Chapter 19 Notes Stars Stars are bright balls of gas that are trillions
... i. While many stars become white dwarves as they get older, very massive stars can become strange objects like pulsars, supernovas, black holes and neutron stars. ii. Supernovas 1. Massive stars use their hydrogen much faster than stars like the sun do. 2. At the end of their lives they may explode ...
... i. While many stars become white dwarves as they get older, very massive stars can become strange objects like pulsars, supernovas, black holes and neutron stars. ii. Supernovas 1. Massive stars use their hydrogen much faster than stars like the sun do. 2. At the end of their lives they may explode ...
chapter10
... • Sun will expand to a red giant in ~ 5 billion years • Expands to ~ Earth’s orbit • Earth will then be incinerated! • Sun may form a planetary nebula (but uncertain) • Sun’s C,O core will become a white dwarf ...
... • Sun will expand to a red giant in ~ 5 billion years • Expands to ~ Earth’s orbit • Earth will then be incinerated! • Sun may form a planetary nebula (but uncertain) • Sun’s C,O core will become a white dwarf ...
Brichler-powerpoint
... –When the most massive stars die, they become black holes – an object with gravity so strong that not ...
... –When the most massive stars die, they become black holes – an object with gravity so strong that not ...
HR Diagram
... H-R Diagram Scientists began to learn about stars by observing properties of stars, including brightness and color. Astronomers tried to make sense of the star data by grouping together stars with similar properties. The Hertzsprung-Russell diagram provides a way to group similar stars. The H-R dia ...
... H-R Diagram Scientists began to learn about stars by observing properties of stars, including brightness and color. Astronomers tried to make sense of the star data by grouping together stars with similar properties. The Hertzsprung-Russell diagram provides a way to group similar stars. The H-R dia ...
Module G - U1_ L3 - Life Cycle of Stars
... • The densest regions, called dense cores, form new stars. • The temperature within dense cores increases for millions of years. • At about 10 million °C, the process of hydrogen nuclear fusion begins, marking the birth of a star. • A star can remain actively fusing hydrogen into helium for billions ...
... • The densest regions, called dense cores, form new stars. • The temperature within dense cores increases for millions of years. • At about 10 million °C, the process of hydrogen nuclear fusion begins, marking the birth of a star. • A star can remain actively fusing hydrogen into helium for billions ...
Introduction to Astronomy
... (temperature)4 For a given size, hotter implies brighter. A bright, cool star must be unusually large (“red giant”). A faint, hot star must be unusually small (“white dwarf”). ...
... (temperature)4 For a given size, hotter implies brighter. A bright, cool star must be unusually large (“red giant”). A faint, hot star must be unusually small (“white dwarf”). ...
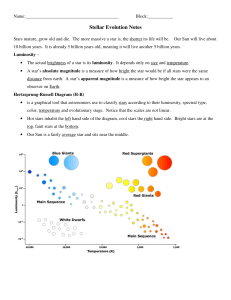
Stellar Evolution Notes
... It takes about 10 billion years for a star with the mass of the Sun to convert all of the hydrogen in its ...
... It takes about 10 billion years for a star with the mass of the Sun to convert all of the hydrogen in its ...
The Milky Way Galaxy
... Globular clusters must orbit around the center of mass of the galaxy! Thus, assuming the clusters are distributed uniformly around the galaxy, he measured the 3D distribution of clusters (using Cepheid variables) and then assumed that the center of that distribution was where the center of the galax ...
... Globular clusters must orbit around the center of mass of the galaxy! Thus, assuming the clusters are distributed uniformly around the galaxy, he measured the 3D distribution of clusters (using Cepheid variables) and then assumed that the center of that distribution was where the center of the galax ...
- Stevenson High School
... 4. Are there any stars that are not part of a constellation? Explain. 5. How is astrology and astronomy different? 6. How is astrology and astronomy related? 7. What is the significance of the zodiac? 8. If your zodiac sign is Virgo, what does that mean about the position of the earth, sun, and the ...
... 4. Are there any stars that are not part of a constellation? Explain. 5. How is astrology and astronomy different? 6. How is astrology and astronomy related? 7. What is the significance of the zodiac? 8. If your zodiac sign is Virgo, what does that mean about the position of the earth, sun, and the ...
Friday, August 28 - Otterbein University
... • Their positions are related because – the direction of Polaris defines the rotation axis of the celestial sphere – The sun is somewhere on the sphere – From a “skewed” perspective everything on the sphere culminates on the meridian ...
... • Their positions are related because – the direction of Polaris defines the rotation axis of the celestial sphere – The sun is somewhere on the sphere – From a “skewed” perspective everything on the sphere culminates on the meridian ...
Superwind - The University of Sydney
... Astronomers at The University of Manchester believe they have found the answer to the mystery of a powerful ‘superwind’ which causes the death of stars. Writing in Nature, the team of researchers, lead by Barnaby Norris from the University of Sydney in Australia, used new techniques which allowed th ...
... Astronomers at The University of Manchester believe they have found the answer to the mystery of a powerful ‘superwind’ which causes the death of stars. Writing in Nature, the team of researchers, lead by Barnaby Norris from the University of Sydney in Australia, used new techniques which allowed th ...