8hrdiagram1s
... If you know the luminosity and you measure the flux you can find the distance (F = L/4pd2) Called spectroscopic parallax ...
... If you know the luminosity and you measure the flux you can find the distance (F = L/4pd2) Called spectroscopic parallax ...
Document
... of massive stars, stars > 8 solar masses, including supernova of these large mass stars. • Units covered: 65, 66, 67. ...
... of massive stars, stars > 8 solar masses, including supernova of these large mass stars. • Units covered: 65, 66, 67. ...
1 WHY DO THE STARS IN ORION LOOK SO DIFFERENT FROM
... Luminosity shows the relationship of stars’ radii and surface temperature. Each of the stars in Table 1 is many times more luminous than our sun, and emits enormous amounts of energy. Luminosity is related to a stars surface area and temperature. Two stars having the same temperature and size will b ...
... Luminosity shows the relationship of stars’ radii and surface temperature. Each of the stars in Table 1 is many times more luminous than our sun, and emits enormous amounts of energy. Luminosity is related to a stars surface area and temperature. Two stars having the same temperature and size will b ...
OUSNMAY06 - The George Abell Observatory
... NGC3587 (M97) (12.0) pn. The "Owl Nebula". Two dark patches in the ghostly disc give the distinct impression of two large eyes requiring moderate apertures to see. It is one of the faintest of the Messier objects. NGC3992 (M109) (10.6) sg. About a degree SE of UMa this object is best observed usin ...
... NGC3587 (M97) (12.0) pn. The "Owl Nebula". Two dark patches in the ghostly disc give the distinct impression of two large eyes requiring moderate apertures to see. It is one of the faintest of the Messier objects. NGC3992 (M109) (10.6) sg. About a degree SE of UMa this object is best observed usin ...
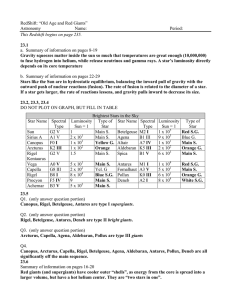
Astro 1 & 100 Levine Homework Stars Name:____________________________
... Brightest ______ ______ ______ ______ ______ ______ Dimmest Or, all have the same luminosity ______________ 2. Rank these stars in order of apparent brightness, from brightest to dimmest: Brightest ______ ______ ______ ______ ______ ______ Dimmest Or, all have the same apparent brightness __________ ...
... Brightest ______ ______ ______ ______ ______ ______ Dimmest Or, all have the same luminosity ______________ 2. Rank these stars in order of apparent brightness, from brightest to dimmest: Brightest ______ ______ ______ ______ ______ ______ Dimmest Or, all have the same apparent brightness __________ ...
A Star is a ball of matter that is pulled together by gravity, and that
... How bright a star is when viewed from___________. A very large, hot star could look dim just because it is so far away. •_____________________Magnitude: the amount of ____________ that is actually given off by a star. 4. Measuring the Distance to Stars: we measure the distance between objects in spa ...
... How bright a star is when viewed from___________. A very large, hot star could look dim just because it is so far away. •_____________________Magnitude: the amount of ____________ that is actually given off by a star. 4. Measuring the Distance to Stars: we measure the distance between objects in spa ...
Distances to the Stars in Leo
... From the strength of the lines in a star's spectrum, we can give it a spectral type (O, B, A, F, G, K & M) and luminosity class. We can use the luminosity to find its absolute magnitude and thus its distance. Finding the distances to stars based upon their spectral type and luminosity is known as s ...
... From the strength of the lines in a star's spectrum, we can give it a spectral type (O, B, A, F, G, K & M) and luminosity class. We can use the luminosity to find its absolute magnitude and thus its distance. Finding the distances to stars based upon their spectral type and luminosity is known as s ...
Stars
... • As Earth rotates, Ursa Major, Ursa Minor, and other constellations in the northern sky circle around Polaris • Because of this, they are called circumpolar constellations. • It appears that the constellations complete one full circle in the sky in about 24 hr. as Earth rotates on its axis. ...
... • As Earth rotates, Ursa Major, Ursa Minor, and other constellations in the northern sky circle around Polaris • Because of this, they are called circumpolar constellations. • It appears that the constellations complete one full circle in the sky in about 24 hr. as Earth rotates on its axis. ...
Integrative Studies 410 Our Place in the Universe
... production rate and available fuel (mass) – Example: Star with 4L and 3M uses 4 times more mass for energy production, but has 3 times more mass, so its life time is a factor ¾=0.75 compared to the sun: 7.5 billion years ([0.75] goes in the box) ...
... production rate and available fuel (mass) – Example: Star with 4L and 3M uses 4 times more mass for energy production, but has 3 times more mass, so its life time is a factor ¾=0.75 compared to the sun: 7.5 billion years ([0.75] goes in the box) ...
Characterizing Stars - Department of Physics and Astronomy
... By carefully examining a star’s spectral lines, astronomers can determine whether that star is a main-sequence star, giant, supergiant, or white dwarf ...
