PowerPoint - Chandra X
... The young Sun-like stars in Orion produce violent X-ray outbursts, or flares, that are much more frequent and energetic than anything seen today from our Sun. The range of flare energies is large, with some of the stars producing flares that are a hundred times larger than others. The different flar ...
... The young Sun-like stars in Orion produce violent X-ray outbursts, or flares, that are much more frequent and energetic than anything seen today from our Sun. The range of flare energies is large, with some of the stars producing flares that are a hundred times larger than others. The different flar ...
Stars and Galaxies - Earth Science: Astronomy
... D. Universe is expanding 1. Doppler shift—light changes as it moves toward or away from an object a. Starlight moving toward Earth shifts to blue-violet end of spectrum b. Starlight moving away from Earth shifts to red end of spectrum ...
... D. Universe is expanding 1. Doppler shift—light changes as it moves toward or away from an object a. Starlight moving toward Earth shifts to blue-violet end of spectrum b. Starlight moving away from Earth shifts to red end of spectrum ...
Structure of the Universe
... by combining smaller elements to form a larger one, specifically two hydrogen atoms form a helium atom, ...
... by combining smaller elements to form a larger one, specifically two hydrogen atoms form a helium atom, ...
Other Objects in Space
... Meteorites are any objects that fall to Earth. The sun is the largest kind of star. All stars become supernovas. ...
... Meteorites are any objects that fall to Earth. The sun is the largest kind of star. All stars become supernovas. ...
When Stars Blow Up
... •When the temperature reaches a few MK, fusion begins •Degenerate fusion is a runaway. •All the H fuses to He and heavier elements in a soundcrossing time (a few minutes) •The star increases in brightness ~ 10,000 times •Most of the matter is ejected ...
... •When the temperature reaches a few MK, fusion begins •Degenerate fusion is a runaway. •All the H fuses to He and heavier elements in a soundcrossing time (a few minutes) •The star increases in brightness ~ 10,000 times •Most of the matter is ejected ...
Place in Space
... distance that light can travel in one year. In one year light travels about 9,460,000,000,000 kilometres. So, this distance is 1 lightyear. ...
... distance that light can travel in one year. In one year light travels about 9,460,000,000,000 kilometres. So, this distance is 1 lightyear. ...
chap17_s05_probs
... ANSWER: Stars appear fainter if located further away, just like any luminous object. The magnitude of a star represents its brightness, either its perceived brightness, known as its apparent magnitude, or its actual, true, brightness, known as its absolute magnitude. More luminous stars have smaller ...
... ANSWER: Stars appear fainter if located further away, just like any luminous object. The magnitude of a star represents its brightness, either its perceived brightness, known as its apparent magnitude, or its actual, true, brightness, known as its absolute magnitude. More luminous stars have smaller ...
How Do Astronomers Measure the Brightness of a Star?
... Apparent magnitudes only tell us how bright stars appear to be, NOT how bright they actually are. Look at the above example: -There are 2 stars that both shine with the exact same amount of light, BUT one of them is 10x further than the other ...
... Apparent magnitudes only tell us how bright stars appear to be, NOT how bright they actually are. Look at the above example: -There are 2 stars that both shine with the exact same amount of light, BUT one of them is 10x further than the other ...
chap17_f04_probs
... ANSWER: Stars appear fainter if located further away, just like any luminous object. The magnitude of a star represents its brightness, either its perceived brightness, known as its apparent magnitude, or its actual, true, brightness, known as its absolute magnitude. More luminous stars have smaller ...
... ANSWER: Stars appear fainter if located further away, just like any luminous object. The magnitude of a star represents its brightness, either its perceived brightness, known as its apparent magnitude, or its actual, true, brightness, known as its absolute magnitude. More luminous stars have smaller ...
ORIGIN OF THE UNIVERSE
... cluster. Our galaxy is found in the “Local Group” which contains about 29 other galaxies Galaxy - A collection of similar stars found within a star group. Our galaxy is called the Milky Way and contains about 200 Billion Stars. - There may be about 100 Billion Galaxies in the Universe. ...
... cluster. Our galaxy is found in the “Local Group” which contains about 29 other galaxies Galaxy - A collection of similar stars found within a star group. Our galaxy is called the Milky Way and contains about 200 Billion Stars. - There may be about 100 Billion Galaxies in the Universe. ...
