Tasks - ESA Science
... The magnification method takes the 1994 image and magnifies it until it exactly matches the 1997 image. Fig. 7 shows the method of subtracting. Note that the image taken in 1994 is not magnified. In each of the nine small images in Fig. 8 the 1994 image was magnified by a different factor, F, (this ...
... The magnification method takes the 1994 image and magnifies it until it exactly matches the 1997 image. Fig. 7 shows the method of subtracting. Note that the image taken in 1994 is not magnified. In each of the nine small images in Fig. 8 the 1994 image was magnified by a different factor, F, (this ...
Document
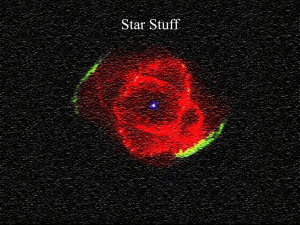
... skins inside the star. However, since fusion of iron uses up energy instead of releasing energy, fusion cannot ignite from Fe -- an iron core cannot support the weight of the outer layers. The collapse of this core — which occurs in a fraction of a second — results in a supernova that nearly obliter ...
... skins inside the star. However, since fusion of iron uses up energy instead of releasing energy, fusion cannot ignite from Fe -- an iron core cannot support the weight of the outer layers. The collapse of this core — which occurs in a fraction of a second — results in a supernova that nearly obliter ...
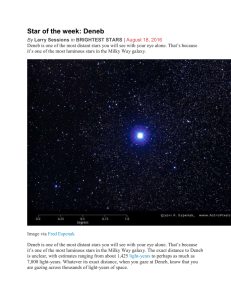
in BRIGHTEST STARS
... In order for us to see it at its enormous distance, Deneb must also be tremendously bright and energetic. Among the 20 brightest stars, only Rigel in Orion surpasses Deneb in intrinsic brightness. Deneb is an A2Ia star, which says that it is white hot (A2) and a supergiant star (Ia). Prof. James Kal ...
... In order for us to see it at its enormous distance, Deneb must also be tremendously bright and energetic. Among the 20 brightest stars, only Rigel in Orion surpasses Deneb in intrinsic brightness. Deneb is an A2Ia star, which says that it is white hot (A2) and a supergiant star (Ia). Prof. James Kal ...
Observational properties of stars
... So you had SN2012A, SN2012B, …to SN2012Z, then SN2012aa, SN2012ab, …to SN2012az, then SN2012ba, …and so on. In 2012 this list ended with SN2012ih, though in 2007 we got to SN2007va. I’m not sure what will happen if we go beyond zz. 1.2 SN types A Type II SN is what has been described so far. What is ...
... So you had SN2012A, SN2012B, …to SN2012Z, then SN2012aa, SN2012ab, …to SN2012az, then SN2012ba, …and so on. In 2012 this list ended with SN2012ih, though in 2007 we got to SN2007va. I’m not sure what will happen if we go beyond zz. 1.2 SN types A Type II SN is what has been described so far. What is ...
Cepheid
... In Shapley’s day, the LMC and SMC were considered as two isolated offshoots of the Milky Way, different from the spiral nebulae. We now realize that they are ‘dwarf’ galaxies in their own right (but not spirals). ...
... In Shapley’s day, the LMC and SMC were considered as two isolated offshoots of the Milky Way, different from the spiral nebulae. We now realize that they are ‘dwarf’ galaxies in their own right (but not spirals). ...
Lab PDF - NMSU Astronomy
... Before this question could be answered, astronomers had to learn to distinguish stable, wellbehaved stars from their more erratic, very young or very old neighbors. They did this by plotting two basic observed quantities (brightness and color) against each other, forming a plot called a Hertzsprung ...
... Before this question could be answered, astronomers had to learn to distinguish stable, wellbehaved stars from their more erratic, very young or very old neighbors. They did this by plotting two basic observed quantities (brightness and color) against each other, forming a plot called a Hertzsprung ...
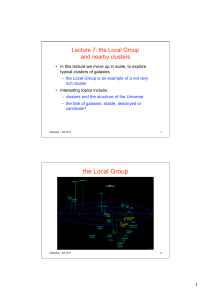
the Local Group - Simon P Driver
... – it’s mostly empty, i.e. galaxies are quite distant from each other – with some exceptions like satellite galaxies – the three spirals are easily the biggest – dwarf galaxies are on the outskirts of the group • how typical is this of other galaxy groups? – turns out that the Local group is no ...
... – it’s mostly empty, i.e. galaxies are quite distant from each other – with some exceptions like satellite galaxies – the three spirals are easily the biggest – dwarf galaxies are on the outskirts of the group • how typical is this of other galaxy groups? – turns out that the Local group is no ...
Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram Outline
... 16631 single stars from the Hipparcos Catalogue with relative distance precision better than 10% and sigma_(B-V) less than or equal to 0.025 mag. Colors indicate number of stars in a cell of 0.01 mag in (B-V) and 0.05 mag in V magnitude ...
... 16631 single stars from the Hipparcos Catalogue with relative distance precision better than 10% and sigma_(B-V) less than or equal to 0.025 mag. Colors indicate number of stars in a cell of 0.01 mag in (B-V) and 0.05 mag in V magnitude ...
