Mountain Skies - Pisgah Astronomical Research Institute
... To the northeast of Lyra is the bright star Deneb that represents the tail of the beautiful swan Cygnus. Tracing a line of stars from Deneb towards the south, we note the body and long neck of the swan terminating in the star Albireo that marks the eye of the swan. (Look at Albireo with a small tele ...
... To the northeast of Lyra is the bright star Deneb that represents the tail of the beautiful swan Cygnus. Tracing a line of stars from Deneb towards the south, we note the body and long neck of the swan terminating in the star Albireo that marks the eye of the swan. (Look at Albireo with a small tele ...
homework assignment 3
... Due Monday, April 22, 2013 at 5 p.m., either electronically or on paper. 1. Most astronomy textbooks use planets orbiting the Sun to illustrate the relevance of Kepler’s third law of planetary motion. In a class on stars and galaxies, describe a more relevant example of Kepler’s third law (i.e., whe ...
... Due Monday, April 22, 2013 at 5 p.m., either electronically or on paper. 1. Most astronomy textbooks use planets orbiting the Sun to illustrate the relevance of Kepler’s third law of planetary motion. In a class on stars and galaxies, describe a more relevant example of Kepler’s third law (i.e., whe ...
The Stars
... Plotting the Properties of Stars Two astronomers created a special kind of graph that compares star brightness with their ________________ ________________. When this was plotted it showed that these properties are related. For example, as the temperature of a star __________________, its colour bec ...
... Plotting the Properties of Stars Two astronomers created a special kind of graph that compares star brightness with their ________________ ________________. When this was plotted it showed that these properties are related. For example, as the temperature of a star __________________, its colour bec ...
Astronomy Tour
... Comets are “dirty snowballs” composed of frozen water and dust. As they approach the Sun they melt and leave a stream of water vapor and dust that is a “tail” Scientists believe that these originate from a large region filled with comet cores called the Oort cloud. ...
... Comets are “dirty snowballs” composed of frozen water and dust. As they approach the Sun they melt and leave a stream of water vapor and dust that is a “tail” Scientists believe that these originate from a large region filled with comet cores called the Oort cloud. ...
Solving the Mystery of Massive Star Birth
... As the cloud gets smaller, it gets clumpy. The clumps may eventually become so compact that they begin to heat up, growing hotter and hotter, until eventually they begin “burning” at their core. When the temperature at the core reaches a scorching 10 million degrees, the clump officially becomes a new ...
... As the cloud gets smaller, it gets clumpy. The clumps may eventually become so compact that they begin to heat up, growing hotter and hotter, until eventually they begin “burning” at their core. When the temperature at the core reaches a scorching 10 million degrees, the clump officially becomes a new ...
un Facts About Venus F
... It’s named after the Roman goddess of love and beauty. It’s the only planet named after a female. It has no moons or rings Unlike most other planets, it rotates clockwise (retrograde rotation). Billions of years ago its climate may have been similar to Earth One day on Venus is longer than one year ...
... It’s named after the Roman goddess of love and beauty. It’s the only planet named after a female. It has no moons or rings Unlike most other planets, it rotates clockwise (retrograde rotation). Billions of years ago its climate may have been similar to Earth One day on Venus is longer than one year ...
Introduction to Stars: Their Properties
... Parallax = 4.24 ± 0.16 mas or 0.00424 ± 0.00016 arc seconds Distance = 1/parallax = 1/0.00424 = 236 pc or ~770 ly ...
... Parallax = 4.24 ± 0.16 mas or 0.00424 ± 0.00016 arc seconds Distance = 1/parallax = 1/0.00424 = 236 pc or ~770 ly ...
How Bright is that Star?
... (Notice that the lower the number is the brighter the star is.) Modern astronomy still uses this system, but has refined it. ...
... (Notice that the lower the number is the brighter the star is.) Modern astronomy still uses this system, but has refined it. ...
Stars - Clover Sites
... 10. Name five constellations that are visible between sunset and midnight in your hemisphere during: a. The summer months. b. The winter months. 11. At what time of year is the constellation Orion best seen? Locate and idenify in the sky the three brightest stars of this constellation. 12. How are ...
... 10. Name five constellations that are visible between sunset and midnight in your hemisphere during: a. The summer months. b. The winter months. 11. At what time of year is the constellation Orion best seen? Locate and idenify in the sky the three brightest stars of this constellation. 12. How are ...
Starry Night¨ Times - October 2008
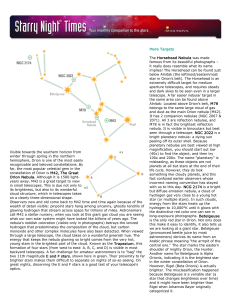
... monoxide and other complex molecules have also been detected. When viewed through a large telescope, the cloud takes on a wonderful greenish hue. The energy that keeps the nebula glowing so bright comes from the very hot, young stars in the brightest part of the cloud. Known as the Trapezium, this f ...
... monoxide and other complex molecules have also been detected. When viewed through a large telescope, the cloud takes on a wonderful greenish hue. The energy that keeps the nebula glowing so bright comes from the very hot, young stars in the brightest part of the cloud. Known as the Trapezium, this f ...
Patterns in the Sky - Plano Independent School District
... the pole star 5,000 years ago. It will become the pole star again in 20,000 years from now. ...
... the pole star 5,000 years ago. It will become the pole star again in 20,000 years from now. ...
Constellation Information
... with the naked eye as a dim, fuzzy patch if you have a clear, moonless evening at an observing site far from light pollution. M44 is also known as the Beehive Cluster, because in binoculars or a low-power, wide-field telescope, it looks like an old-fashion done-shaped beehive with many extra bees ...
... with the naked eye as a dim, fuzzy patch if you have a clear, moonless evening at an observing site far from light pollution. M44 is also known as the Beehive Cluster, because in binoculars or a low-power, wide-field telescope, it looks like an old-fashion done-shaped beehive with many extra bees ...
Studying Space
... Parallax of stars • Aids scientists in measuring distance. • It is the apparent shift of a star over a 6 month period. • It is just like when you shut 1 eye & look at an object; then open the other & the object appears to have moved. ...
... Parallax of stars • Aids scientists in measuring distance. • It is the apparent shift of a star over a 6 month period. • It is just like when you shut 1 eye & look at an object; then open the other & the object appears to have moved. ...
Cygnus (constellation)

Cygnus /ˈsɪɡnəs/ is a northern constellation lying on the plane of the Milky Way, deriving its name from the Latinized Greek word for swan. The swan is one of the most recognizable constellations of the northern summer and autumn, it features a prominent asterism known as the Northern Cross (in contrast to the Southern Cross). Cygnus was among the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations.Cygnus contains Deneb, one of the brightest stars in the night sky and one corner of the Summer Triangle, as well as some notable X-ray sources and the giant stellar association of Cygnus OB2. One of the stars of this association, NML Cygni, is one of the largest stars currently known. The constellation is also home to Cygnus X-1, a distant X-ray binary containing a supergiant and unseen massive companion that was the first object widely held to be a black hole. Many star systems in Cygnus have known planets as a result of the Kepler Mission observing one patch of the sky, the patch is the area around Cygnus. In addition, most of the eastern part of Cygnus is dominated by the Hercules–Corona Borealis Great Wall, a giant galaxy filament that is the largest known structure in the observable universe; covering most of the northern sky.