Star clusters and constellations
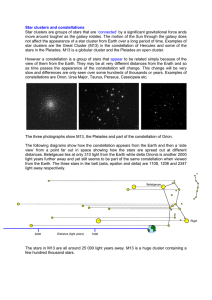
... slow and differences are only seen over some hundreds of thousands or years. Examples of constellations are Orion, Ursa Major, Taurus, Perseus, Cassiopeia etc. ...
... slow and differences are only seen over some hundreds of thousands or years. Examples of constellations are Orion, Ursa Major, Taurus, Perseus, Cassiopeia etc. ...
STARS and GALAXIES
... • Absolute Luminosity (brightness)Measures how bright a star is in relation to the sun, if all the stars were the same distance from the Earth. ...
... • Absolute Luminosity (brightness)Measures how bright a star is in relation to the sun, if all the stars were the same distance from the Earth. ...
Document
... • When two stars are gravitationally bound to each other, they orbit a common center of mass • Often appear bound to each other, even with a telescope ...
... • When two stars are gravitationally bound to each other, they orbit a common center of mass • Often appear bound to each other, even with a telescope ...
New Directions in Star Cluster Research
... (a) Violation of first condition - self gravity (breakup of star scattering material into space) (b) Violation second condition - internally supplied radiation (exhaustion nuclear fuel) ...
... (a) Violation of first condition - self gravity (breakup of star scattering material into space) (b) Violation second condition - internally supplied radiation (exhaustion nuclear fuel) ...
Allison McGraw - WordPress.com
... M31. It orbits M31 much like the Moon orbits the Earth. It lies at the same distance as M31 but is much smaller (8,000 lightyears across). ...
... M31. It orbits M31 much like the Moon orbits the Earth. It lies at the same distance as M31 but is much smaller (8,000 lightyears across). ...
Chapter 30 Study Notes
... A star with the sun’s mass would stay on the main sequence of the H-R diagram for about _____ 10 billion years. ...
... A star with the sun’s mass would stay on the main sequence of the H-R diagram for about _____ 10 billion years. ...
Document
... Most of the stars on the HR Diagram are classified as which type of star? ___________________________________________ ...
... Most of the stars on the HR Diagram are classified as which type of star? ___________________________________________ ...
KMS Universe Test Study Guide
... average absolute magnitude? The Sun is very close to us, so it appears to be brighter than it is compared to other stars in the Universe. 7) Why are red giant stars so bright, when they are among the coolest of stars? Because they are very large. 8) Why do white dwarf stars appear so dim, when they ...
... average absolute magnitude? The Sun is very close to us, so it appears to be brighter than it is compared to other stars in the Universe. 7) Why are red giant stars so bright, when they are among the coolest of stars? Because they are very large. 8) Why do white dwarf stars appear so dim, when they ...
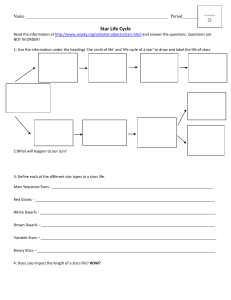
the life cycle of stars
... • Energy is generated in the core and causes the star to shine. • The size of the star changes very little as long as its supply of hydrogen nuclei fuse into helium nuclei. ...
... • Energy is generated in the core and causes the star to shine. • The size of the star changes very little as long as its supply of hydrogen nuclei fuse into helium nuclei. ...
Name: ____________________________ Date: _____________ Per. _________ Stars Study Guide (Ch. 21)
... 14. What is the main sequence?____________________________________________ 15. Why do stars follow two different paths in the Life Cycle of Star? _________________ ___________________________________________________________________ 16. Which type of star lives longer & why? _________________________ ...
... 14. What is the main sequence?____________________________________________ 15. Why do stars follow two different paths in the Life Cycle of Star? _________________ ___________________________________________________________________ 16. Which type of star lives longer & why? _________________________ ...
Scale of Apparent Magnitudes of Celestial Objects
... The creator of the system for measuring the apparent brightness of stars is believed to be Hipparchus, who lived in Nicaea (Turkey) during the second century BCE. Hipparchus is believed by many to be the greatest of the ancient astronomers. The original scale of apparent magnitude gave the brightest ...
... The creator of the system for measuring the apparent brightness of stars is believed to be Hipparchus, who lived in Nicaea (Turkey) during the second century BCE. Hipparchus is believed by many to be the greatest of the ancient astronomers. The original scale of apparent magnitude gave the brightest ...
Life Cycle of Star Flipbook
... 4. Cut out pages and staple so that it flips in order from birth to death. ...
... 4. Cut out pages and staple so that it flips in order from birth to death. ...
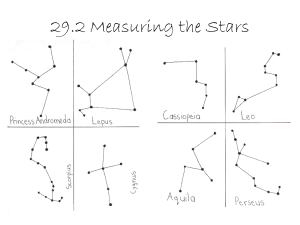
Worksheet 4.1 Coordinates and Star Maps
... 5. What is another name for Ori? Another name for that star is Betelgeuse. 6. On a given day, the coordinates of Jupiter are (1:58, +10º25’). a. What constellation is Jupiter in? Jupiter is in the constellation Pisces with those coordinates. ...
... 5. What is another name for Ori? Another name for that star is Betelgeuse. 6. On a given day, the coordinates of Jupiter are (1:58, +10º25’). a. What constellation is Jupiter in? Jupiter is in the constellation Pisces with those coordinates. ...
Solving the Mystery of Massive Star Birth
... they begin to heat up, growing hotter and hotter, until eventually they begin “burning” at their core. When the temperature at the core reaches a scorching 10 million degrees, the clump officially becomes a new star. We know this is how small and medium-sized stars form, but what about the most massiv ...
... they begin to heat up, growing hotter and hotter, until eventually they begin “burning” at their core. When the temperature at the core reaches a scorching 10 million degrees, the clump officially becomes a new star. We know this is how small and medium-sized stars form, but what about the most massiv ...
Star Life Cycle Web Quest
... 10: Our solar system formed from a ____________________________________________________generation nebula. 11. What two pieces of information classify stars? ...
... 10: Our solar system formed from a ____________________________________________________generation nebula. 11. What two pieces of information classify stars? ...
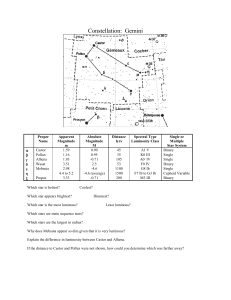
Gemini
... corresponds to a linear diameter of about 24 light years; its central density is about 6.21 stars per cubic parsec. Some authors have estimated a larger diameter of up to 46' (H. Shapley in 1930). With about 100 million years (WEBDA gives a value 95, the Sky Catalogue 2000.0 of 110 million years), i ...
... corresponds to a linear diameter of about 24 light years; its central density is about 6.21 stars per cubic parsec. Some authors have estimated a larger diameter of up to 46' (H. Shapley in 1930). With about 100 million years (WEBDA gives a value 95, the Sky Catalogue 2000.0 of 110 million years), i ...