The Life Cycle of the Stars
... The star-filled sky is in many ways like a large crowd of people. Within that group you may find babies, children, teenagers, adults and even senior citizens. Like humans, stars pass through different stages in their lives. They are born, they mature and, eventually, they die. However, unlike humans ...
... The star-filled sky is in many ways like a large crowd of people. Within that group you may find babies, children, teenagers, adults and even senior citizens. Like humans, stars pass through different stages in their lives. They are born, they mature and, eventually, they die. However, unlike humans ...
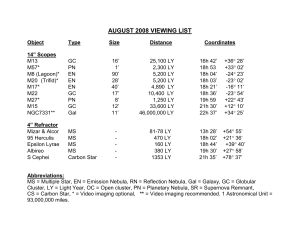
August
... star splits into a close binary. While some observers see color differences, most see the stars as two pairs of white headlights oriented nearly perpendicular to each other. Albireo Beta Cygni, in the constellation Cygnus (SIG-nus) is probably not a true binary, but a visual double star with extraor ...
... star splits into a close binary. While some observers see color differences, most see the stars as two pairs of white headlights oriented nearly perpendicular to each other. Albireo Beta Cygni, in the constellation Cygnus (SIG-nus) is probably not a true binary, but a visual double star with extraor ...
Life Cycle of Stars
... • Luminosity – brightness, or energy output of a star per second • Temperature- in stars, the temperature determines the luminosity and the rate of nuclear reactions (fusion) ...
... • Luminosity – brightness, or energy output of a star per second • Temperature- in stars, the temperature determines the luminosity and the rate of nuclear reactions (fusion) ...
1” “Sky-Notes” of the Open University Astronomy Club. October 2005
... almost three weeks to follow one rotation. An excellent target for webcam imaging. Make the most of the next 8 weeks! During the month brightness increases from –1.8 (diameter 18.6”, phase 0.95) on the 7th to –2.2 (diameter 20.1”, phase 0.99) on the 27th. ...
... almost three weeks to follow one rotation. An excellent target for webcam imaging. Make the most of the next 8 weeks! During the month brightness increases from –1.8 (diameter 18.6”, phase 0.95) on the 7th to –2.2 (diameter 20.1”, phase 0.99) on the 27th. ...
Introduction to Stars ppt
... Most stars fall along the main sequence – upper left to lower right. These stars fuse hydrogen into helium in their cores and have a wide range of life spans, which depend on their mass. Higher mass stars on main sequence have shorter life spans. A star has a limited supply of core hydrogen and ther ...
... Most stars fall along the main sequence – upper left to lower right. These stars fuse hydrogen into helium in their cores and have a wide range of life spans, which depend on their mass. Higher mass stars on main sequence have shorter life spans. A star has a limited supply of core hydrogen and ther ...
Summer 2001 Day 07: Intro to Solar System
... C) Calculate the brightness of the Sun as seen from Earth B=1,355 W/m2 i) Typical stellar brightness is about 2x10-8W D) Distances can be calculated by measuring B and modeling L Practice Problem #3 i) Example: Distance to Alkaid (η UMa) (1) Luminosity = 700 LSun = 2.68x1029 W (2) Brightness = 2.337 ...
... C) Calculate the brightness of the Sun as seen from Earth B=1,355 W/m2 i) Typical stellar brightness is about 2x10-8W D) Distances can be calculated by measuring B and modeling L Practice Problem #3 i) Example: Distance to Alkaid (η UMa) (1) Luminosity = 700 LSun = 2.68x1029 W (2) Brightness = 2.337 ...
Our Community`s Place Among the Stars
... years •small, cooler stars live twice as long •massive, supergiant stars consume their mass too quickly only live a few tens of million of years •very hot stars go through their fuel very quickly ...
... years •small, cooler stars live twice as long •massive, supergiant stars consume their mass too quickly only live a few tens of million of years •very hot stars go through their fuel very quickly ...
OUSNMAR05 - The Open University
... orientation of the map may differ from that of the observed image of the Moon depending on the type of telescope used. If you find the Moon too bright use a filter to reduce the glare. At times features along different parts of the limb are better presented due the effect of libration – an apparent ...
... orientation of the map may differ from that of the observed image of the Moon depending on the type of telescope used. If you find the Moon too bright use a filter to reduce the glare. At times features along different parts of the limb are better presented due the effect of libration – an apparent ...
DOC - Cool Cosmos
... Simply put, a star is a large amount of gas and dust that is collapsing under the force of gravity. At first, this crush of gravity makes the inside of the star hot enough to ignite a nuclear explosion. This explosion supports the star against gravity and makes it shine. In our Sun's case, this stag ...
... Simply put, a star is a large amount of gas and dust that is collapsing under the force of gravity. At first, this crush of gravity makes the inside of the star hot enough to ignite a nuclear explosion. This explosion supports the star against gravity and makes it shine. In our Sun's case, this stag ...
Nebula - NICADD
... • Any source of light in the night sky that was not a point was called a nebula. ...
... • Any source of light in the night sky that was not a point was called a nebula. ...
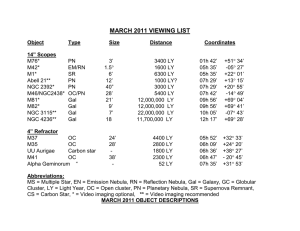
March
... standard planetary nebula with a 16th magnitude central star. The unusual appearance is due to the angle of the nebular ring that is expanding outward from the white dwarf at about 42 K/sec. Most of the visible light is emitted in the OIII doubly ionized Oxygen band so the use of a nebula or OIII fi ...
... standard planetary nebula with a 16th magnitude central star. The unusual appearance is due to the angle of the nebular ring that is expanding outward from the white dwarf at about 42 K/sec. Most of the visible light is emitted in the OIII doubly ionized Oxygen band so the use of a nebula or OIII fi ...
Milky Way
... • For any star in the sky, we KNOW: – Apparent Magnitude (m) – Spectral Type (O, B, A, F, G, K, M) – Luminosity Class (Main Sequence, Giant, etc…). These are denoted by a roman numeral (V, III, I,…). ...
... • For any star in the sky, we KNOW: – Apparent Magnitude (m) – Spectral Type (O, B, A, F, G, K, M) – Luminosity Class (Main Sequence, Giant, etc…). These are denoted by a roman numeral (V, III, I,…). ...
April11
... • Iron cannot be fused into any heavier element, so it collects at the center of the star • Gravity pulls the core of the star to a size smaller than the Earth’s diameter! • The core compresses so much that protons and electrons merge into neutrons, taking energy away from the core • The core collap ...
... • Iron cannot be fused into any heavier element, so it collects at the center of the star • Gravity pulls the core of the star to a size smaller than the Earth’s diameter! • The core compresses so much that protons and electrons merge into neutrons, taking energy away from the core • The core collap ...