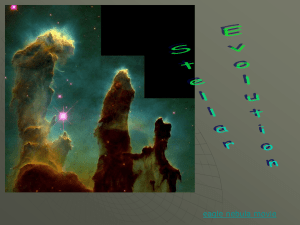
Stellar Evolution Slideshow
... only neutrons are left (Guess where the name “Neutron Stars” came from?) Also called Pulsars because they emit radio waves with incredible regularity. Appear to be rapidly rotating neutron star ...
... only neutrons are left (Guess where the name “Neutron Stars” came from?) Also called Pulsars because they emit radio waves with incredible regularity. Appear to be rapidly rotating neutron star ...
Problem set 1 1. The binding energy per nucleon for 56Fe is 8.8MeV
... 2. The main sequence of the Pleiades cluster of stars consists of stars with mass less than 6M ; the more massive stars have already evolved off the main sequence. Estimate the age of the Pleiades cluster. 3. Given that the luminosity of the sun is 3.8 × 1026 W and that the absolute bolometric magn ...
... 2. The main sequence of the Pleiades cluster of stars consists of stars with mass less than 6M ; the more massive stars have already evolved off the main sequence. Estimate the age of the Pleiades cluster. 3. Given that the luminosity of the sun is 3.8 × 1026 W and that the absolute bolometric magn ...
LIfe of a Star
... Used to study the lives of stars Most stars lie along the main sequence portion of the diagram ...
... Used to study the lives of stars Most stars lie along the main sequence portion of the diagram ...
Lecture4
... mass star is about a million times brighter than the Sun. It has 100 times more fuel but uses it up a million times faster. It therefore lives only about 10-4 times as long as the Sun. Since the Sun lives 10 billion years, a 100 solar mass star lives only about one million years. ...
... mass star is about a million times brighter than the Sun. It has 100 times more fuel but uses it up a million times faster. It therefore lives only about 10-4 times as long as the Sun. Since the Sun lives 10 billion years, a 100 solar mass star lives only about one million years. ...
25 Study Guide
... • Binary stars can be used to determine stellar mass. • The nearest stars have the largest parallax angles, while those of distant stars are too small to measure. • Three factors control the apparent brightness of a star as seen from Earth: how big it is, how hot it is, and how far away it is. • A H ...
... • Binary stars can be used to determine stellar mass. • The nearest stars have the largest parallax angles, while those of distant stars are too small to measure. • Three factors control the apparent brightness of a star as seen from Earth: how big it is, how hot it is, and how far away it is. • A H ...
Stellar Evolution Notes
... formed iron, no more reactions can occur, and the core violently collapses in on itself Supernova ...
... formed iron, no more reactions can occur, and the core violently collapses in on itself Supernova ...
the life cycle of stars
... • Energy is generated in the core and causes the star to shine. • The size of the star changes very little as long as its supply of hydrogen nuclei fuse into helium nuclei. ...
... • Energy is generated in the core and causes the star to shine. • The size of the star changes very little as long as its supply of hydrogen nuclei fuse into helium nuclei. ...
Cygnus (constellation)

Cygnus /ˈsɪɡnəs/ is a northern constellation lying on the plane of the Milky Way, deriving its name from the Latinized Greek word for swan. The swan is one of the most recognizable constellations of the northern summer and autumn, it features a prominent asterism known as the Northern Cross (in contrast to the Southern Cross). Cygnus was among the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations.Cygnus contains Deneb, one of the brightest stars in the night sky and one corner of the Summer Triangle, as well as some notable X-ray sources and the giant stellar association of Cygnus OB2. One of the stars of this association, NML Cygni, is one of the largest stars currently known. The constellation is also home to Cygnus X-1, a distant X-ray binary containing a supergiant and unseen massive companion that was the first object widely held to be a black hole. Many star systems in Cygnus have known planets as a result of the Kepler Mission observing one patch of the sky, the patch is the area around Cygnus. In addition, most of the eastern part of Cygnus is dominated by the Hercules–Corona Borealis Great Wall, a giant galaxy filament that is the largest known structure in the observable universe; covering most of the northern sky.