... By carefully examining a star’s spectral lines, astronomers can determine whether that star is a main-sequence star, giant, supergiant, or white dwarf ...
The Milky Way
... bright it looks from Earth, you can determine how far away it must be to look that faint. • For any star in the sky, we KNOW: – Apparent Magnitude (m) – Spectral Type (O, B, A, F, G, K, M) – Luminosity Class (Main Sequence, Giant, etc…). These are denoted by a roman numeral (V, III, I,…). ...
... bright it looks from Earth, you can determine how far away it must be to look that faint. • For any star in the sky, we KNOW: – Apparent Magnitude (m) – Spectral Type (O, B, A, F, G, K, M) – Luminosity Class (Main Sequence, Giant, etc…). These are denoted by a roman numeral (V, III, I,…). ...
answers
... nearby stars using parallax and we get the distance to more distant stars by using standard candles that are in the same galaxy. 2) The Sun has a mass of 2 x 1030 kg and the other stars have masses ranging from 1/10th of this to over 200 times more. How do we know the mass of the other stars? This i ...
... nearby stars using parallax and we get the distance to more distant stars by using standard candles that are in the same galaxy. 2) The Sun has a mass of 2 x 1030 kg and the other stars have masses ranging from 1/10th of this to over 200 times more. How do we know the mass of the other stars? This i ...
8 clusters stellar evo
... High mass (higher luminosity) stars progress through life more quickly Lower mass stars take longer to be born, consume their fuel more slowly. ...
... High mass (higher luminosity) stars progress through life more quickly Lower mass stars take longer to be born, consume their fuel more slowly. ...
Dim Stars - granthamkuehl
... Stars come in a range of sizes and masses. Our Sun is a mediumsized star. The largest stars, giant stars have a mass of about 60 times the mass of the Sun. ...
... Stars come in a range of sizes and masses. Our Sun is a mediumsized star. The largest stars, giant stars have a mass of about 60 times the mass of the Sun. ...
The future sun March 18 −
... H-R Diagrams of star clusters 1. There are no A stars in M80 because a. they never formed. b. they died and disappeared c. all stars became redder as they get older. d. they are too faint to see. ...
... H-R Diagrams of star clusters 1. There are no A stars in M80 because a. they never formed. b. they died and disappeared c. all stars became redder as they get older. d. they are too faint to see. ...
Chapter 26 Book Questions
... Hubble’s Law (pages 852–853) 22. True or false? The apparent change in frequency and wavelength of a wave as it moves towards or away from an observer is known as the Doppler effect. __________________ 23. How can astronomers use the Doppler effect? ______________________________________________ ___ ...
... Hubble’s Law (pages 852–853) 22. True or false? The apparent change in frequency and wavelength of a wave as it moves towards or away from an observer is known as the Doppler effect. __________________ 23. How can astronomers use the Doppler effect? ______________________________________________ ___ ...
Stars
... light years away from the Milky way. The biggest galaxy was the IC 1101. It is 1 billion light years away. IC 1101 is six million light years in size. The galaxy sixty times larger then the milky way. When you look up at night do you wonder how many stars there are? Well there are about 2,000 stars! ...
... light years away from the Milky way. The biggest galaxy was the IC 1101. It is 1 billion light years away. IC 1101 is six million light years in size. The galaxy sixty times larger then the milky way. When you look up at night do you wonder how many stars there are? Well there are about 2,000 stars! ...
word document - FacStaff Home Page for CBU
... explosions and not in the interior of stars like carbon and oxygen are. _____ h) The sun will eventually (in about 5.5 billion years) turn into a red giant whose radius will reach out to about the earth's orbit. _____ i) Closed or globular clusters of stars are groups of tens to hundreds of young of ...
... explosions and not in the interior of stars like carbon and oxygen are. _____ h) The sun will eventually (in about 5.5 billion years) turn into a red giant whose radius will reach out to about the earth's orbit. _____ i) Closed or globular clusters of stars are groups of tens to hundreds of young of ...
STARS Chapter 8 Section 1
... astronomers can tell what elements a star is made of from the light they observe from the star. This is called the spectrum. ...
... astronomers can tell what elements a star is made of from the light they observe from the star. This is called the spectrum. ...
NOVAE and SUPERNOVAE
... dwarfs (WD). Fusion reactions occur on the “outside” of the otherwise dead white dwarf, instead of in the core, as in normal stars. Hydrogen fuses into helium within a thin shell, releasing enormous amounts of energy. Novae are caused by the transfer of matter onto a white dwarf within a binary ...
... dwarfs (WD). Fusion reactions occur on the “outside” of the otherwise dead white dwarf, instead of in the core, as in normal stars. Hydrogen fuses into helium within a thin shell, releasing enormous amounts of energy. Novae are caused by the transfer of matter onto a white dwarf within a binary ...
Lesson 4, Stars
... Why will the Sun not become a black hole someday? The Sun does not have enough mass to ...
... Why will the Sun not become a black hole someday? The Sun does not have enough mass to ...