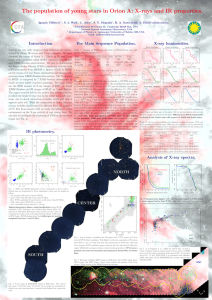
The population of young stars in Orion A: X-rays and... Ignazio Pillitteri , S. J. Wolk , L. Allen
... supports the guess that the population of low mass WTTs missed in Xrays is above 50%. By using a fork of 30%–50% of X-ray detected WTTs, we bracket the total population of PMS stars in this region to be between 1500 and 2130 stars with masses of a few solar masses to the limit of Brown Dwarfs, a pop ...
... supports the guess that the population of low mass WTTs missed in Xrays is above 50%. By using a fork of 30%–50% of X-ray detected WTTs, we bracket the total population of PMS stars in this region to be between 1500 and 2130 stars with masses of a few solar masses to the limit of Brown Dwarfs, a pop ...
The Bigger Picture - Astronomy and Astrophysics
... • Imagine a star with a relatively cool (4000k) atmosphere. Temperature is just a measure of the average velocity of the atoms and molecules in a gas. For a relatively cool gas there are: (1) Few atomic collisions with enough energy to knock electrons up to the 1st excited state so the majority of t ...
... • Imagine a star with a relatively cool (4000k) atmosphere. Temperature is just a measure of the average velocity of the atoms and molecules in a gas. For a relatively cool gas there are: (1) Few atomic collisions with enough energy to knock electrons up to the 1st excited state so the majority of t ...
The colours of the Universe, the amateur astronomical spectroscopy.
... I have been interested in spectroscopy since one year, when I had a physic's lesson about emission and absorption spectrum of chemical elements in different states of aggregation. It was interesting, in that simple way that I can independently receive substance's spectrum, make analyze and explore c ...
... I have been interested in spectroscopy since one year, when I had a physic's lesson about emission and absorption spectrum of chemical elements in different states of aggregation. It was interesting, in that simple way that I can independently receive substance's spectrum, make analyze and explore c ...
sections 12-15 instructor notes
... resulting from the tilt of the local spiral feature to the Galactic plane, with the tilt being below the plane in the direction of the anticentre and above the plane in the direction of the Galactic centre. Investigations of the distribution of dark clouds by Lynds (ApJS, 7, 1, 1962) for the norther ...
... resulting from the tilt of the local spiral feature to the Galactic plane, with the tilt being below the plane in the direction of the anticentre and above the plane in the direction of the Galactic centre. Investigations of the distribution of dark clouds by Lynds (ApJS, 7, 1, 1962) for the norther ...
Mysterious transient objects - NCRA
... Flashes of gamma-rays from random directions in sky Few milliseconds to few seconds timescale Even 100 times more energetic than supernovae Brightest sources of cosmic gamma-ray photons in the universe In universe roughly 1 GRB is detected per day Short duration (< 2 sec) and long duration (> ...
... Flashes of gamma-rays from random directions in sky Few milliseconds to few seconds timescale Even 100 times more energetic than supernovae Brightest sources of cosmic gamma-ray photons in the universe In universe roughly 1 GRB is detected per day Short duration (< 2 sec) and long duration (> ...
Stars A globular cluster is a tightly grouped swarm of stars held
... galaxy may be 100 billion. Thus, more than 10 billion trillion stars may exist. But if you look at the night sky far from city lights, you can see only about 3,000 of them without using binoculars or a telescope. Stars, like people, have life cycles -- they are born, pass through several phases, and ...
... galaxy may be 100 billion. Thus, more than 10 billion trillion stars may exist. But if you look at the night sky far from city lights, you can see only about 3,000 of them without using binoculars or a telescope. Stars, like people, have life cycles -- they are born, pass through several phases, and ...
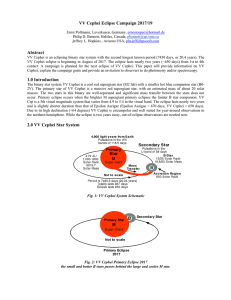
VV Cephei Eclipse Campaign 2017/19
... The binary star system VV Cephei is a cool red supergiant star (M2 Iab) with a smaller hot blue companion star (B02V). The primary star of VV Cephei is a massive red supergiant star, with an estimated mass of about 20 solar masses. The two stars in this binary are well-separated and significant mass ...
... The binary star system VV Cephei is a cool red supergiant star (M2 Iab) with a smaller hot blue companion star (B02V). The primary star of VV Cephei is a massive red supergiant star, with an estimated mass of about 20 solar masses. The two stars in this binary are well-separated and significant mass ...
supernova remnants: a link between massive stars and the
... that when the NS forms, the new star overshoots its equilibrium configuration giving a large compression to the neutron core (the core collapses in about 1 sec). This produces a rebound that sends a strong supersonic shock wave in about 0.01 sec that travels through the infalling matter. In a short ...
... that when the NS forms, the new star overshoots its equilibrium configuration giving a large compression to the neutron core (the core collapses in about 1 sec). This produces a rebound that sends a strong supersonic shock wave in about 0.01 sec that travels through the infalling matter. In a short ...
