we learn about the stages in a star’s life? We can take a celestial census, getting a snapshot of many stars at different stages of their life We can then try to infer the stages ...
... Stars live for a very long time, up to 100 million years or more No humans can possibly observe a star this long! How can we learn about the stages in a star’s life? We can take a celestial census, getting a snapshot of many stars at different stages of their life We can then try to infer the stages ...
Quiz 2 Lecture 12
... a. Ring galaxies can be produced by head-on collisions between galaxies. b. The ratio of the number of elliptical to spiral galaxies remains constant over time. c. The Magellanic Clouds may eventually be "cannibalized" by our Galaxy. d. The shape of a galaxy can be influenced by collision with anoth ...
... a. Ring galaxies can be produced by head-on collisions between galaxies. b. The ratio of the number of elliptical to spiral galaxies remains constant over time. c. The Magellanic Clouds may eventually be "cannibalized" by our Galaxy. d. The shape of a galaxy can be influenced by collision with anoth ...
Lecture 8: The Stars - Department of Physics and Astronomy
... Out to a distance of 4 pc, 12 light, from the Sun, there are 30 stars. The brightest is Sirius, which can be seen in the night sky. Only 10 are bright enough to see with the naked eye. The rest have been discovered through telescopic surveys of the sky. ...
... Out to a distance of 4 pc, 12 light, from the Sun, there are 30 stars. The brightest is Sirius, which can be seen in the night sky. Only 10 are bright enough to see with the naked eye. The rest have been discovered through telescopic surveys of the sky. ...
H-RDiagramSE
... luminosity—or how bright a star is. Using the H-R Diagram Gizmo™, you will discover how some of these characteristics are related. Start by moving your cursor over the stars in the Star collection. Information about each star is displayed on the right side of the Gizmo. The numbers given for Luminos ...
... luminosity—or how bright a star is. Using the H-R Diagram Gizmo™, you will discover how some of these characteristics are related. Start by moving your cursor over the stars in the Star collection. Information about each star is displayed on the right side of the Gizmo. The numbers given for Luminos ...
Spatial distribution of stars in the Milky Way
... Andromeda galaxy he found that the disk stars in M31 were like nearby disk stars in our Galaxy, while the bulge stars resembled those of the Galaxy's globular clusters. ...
... Andromeda galaxy he found that the disk stars in M31 were like nearby disk stars in our Galaxy, while the bulge stars resembled those of the Galaxy's globular clusters. ...
Chapter 17 Measuring the Stars
... diagram, a pattern begins to form: These are the 80 closest stars to us; note the dashed lines of constant radius. The darkened curve is called the main sequence, as this is where most stars are. Also indicated is the white dwarf region; these stars are hot but not very luminous, as they are quite s ...
... diagram, a pattern begins to form: These are the 80 closest stars to us; note the dashed lines of constant radius. The darkened curve is called the main sequence, as this is where most stars are. Also indicated is the white dwarf region; these stars are hot but not very luminous, as they are quite s ...
description
... to season as the Earth orbits the Sun. The stars will be in a different location (west of) as it was the previous night at the same exact time. Which stars & constellations you see depends on your latitude on Earth. People in the Southern hemisphere see different constellations at different times of ...
... to season as the Earth orbits the Sun. The stars will be in a different location (west of) as it was the previous night at the same exact time. Which stars & constellations you see depends on your latitude on Earth. People in the Southern hemisphere see different constellations at different times of ...
Galaxies and Stars
... D) blue supergiant star with a temperature of approximately 20,000ºC and a luminosity of 700,000 ...
... D) blue supergiant star with a temperature of approximately 20,000ºC and a luminosity of 700,000 ...
Visual Photometry - El Camino College
... more) new sources of error introduced by doing this experiment using a real telescope. 3) Answer the appropriate question: a. Clear night question: Based on your results above, would an 8th magnitude star be easily visible, barely visible, or invisible through the FINDER telescope? How about a 12th ...
... more) new sources of error introduced by doing this experiment using a real telescope. 3) Answer the appropriate question: a. Clear night question: Based on your results above, would an 8th magnitude star be easily visible, barely visible, or invisible through the FINDER telescope? How about a 12th ...
visual photometry - El Camino College
... more) new sources of error introduced by doing this experiment using a real telescope. 3) Answer the appropriate question: a. Clear night question: Based on your results above, would an 8th magnitude star be easily visible, barely visible, or invisible through the FINDER telescope? How about a 12th ...
... more) new sources of error introduced by doing this experiment using a real telescope. 3) Answer the appropriate question: a. Clear night question: Based on your results above, would an 8th magnitude star be easily visible, barely visible, or invisible through the FINDER telescope? How about a 12th ...
The Milky Way
... disk, where the number of stars is much greater • Originally astronomers thought the Milky Way WAS the Whole Universe & SS central to it (because of visible light extinction by dust) • Location of Globular Clusters in halo implied center towards Sagittarius and SS actually towards one side in early ...
... disk, where the number of stars is much greater • Originally astronomers thought the Milky Way WAS the Whole Universe & SS central to it (because of visible light extinction by dust) • Location of Globular Clusters in halo implied center towards Sagittarius and SS actually towards one side in early ...
Serpens

Serpens (""the Serpent"", Greek Ὄφις) is a constellation of the northern hemisphere. One of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, it remains one of the 88 modern constellations defined by the International Astronomical Union. It is unique among the modern constellations in being split into two non-contiguous parts, Serpens Caput (Serpent's Head) to the west and Serpens Cauda (Serpent's Tail) to the east. Between these two halves lies the constellation of Ophiuchus, the ""Serpent-Bearer"". In figurative representations, the body of the serpent is represented as passing behind Ophiuchus between Mu Serpentis in Serpens Caput and Nu Serpentis in Serpens Cauda.The brightest star in Serpens is the red giant star Alpha Serpentis, or Unukalhai, in Serpens Caput, with an apparent magnitude of 2.63. Also located in Serpens Caput are the naked-eye globular cluster Messier 5 and the naked-eye variables R Serpentis and Tau4 Serpentis. Notable extragalactic objects include Seyfert's Sextet, one of the densest galaxy clusters known; Arp 220, the prototypical ultraluminous infrared galaxy; and Hoag's Object, the most famous of the very rare class of galaxies known as ring galaxies.Part of the Milky Way's galactic plane passes through Serpens Cauda, which is therefore rich in galactic deep-sky objects, such as the Eagle Nebula (IC 4703) and its associated star cluster Messier 16. The nebula measures 70 light-years by 50 light-years and contains the Pillars of Creation, three dust clouds that became famous for the image taken by the Hubble Space Telescope. Other striking objects include the Red Square Nebula, one of the few objects in astronomy to take on a square shape; and Westerhout 40, a massive nearby star-forming region consisting of a molecular cloud and an H II region.