HW #4 (due March 27)
... When astronomers look through their telescopes, they see billions of stars. What can they learn from their observations? In class, we’ve learned that the shape of the spectrum (especially, the wavelength at which it reaches its maximum intensity) can be used to determine a star’s temperature. In add ...
... When astronomers look through their telescopes, they see billions of stars. What can they learn from their observations? In class, we’ve learned that the shape of the spectrum (especially, the wavelength at which it reaches its maximum intensity) can be used to determine a star’s temperature. In add ...
TYPES OF STARS
... When astronomers look through their telescopes, they see billions of stars. What can they learn from their observations? In class, we’ve learned that the shape of the spectrum (especially, the wavelength at which it reaches its maximum intensity) can be used to determine a star’s temperature. In add ...
... When astronomers look through their telescopes, they see billions of stars. What can they learn from their observations? In class, we’ve learned that the shape of the spectrum (especially, the wavelength at which it reaches its maximum intensity) can be used to determine a star’s temperature. In add ...
Chapter 28 – Stars and Galaxies
... 1. The actual brightness of the star is luminosity 2. If two stars have the same surface temperature, the larger star would be more luminous 3. If the same size, hotter one would be brighter 4. Types of magnitude a. Absolute – as if all stars were same distance from earth b. Apparent – as they appea ...
... 1. The actual brightness of the star is luminosity 2. If two stars have the same surface temperature, the larger star would be more luminous 3. If the same size, hotter one would be brighter 4. Types of magnitude a. Absolute – as if all stars were same distance from earth b. Apparent – as they appea ...
April - Bristol Astronomical Society
... Alpha (α) Corvi marks the beak of the crow, it is a F-class (F0) yellow dwarf star. Despite its alpha designation it only 5th in brightness at magnitude +4.00. The star’s proper name, Alchiba means ‘tent’ in Arabic and is thought to refer to the four stars that make up the main body of the crow. Bet ...
... Alpha (α) Corvi marks the beak of the crow, it is a F-class (F0) yellow dwarf star. Despite its alpha designation it only 5th in brightness at magnitude +4.00. The star’s proper name, Alchiba means ‘tent’ in Arabic and is thought to refer to the four stars that make up the main body of the crow. Bet ...
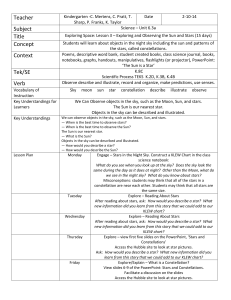
Teacher Subject Title Concept Context Tek/SE Verb
... Objects in the sky can be described and illustrated. We can observe objects in the sky, such as the Moon, Sun, and stars. — When is the best time to observe stars? — When is the best time to observe the Sun? The Sun is our nearest star. — What is the Sun? Objects in the sky can be described and illu ...
... Objects in the sky can be described and illustrated. We can observe objects in the sky, such as the Moon, Sun, and stars. — When is the best time to observe stars? — When is the best time to observe the Sun? The Sun is our nearest star. — What is the Sun? Objects in the sky can be described and illu ...
Hertzsprung2 - courses.psu.edu
... What is the luminosity (relative to the sun) of a star 3 times more massive than the sun? ...
... What is the luminosity (relative to the sun) of a star 3 times more massive than the sun? ...
Stellar Evolution 1 Star Formation 2 Nebulae
... What are the basic properties of giant molecular clouds? How do clumps form in giant molecular clouds? How do clumps in giant molecular clouds evolve? What are the conditions for which this kind of evolution takes place? Where are protostars found on an H-R diagram? How do their locations on ...
... What are the basic properties of giant molecular clouds? How do clumps form in giant molecular clouds? How do clumps in giant molecular clouds evolve? What are the conditions for which this kind of evolution takes place? Where are protostars found on an H-R diagram? How do their locations on ...
Star Types
... The H-R diagram “The stars are distant and unobtrusive, but bright and enduring as our fairest and most ...
... The H-R diagram “The stars are distant and unobtrusive, but bright and enduring as our fairest and most ...
Lifecycle of the stars.
... Small proto star-a brown dwarf that was too small to generate enough heat to start fusion. ...
... Small proto star-a brown dwarf that was too small to generate enough heat to start fusion. ...
Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram
... The Main Sequence At one end, the stars are big, hot and bright. Due to their color and size they are called blue giants, and the very largest are blue supergiants. At the other end they are small, cool and dim and are known as red dwarfs. The sun is right in the middle. ...
... The Main Sequence At one end, the stars are big, hot and bright. Due to their color and size they are called blue giants, and the very largest are blue supergiants. At the other end they are small, cool and dim and are known as red dwarfs. The sun is right in the middle. ...