On my webpage, find the link Star Life Cycle and use it to answer the
... A Solar Mass is equal to the mass of the Sun. If, for example, a star has 2 solar masses, it means it has twice as much mass as the Sun. Click the “brown dwarf” link in Option 1 6. How many solar masses are brown dwarfs on average? ...
... A Solar Mass is equal to the mass of the Sun. If, for example, a star has 2 solar masses, it means it has twice as much mass as the Sun. Click the “brown dwarf” link in Option 1 6. How many solar masses are brown dwarfs on average? ...
What Can We See in the Night Sky?
... • Groups of stars that are close together and travel together are known as star clusters • Star clusters are part of galaxies • Open clusters – contain about 50 to 1000 stars – dispersed along the Milky Way’s main band ...
... • Groups of stars that are close together and travel together are known as star clusters • Star clusters are part of galaxies • Open clusters – contain about 50 to 1000 stars – dispersed along the Milky Way’s main band ...
Notes - CH 12
... 2) As they move closer, they move faster and heat up 3) As the clump contracts, it becomes spherical 4) When mass gets large enough it become a protostar 5) Temperature continues to increase and sphere becomes ...
... 2) As they move closer, they move faster and heat up 3) As the clump contracts, it becomes spherical 4) When mass gets large enough it become a protostar 5) Temperature continues to increase and sphere becomes ...
Space Key Word Search
... supermassive black holes; radiation is emitted into space as material falls into a black hole, usually at the center of a galaxy - this is referred to as an AGN - Active Galactic Nucleus; extremely far away. ...
... supermassive black holes; radiation is emitted into space as material falls into a black hole, usually at the center of a galaxy - this is referred to as an AGN - Active Galactic Nucleus; extremely far away. ...
Diapositiva 1
... enormous but extremely faint halo of gaseous material, over three lightyears across, which surrounds the brighter, familiar planetary nebula. Made with data from the Nordic Optical Telescope in the Canary Islands, the composite picture shows extended emission from the nebula. Planetary nebulae have ...
... enormous but extremely faint halo of gaseous material, over three lightyears across, which surrounds the brighter, familiar planetary nebula. Made with data from the Nordic Optical Telescope in the Canary Islands, the composite picture shows extended emission from the nebula. Planetary nebulae have ...
F03HW09
... Why are earth-based parallax measurements limited to the nearest stars? Parallax measurements are limited because we measure the motion of a star due to the motion of Earth around the sun. Earth’s orbit is so small compared to the distance to stars that even the nearest stars show very small apparen ...
... Why are earth-based parallax measurements limited to the nearest stars? Parallax measurements are limited because we measure the motion of a star due to the motion of Earth around the sun. Earth’s orbit is so small compared to the distance to stars that even the nearest stars show very small apparen ...
Sun, Earth and Moon Model
... is a planet orbiting a distant star.) The strange new world was discovered orbiting a star in a triple star system. That means its parent star orbits alongside two other stars. This makes sunrises and sunsets something special — sometimes one sun rises in the sky, sometimes it’s two or three! But de ...
... is a planet orbiting a distant star.) The strange new world was discovered orbiting a star in a triple star system. That means its parent star orbits alongside two other stars. This makes sunrises and sunsets something special — sometimes one sun rises in the sky, sometimes it’s two or three! But de ...
Night Sky Checklist July–August–September Unaided Eye Astronomy
... Cygnus, the Swan, looks like a stick figure of a swan, wings outstretched, gliding into the Summer Triangle. The bright star at the swan’s tail, Deneb, marks the Triangle’s third corner. Delphinus, the Dolphin, is a faint little constellation that is noticeable mainly because it lies just outside th ...
... Cygnus, the Swan, looks like a stick figure of a swan, wings outstretched, gliding into the Summer Triangle. The bright star at the swan’s tail, Deneb, marks the Triangle’s third corner. Delphinus, the Dolphin, is a faint little constellation that is noticeable mainly because it lies just outside th ...
The Lives of Stars
... The core will shrink and grow hocer, burning more Hydrogen. The increased oudlow of energy will push out the outer layers, which will cool and become red. The sun will become a “R ...
... The core will shrink and grow hocer, burning more Hydrogen. The increased oudlow of energy will push out the outer layers, which will cool and become red. The sun will become a “R ...
An Introduction to the Night Sky Stars and Constellations
... An Introduction to the Night Sky Stars and Constellations 1. What is the Latin root word of star? 2. Why do stars “twinkle”? 3. Why do planets “shine”? ...
... An Introduction to the Night Sky Stars and Constellations 1. What is the Latin root word of star? 2. Why do stars “twinkle”? 3. Why do planets “shine”? ...
