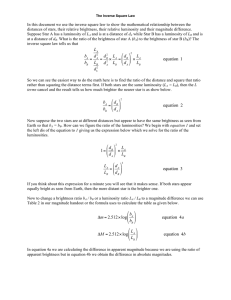
Exercise 4 (Stars and the universe) Suggested answers
... radiation curve. On the curve, there is a peak which shifts to shorter wavelength when the temperature of the blackbody increases. From the position of the peak, astronomers can deduce the surface temperature of the star. In general, the spectra of hot stars peak at shorter wavelengths and therefore ...
... radiation curve. On the curve, there is a peak which shifts to shorter wavelength when the temperature of the blackbody increases. From the position of the peak, astronomers can deduce the surface temperature of the star. In general, the spectra of hot stars peak at shorter wavelengths and therefore ...
BrainPOP - The Science Spot
... pulls the clouds together causing clumps to form. If the clump is large enough, the __________ caused by gravity inside a ____________ begins to generate _________. 2. The heat and pressure builds until __________ __________ reactions begin to take place inside the core. Gravity pulls _____________ ...
... pulls the clouds together causing clumps to form. If the clump is large enough, the __________ caused by gravity inside a ____________ begins to generate _________. 2. The heat and pressure builds until __________ __________ reactions begin to take place inside the core. Gravity pulls _____________ ...
Stellar Evolution and the HR Diagram – Study Guide
... c. Which is brighter, the sun or a white dwarf? The Sun (but not as hot) d. Is Vega brighter than our sun? Yes (closer to upper top of diagram) e. Is Antares hotter than our sun? No, it’s a giant, class K or M (lower on diagram) 23. Stars that move off the main sequence first move to the _Giant_ reg ...
... c. Which is brighter, the sun or a white dwarf? The Sun (but not as hot) d. Is Vega brighter than our sun? Yes (closer to upper top of diagram) e. Is Antares hotter than our sun? No, it’s a giant, class K or M (lower on diagram) 23. Stars that move off the main sequence first move to the _Giant_ reg ...
How it works:
... How it works: On the reverse of this sheet are four constellations, all of which can be seen on summer nights in Colorado. Each constellation has five stars. For every book read, fill in one star. Each time you complete a constellation, bring this sheet to the teenseen to receive a prize and a raffl ...
... How it works: On the reverse of this sheet are four constellations, all of which can be seen on summer nights in Colorado. Each constellation has five stars. For every book read, fill in one star. Each time you complete a constellation, bring this sheet to the teenseen to receive a prize and a raffl ...
Measuring Distance with Spectroscopic Parallax
... 1. Print out the HR diagram. 2. Using a pen or pencil, draw a smooth best-fit curve that runs through the middle of all of your main sequence stars. Just ignore the red giants and white dwarfs for this activity. Note that this will not be a straight line; it will curve slightly. And, it will not go ...
... 1. Print out the HR diagram. 2. Using a pen or pencil, draw a smooth best-fit curve that runs through the middle of all of your main sequence stars. Just ignore the red giants and white dwarfs for this activity. Note that this will not be a straight line; it will curve slightly. And, it will not go ...
binary stars - El Camino College
... Two-thirds of all stars are part of multiple star systems, where two or more stars are born at the same time from the same gas cloud. Only about 30% of all stars are single, like the Sun. The distances between companion stars ranges from less than 10 million miles (0.1 AU), to over 10,000 AU. Simila ...
... Two-thirds of all stars are part of multiple star systems, where two or more stars are born at the same time from the same gas cloud. Only about 30% of all stars are single, like the Sun. The distances between companion stars ranges from less than 10 million miles (0.1 AU), to over 10,000 AU. Simila ...
Chapter 15 (Star Lives)
... D. are at different stages of their lives. 2. In making a model of a star, an astronomer does NOT have to know or assume: A. that the energy given off is produced in the interior. B. the mass of the star. C. the chemical composition of the star. D. the distance to that star. 3. For a star like our s ...
... D. are at different stages of their lives. 2. In making a model of a star, an astronomer does NOT have to know or assume: A. that the energy given off is produced in the interior. B. the mass of the star. C. the chemical composition of the star. D. the distance to that star. 3. For a star like our s ...
Chap 11 Characterizing Stars v2
... A spectroscopic binary is a system detected from the periodic shift of its spectral lines. This shift is caused by the Doppler effect as the orbits of the stars carry them alternately toward and away from Earth. An eclipsing binary is a system whose orbits are viewed nearly edge-on from Earth, so th ...
... A spectroscopic binary is a system detected from the periodic shift of its spectral lines. This shift is caused by the Doppler effect as the orbits of the stars carry them alternately toward and away from Earth. An eclipsing binary is a system whose orbits are viewed nearly edge-on from Earth, so th ...
May
... Saturn is guaranteed to be the most exciting object in the late spring and early summer sky. It is important to have some interesting stats for the public as they observe this planet. See the last page of the Object Descriptions for relevant facts. We are currently moving apart from our closest poin ...
... Saturn is guaranteed to be the most exciting object in the late spring and early summer sky. It is important to have some interesting stats for the public as they observe this planet. See the last page of the Object Descriptions for relevant facts. We are currently moving apart from our closest poin ...
Evolution of Stars and Galaxies
... Prominences: huge, arching gas columns possibly caused by magnetic fields ...
... Prominences: huge, arching gas columns possibly caused by magnetic fields ...
Red Giants - Uplift North Hills Prep
... • done independently by Enjar Hertzsprung and Henry Norris Russell Henry Norris Russell dissuaded Cecilia Payne-Gaposchkin from concluding that the composition of the Sun is different from that of the Earth in her papers, as it contradicted the accepted wisdom at the time. However, he changed his mi ...
... • done independently by Enjar Hertzsprung and Henry Norris Russell Henry Norris Russell dissuaded Cecilia Payne-Gaposchkin from concluding that the composition of the Sun is different from that of the Earth in her papers, as it contradicted the accepted wisdom at the time. However, he changed his mi ...
Chapter 2: The Sky
... Stars are named by a Greek letter (a, b, g) according to their relative brightness within a given constellation + the possessive form of the name of the constellation: Betelgeuse = a Orionis, Rigel = b Orionis ...
... Stars are named by a Greek letter (a, b, g) according to their relative brightness within a given constellation + the possessive form of the name of the constellation: Betelgeuse = a Orionis, Rigel = b Orionis ...
Name - MIT
... A) A 100 kg mass moving at 1 km/s. B) A 20 kg mass moving at 2 km/s. C) A 2 kg mass moving at 5 km/s. D) A 10 kg mass moving at 4 km/s. E) A 5 kg mass moving at 2 km/s. 7) The Homestake Gold Mine experiment was designed to detect neutrinos. What insight can be gained from such an experiment? A) The ...
... A) A 100 kg mass moving at 1 km/s. B) A 20 kg mass moving at 2 km/s. C) A 2 kg mass moving at 5 km/s. D) A 10 kg mass moving at 4 km/s. E) A 5 kg mass moving at 2 km/s. 7) The Homestake Gold Mine experiment was designed to detect neutrinos. What insight can be gained from such an experiment? A) The ...