
HR DIAGRAM ACTIVITY
... the various stages the Sun will go through until the end of its life cycle. (page 632) ...
... the various stages the Sun will go through until the end of its life cycle. (page 632) ...
Note
... • You want to detect the faint star of an unresolved binary system comprising a B5V star and an M0V companion. What wavelength regime would you choose to try to detect the M0V star? What is the ratio of the flux from the B star to the flux from the M star at that wavelength? • You want to detect the ...
... • You want to detect the faint star of an unresolved binary system comprising a B5V star and an M0V companion. What wavelength regime would you choose to try to detect the M0V star? What is the ratio of the flux from the B star to the flux from the M star at that wavelength? • You want to detect the ...
Lec7_2D
... blackbody law, hot things emit more light. But a star’s brightness also depends on its size – the larger the area, the more light that is emitted. The relationship between luminosity, radius, and temperature is ...
... blackbody law, hot things emit more light. But a star’s brightness also depends on its size – the larger the area, the more light that is emitted. The relationship between luminosity, radius, and temperature is ...
formation of stars
... In a stable state a star’s diameter and radiation remain constant for billions of years. When so many of the core’s light nuclei are used up that the energy of fusion no longer balances the force of gravity the star loses its stability. When the star loses its stability the centre of the star contra ...
... In a stable state a star’s diameter and radiation remain constant for billions of years. When so many of the core’s light nuclei are used up that the energy of fusion no longer balances the force of gravity the star loses its stability. When the star loses its stability the centre of the star contra ...
For instance, two hydrogen atoms may fuse together to form one
... As it turns out, over ninety-five percent of all stars are smaller and cooler than our sun. Any planets around such stars would have to orbit very close to the star to be in its habit able zone. However, orbiting close to a star is dangerous. Planets very close to a star become tidally locked, meani ...
... As it turns out, over ninety-five percent of all stars are smaller and cooler than our sun. Any planets around such stars would have to orbit very close to the star to be in its habit able zone. However, orbiting close to a star is dangerous. Planets very close to a star become tidally locked, meani ...
LIGO Star Chart
... reach us, the distance between the two galaxies is getting smaller. Andromeda is moving toward the Milky Way at about 700,000 miles per hour! The best explanation for this is that the Milky Way and Andromeda are in fact a bound pair of galaxies in orbit around one another. Both galaxies are thought ...
... reach us, the distance between the two galaxies is getting smaller. Andromeda is moving toward the Milky Way at about 700,000 miles per hour! The best explanation for this is that the Milky Way and Andromeda are in fact a bound pair of galaxies in orbit around one another. Both galaxies are thought ...
Magnitude scale theory
... The magnitudes of stars - theory How bright a star looks is given by its apparent magnitude. This is different from its absolute magnitude. The absolute magnitude of a star is defined as the apparent magnitude that it would have if placed at a distance of 10 parsecs from the Earth. Consider two star ...
... The magnitudes of stars - theory How bright a star looks is given by its apparent magnitude. This is different from its absolute magnitude. The absolute magnitude of a star is defined as the apparent magnitude that it would have if placed at a distance of 10 parsecs from the Earth. Consider two star ...
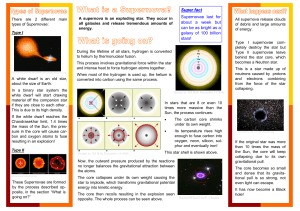
Stars with mass less than 0.5 solar masses
... helium. This star is going to die in a white dwarf. These are little stars, very hot initially, which cool slowly till they swich off completely, in black dwarf. If a white dwarf is part of a bynar system, for example with a red giant, the first one can steal some of the red giant’s mass and prime t ...
... helium. This star is going to die in a white dwarf. These are little stars, very hot initially, which cool slowly till they swich off completely, in black dwarf. If a white dwarf is part of a bynar system, for example with a red giant, the first one can steal some of the red giant’s mass and prime t ...
The H-R Diagram
... main sequence. Most white dwarfs have approximately the mass of the sun, but a radius about 0.01 to 0.001 of the radius of the sun (roughly about the size of a the earth). Their average density is about 106 to 108 solar density. They have exhausted all of their nuclear fuel, are no longer generating ...
... main sequence. Most white dwarfs have approximately the mass of the sun, but a radius about 0.01 to 0.001 of the radius of the sun (roughly about the size of a the earth). Their average density is about 106 to 108 solar density. They have exhausted all of their nuclear fuel, are no longer generating ...
Sky Watching Talk
... cannot see the Constellations near where the Sun is in the sky – Sun so bright it washes out rest of stars ...
... cannot see the Constellations near where the Sun is in the sky – Sun so bright it washes out rest of stars ...
The Family of Stars
... The flux received from both stars is the same, but star B is 5 times more luminous than star A, so star B must be further away. The flux received from both stars is the same, but star B is 100 times more luminous than star A, so star B must be further away. Both stars are equally luminous, but the f ...
... The flux received from both stars is the same, but star B is 5 times more luminous than star A, so star B must be further away. The flux received from both stars is the same, but star B is 100 times more luminous than star A, so star B must be further away. Both stars are equally luminous, but the f ...
For stars
... By comparing the apparent (m) and absolute magnitude (M) numbers we can estimate a stars distance from Earth. • When m = M, then the star is located exactly 10 pc away • When mM, then the ...
... By comparing the apparent (m) and absolute magnitude (M) numbers we can estimate a stars distance from Earth. • When m = M, then the star is located exactly 10 pc away • When m
2-2 wkst - Home [www.petoskeyschools.org]
... ____________ 22. small hot stars that are dimmer than the sun ____________ 23. high-temperature stars that quickly use up their hydrogen ____________ 24. cool stars with high absolute magnitude ...
... ____________ 22. small hot stars that are dimmer than the sun ____________ 23. high-temperature stars that quickly use up their hydrogen ____________ 24. cool stars with high absolute magnitude ...
Day 1212
... temperature increases. • When interior temperatures reach 1 million K the center is called a protostar. • When the temperature reaches 10 million K hydrogen fuses to create helium = star! ...
... temperature increases. • When interior temperatures reach 1 million K the center is called a protostar. • When the temperature reaches 10 million K hydrogen fuses to create helium = star! ...





















![2-2 wkst - Home [www.petoskeyschools.org]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/009700019_1-9e7a7c15444658cfc76a04a9cf1ba291-300x300.png)
