review
... • The fastest pulsars, called millisecond pulsars, have periods of about 1/1000 second. The reason they pulse so much faster than (for example) the Crab and Vela pulsars is that they • A. were formed from much more massive stars than were the Crab and Vela pulsars, and were spun up more as their cor ...
... • The fastest pulsars, called millisecond pulsars, have periods of about 1/1000 second. The reason they pulse so much faster than (for example) the Crab and Vela pulsars is that they • A. were formed from much more massive stars than were the Crab and Vela pulsars, and were spun up more as their cor ...
Night Sky Checklist July–August–September Unaided Eye Astronomy
... just outside the Summer Triangle between Cygnus and Aquila. Stars (The stars on the checklist are easily visible to the unaided eye except in the most light polluted parts of cities.) Antares is a red supergiant star estimated to be some 800 times bigger than the sun. It’s bigger than the orbits of ...
... just outside the Summer Triangle between Cygnus and Aquila. Stars (The stars on the checklist are easily visible to the unaided eye except in the most light polluted parts of cities.) Antares is a red supergiant star estimated to be some 800 times bigger than the sun. It’s bigger than the orbits of ...
Star Types - University of Massachusetts Amherst
... How may a star’s luminosity be inferred? How may a star’s Temperature be inferred? How may a stsar’s distance be inferred Parallax as a measure of distance: how does the parallax of a star depend on its distance? How may a star’s radius be inferred? ...
... How may a star’s luminosity be inferred? How may a star’s Temperature be inferred? How may a stsar’s distance be inferred Parallax as a measure of distance: how does the parallax of a star depend on its distance? How may a star’s radius be inferred? ...
TYPES OF STARS
... When astronomers look through their telescopes, they see billions of stars. How do they make sense of all these stars? The goal of this problem set is for you to understand that astronomers classify stars on the basis of two different criteria: (1) the intensity of one of the H absorption lines (cal ...
... When astronomers look through their telescopes, they see billions of stars. How do they make sense of all these stars? The goal of this problem set is for you to understand that astronomers classify stars on the basis of two different criteria: (1) the intensity of one of the H absorption lines (cal ...
_____ 1. Which of the following statements is NOT true about stars
... ___________________ once it has used up all of its hydrogen. The center of the star will _________________ as the atmosphere begins to grow large. The mass of the star will determine if it will be a red giant or a supergiant. 11. What is the difference between a red giant and a supergiant? _________ ...
... ___________________ once it has used up all of its hydrogen. The center of the star will _________________ as the atmosphere begins to grow large. The mass of the star will determine if it will be a red giant or a supergiant. 11. What is the difference between a red giant and a supergiant? _________ ...
Lecture 13
... 1cm shifts to .9999999 cm. Not much. To say you were 5mph over the limit needs to measure one part in 100million! ...
... 1cm shifts to .9999999 cm. Not much. To say you were 5mph over the limit needs to measure one part in 100million! ...
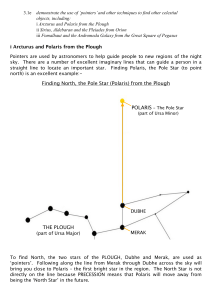
3.1e Finding Polaris and Sirius
... have very dark skies, the Andromeda Galaxy is the furthest object that you can see with your naked eye – 2.4 million light years away! The galaxy appears as a small, white, fuzzy patch. When you have found the Great Square of Pegasus, you need to find the top left hand star of the square (the star d ...
... have very dark skies, the Andromeda Galaxy is the furthest object that you can see with your naked eye – 2.4 million light years away! The galaxy appears as a small, white, fuzzy patch. When you have found the Great Square of Pegasus, you need to find the top left hand star of the square (the star d ...
HR-Diagram
... When a star is on the main sequence it is considered an adult star. It will spend approx. 90% of its life span on as an adult star on the main sequence. This begins the moment Hydrogen fusion begins The more massive the star, the more nuclear fusion takes place to produce energy The mass of the star ...
... When a star is on the main sequence it is considered an adult star. It will spend approx. 90% of its life span on as an adult star on the main sequence. This begins the moment Hydrogen fusion begins The more massive the star, the more nuclear fusion takes place to produce energy The mass of the star ...
Introduction to Accretion Phenomena in Astrophysics
... 1889 Edward Pickering found that it is a binary star.This binary is 35 times brighter than the Sun. • Orbital period ~20 days. • There exist double-lined (SB2) and single-lined (SB1) spectroscopic binaries. • Famous SB1 - Cygnus X-1 System. ...
... 1889 Edward Pickering found that it is a binary star.This binary is 35 times brighter than the Sun. • Orbital period ~20 days. • There exist double-lined (SB2) and single-lined (SB1) spectroscopic binaries. • Famous SB1 - Cygnus X-1 System. ...
The Life of a Star - Department of Physics and Astronomy
... Young star clusters give insight into star formation and evolution • Newborn stars may form an open or galactic cluster • Stars are held together in such a cluster by gravity • Occasionally a star moving more rapidly than average will escape, or leave the cluster • A stellar association is a group ...
... Young star clusters give insight into star formation and evolution • Newborn stars may form an open or galactic cluster • Stars are held together in such a cluster by gravity • Occasionally a star moving more rapidly than average will escape, or leave the cluster • A stellar association is a group ...
16. Properties of Stars
... Lifetime on the Main Sequence How long will it be before MS stars run out of fuel? i.e. Hydrogen? How much fuel is there? M How fast is it consumed? L M How long before it is used up? Time = Amount/(rate it is being used) ...
... Lifetime on the Main Sequence How long will it be before MS stars run out of fuel? i.e. Hydrogen? How much fuel is there? M How fast is it consumed? L M How long before it is used up? Time = Amount/(rate it is being used) ...
Astronomy 12: Introduction to Astronomy
... 4. When a star’s gravitational force pulling inwards and its internal pressure pushing outward are balanced, it is considered to be in what? a. Hydrostatic equilibrium b. Supernova c. Structural Balance d. Proton-proton fusion 5. What is a helium flash? a. The rapid fusion of helium in a red giant’s ...
... 4. When a star’s gravitational force pulling inwards and its internal pressure pushing outward are balanced, it is considered to be in what? a. Hydrostatic equilibrium b. Supernova c. Structural Balance d. Proton-proton fusion 5. What is a helium flash? a. The rapid fusion of helium in a red giant’s ...
The winter sky over Bosham
... constellation contains two of the brightest stars in the sky, with Betelgeuse marking the top left ‘shoulder’ and Rigel the lower right ‘foot’— the name itself is derived from the Arabic word ‘rijl’. Both are about ten million years old and near the end of their lives, but can you see a difference i ...
... constellation contains two of the brightest stars in the sky, with Betelgeuse marking the top left ‘shoulder’ and Rigel the lower right ‘foot’— the name itself is derived from the Arabic word ‘rijl’. Both are about ten million years old and near the end of their lives, but can you see a difference i ...
May 2009 Tz 2
... (d) Alnitak is a main sequence star with a luminosity similar to that of Antares. Use the value quoted in (c)(ii) to deduce that the mass of Alnitak is in the range 16 MS to 40 MS, where MS is the mass of the Sun. ...
... (d) Alnitak is a main sequence star with a luminosity similar to that of Antares. Use the value quoted in (c)(ii) to deduce that the mass of Alnitak is in the range 16 MS to 40 MS, where MS is the mass of the Sun. ...
Stellar Evolution - Hays High Indians
... form – More massive stars can completely form in a few hundred thousand years ...
... form – More massive stars can completely form in a few hundred thousand years ...