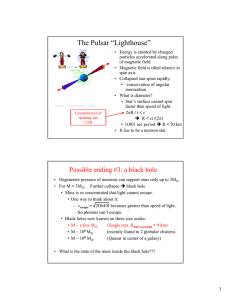
The Pulsar “Lighthouse”
... • Degenerate pressure of neutrons can support stars only up to 3M • For M > 3M: Further collapse Î black hole • Mass is so concentrated that light cannot escape. • One way to think about it: – vescape = 2GM/R becomes greater than speed of light. – So photons can’t escape. • Black holes now known o ...
... • Degenerate pressure of neutrons can support stars only up to 3M • For M > 3M: Further collapse Î black hole • Mass is so concentrated that light cannot escape. • One way to think about it: – vescape = 2GM/R becomes greater than speed of light. – So photons can’t escape. • Black holes now known o ...
Stellar Brightness Apparent magnitude
... to the magnitude scale since the ancient Greeks We now have lower, even negative, magnitudes for very bright objects like the sun and moon We have magnitudes higher than six for very dim stars seen with telescopes ...
... to the magnitude scale since the ancient Greeks We now have lower, even negative, magnitudes for very bright objects like the sun and moon We have magnitudes higher than six for very dim stars seen with telescopes ...
Universe CBA Review - cms16-17
... 22.) When a scientist looks at a galaxy that is 12 billion light years away and is red shifted, what does that tell you about the galaxy? 23.) What is the name of the effect caused by motion of an object causing wavelengths to compress in front of it and expand behind it? Use the diagram below to an ...
... 22.) When a scientist looks at a galaxy that is 12 billion light years away and is red shifted, what does that tell you about the galaxy? 23.) What is the name of the effect caused by motion of an object causing wavelengths to compress in front of it and expand behind it? Use the diagram below to an ...
The Planet with Three Suns
... star.) The strange new world was discovered orbiting a star in a triple star system. That means its parent star orbits alongside two other stars. This makes sunrises and sunsets something special — sometimes one sun rises in the sky, sometimes it’s two or three! But despite this, this planet is not ...
... star.) The strange new world was discovered orbiting a star in a triple star system. That means its parent star orbits alongside two other stars. This makes sunrises and sunsets something special — sometimes one sun rises in the sky, sometimes it’s two or three! But despite this, this planet is not ...
1. Compute the deflection angle of a star whose light... limb of the Sun. Also compute the deflection angle of...
... limb of the Sun. Also compute the deflection angle of a star whose light just grazes the limb of a 1.4M neutron star, if the neutron star was at the same distance from the Earth as the Sun. State assumptions. 2. Use the Plummer potential model, with a value of a = 100 kpc, together with the Viral t ...
... limb of the Sun. Also compute the deflection angle of a star whose light just grazes the limb of a 1.4M neutron star, if the neutron star was at the same distance from the Earth as the Sun. State assumptions. 2. Use the Plummer potential model, with a value of a = 100 kpc, together with the Viral t ...
Variable and Binary Stars
... – 75% of O-type stars seem to have a companion – If Jupiter had been ~100 times more massive, the Sun would have a companion star ...
... – 75% of O-type stars seem to have a companion – If Jupiter had been ~100 times more massive, the Sun would have a companion star ...
Properties of Stars
... • Very hot (30,000 K) stars emit their light in the blue spectrum, red stars are much cooler, stars with temperatures between 5000 and 6000 K appear yellow • Binary Stars – pairs of stars, pulled together by gravity, that orbit each other • Binary stars are used to determine the star property most d ...
... • Very hot (30,000 K) stars emit their light in the blue spectrum, red stars are much cooler, stars with temperatures between 5000 and 6000 K appear yellow • Binary Stars – pairs of stars, pulled together by gravity, that orbit each other • Binary stars are used to determine the star property most d ...
Cygnus (constellation)

Cygnus /ˈsɪɡnəs/ is a northern constellation lying on the plane of the Milky Way, deriving its name from the Latinized Greek word for swan. The swan is one of the most recognizable constellations of the northern summer and autumn, it features a prominent asterism known as the Northern Cross (in contrast to the Southern Cross). Cygnus was among the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations.Cygnus contains Deneb, one of the brightest stars in the night sky and one corner of the Summer Triangle, as well as some notable X-ray sources and the giant stellar association of Cygnus OB2. One of the stars of this association, NML Cygni, is one of the largest stars currently known. The constellation is also home to Cygnus X-1, a distant X-ray binary containing a supergiant and unseen massive companion that was the first object widely held to be a black hole. Many star systems in Cygnus have known planets as a result of the Kepler Mission observing one patch of the sky, the patch is the area around Cygnus. In addition, most of the eastern part of Cygnus is dominated by the Hercules–Corona Borealis Great Wall, a giant galaxy filament that is the largest known structure in the observable universe; covering most of the northern sky.