Milky Way inner halo reveals its age | COSMOS magazine
... halo region to date is 13.5 billion years old. White dwarf stars form when normal stars like the sun have burnt up all their fuel and lost their outer layers. The centre of the star becomes white hot before cooling over many years. “White dwarfs are remarkable objects,” said Kalirai. “They contain a ...
... halo region to date is 13.5 billion years old. White dwarf stars form when normal stars like the sun have burnt up all their fuel and lost their outer layers. The centre of the star becomes white hot before cooling over many years. “White dwarfs are remarkable objects,” said Kalirai. “They contain a ...
DSLR Photometry
... Des says in theory it is advisable to also construct master flat field frames in order to remove the effects of the edge distortions of lens. Des has found, however, that the field of view of a DSLR is so wide that a flat field is not required, if you are using high quality lenses, provided the targ ...
... Des says in theory it is advisable to also construct master flat field frames in order to remove the effects of the edge distortions of lens. Des has found, however, that the field of view of a DSLR is so wide that a flat field is not required, if you are using high quality lenses, provided the targ ...
Spectroscopic confirmation of a galaxy at redshift z=8.6
... function, for galaxies with z 5 6–7 (refs 13, 14). If the observed evolution of the luminosity function from z < 3 to z < 7 continues to z < 8.6, this would imply that UDFy-38135539 is a typical MUV* galaxy5. Although we cannot derive the characteristics of the stellar population in UDFy-38135539, s ...
... function, for galaxies with z 5 6–7 (refs 13, 14). If the observed evolution of the luminosity function from z < 3 to z < 7 continues to z < 8.6, this would imply that UDFy-38135539 is a typical MUV* galaxy5. Although we cannot derive the characteristics of the stellar population in UDFy-38135539, s ...
The Be/X-ray transient V0332153: evidence for a tilt between the
... Most Be/X-ray binaries have relatively eccentric orbits, and the neutron star companion is normally far away from the disc surrounding the Be star. Due to their different geometries and the varying physical conditions in the circumstellar disc, Be/X-ray binaries can present very different states of ...
... Most Be/X-ray binaries have relatively eccentric orbits, and the neutron star companion is normally far away from the disc surrounding the Be star. Due to their different geometries and the varying physical conditions in the circumstellar disc, Be/X-ray binaries can present very different states of ...
Standards
... Wavelength activity – students will become familiar with properties of waves, such as wavelength, frequency, and amplitude. Spectroscope activity - facilitates developing the relationship between temperature and color of stars. Star Characteristic Card Match and discussion of characteristics This ac ...
... Wavelength activity – students will become familiar with properties of waves, such as wavelength, frequency, and amplitude. Spectroscope activity - facilitates developing the relationship between temperature and color of stars. Star Characteristic Card Match and discussion of characteristics This ac ...
Word version of Episode 704
... The Andromeda galaxy M31 can just, but only just, be seen with the naked eye. Its light, 2 million years old, is the oldest light you can see with the unaided eye. The Andromeda galaxy, M31, is the nearest neighbour large galaxy to our own Galaxy, the Milky Way. It is about 2.2 million light years a ...
... The Andromeda galaxy M31 can just, but only just, be seen with the naked eye. Its light, 2 million years old, is the oldest light you can see with the unaided eye. The Andromeda galaxy, M31, is the nearest neighbour large galaxy to our own Galaxy, the Milky Way. It is about 2.2 million light years a ...
Serpens

Serpens (""the Serpent"", Greek Ὄφις) is a constellation of the northern hemisphere. One of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, it remains one of the 88 modern constellations defined by the International Astronomical Union. It is unique among the modern constellations in being split into two non-contiguous parts, Serpens Caput (Serpent's Head) to the west and Serpens Cauda (Serpent's Tail) to the east. Between these two halves lies the constellation of Ophiuchus, the ""Serpent-Bearer"". In figurative representations, the body of the serpent is represented as passing behind Ophiuchus between Mu Serpentis in Serpens Caput and Nu Serpentis in Serpens Cauda.The brightest star in Serpens is the red giant star Alpha Serpentis, or Unukalhai, in Serpens Caput, with an apparent magnitude of 2.63. Also located in Serpens Caput are the naked-eye globular cluster Messier 5 and the naked-eye variables R Serpentis and Tau4 Serpentis. Notable extragalactic objects include Seyfert's Sextet, one of the densest galaxy clusters known; Arp 220, the prototypical ultraluminous infrared galaxy; and Hoag's Object, the most famous of the very rare class of galaxies known as ring galaxies.Part of the Milky Way's galactic plane passes through Serpens Cauda, which is therefore rich in galactic deep-sky objects, such as the Eagle Nebula (IC 4703) and its associated star cluster Messier 16. The nebula measures 70 light-years by 50 light-years and contains the Pillars of Creation, three dust clouds that became famous for the image taken by the Hubble Space Telescope. Other striking objects include the Red Square Nebula, one of the few objects in astronomy to take on a square shape; and Westerhout 40, a massive nearby star-forming region consisting of a molecular cloud and an H II region.