Finding Black Holes
... Monitor the motion of any star found at exactly that location. Is it orbiting around an unseen companion? If so, use Newton’s laws to deduce the mass of the dark companion. Perhaps it’s a black hole?! ...
... Monitor the motion of any star found at exactly that location. Is it orbiting around an unseen companion? If so, use Newton’s laws to deduce the mass of the dark companion. Perhaps it’s a black hole?! ...
Linking Asteroids and Meteorites through Reflectance
... • 90% of classified stars are on main sequence • Main sequence stars are “young” stars • If a star is leaving the main sequence, it is at the end of its lifespan of burning hydrogen into ...
... • 90% of classified stars are on main sequence • Main sequence stars are “young” stars • If a star is leaving the main sequence, it is at the end of its lifespan of burning hydrogen into ...
Finding Black Holes Left Behind by Single Stars
... Monitor the motion of any star found at exactly that location. Is it orbiting around an unseen companion? If so, use Newton’s laws to deduce the mass of the dark companion. Perhaps it’s a black hole?! ...
... Monitor the motion of any star found at exactly that location. Is it orbiting around an unseen companion? If so, use Newton’s laws to deduce the mass of the dark companion. Perhaps it’s a black hole?! ...
Stars_Galaxies_Introduction - Etiwanda E
... What is the source of light in a galaxy? – How is energy produced by the sun? – How are sunspots, prominences, and solar flares related? – Why is our sun considered to be an average star? – How does our sun differ from stars in binary systems? ...
... What is the source of light in a galaxy? – How is energy produced by the sun? – How are sunspots, prominences, and solar flares related? – Why is our sun considered to be an average star? – How does our sun differ from stars in binary systems? ...
Search for Student Research Assistant
... (Sco X-1 for short) is a double star system. It’s actually the brightest spot in the sky in X-rays (other than the Sun). Of the two stars, one is a normal star, slightly less massive than our own Sun, but the other is a neutron star (a collapsed star only about 10 km across). Sco X-1 was the first d ...
... (Sco X-1 for short) is a double star system. It’s actually the brightest spot in the sky in X-rays (other than the Sun). Of the two stars, one is a normal star, slightly less massive than our own Sun, but the other is a neutron star (a collapsed star only about 10 km across). Sco X-1 was the first d ...
hubble amazing universe worksheet
... 7. In 2005, the Corina nebula was revealed. The data comes back in ________________ and ____________________, and gasses are assigned colors. Blue is ___________, and green is ___________________. 8. This region is _____________ light years across! 9. Hubble even showed a star about to die! As a sta ...
... 7. In 2005, the Corina nebula was revealed. The data comes back in ________________ and ____________________, and gasses are assigned colors. Blue is ___________, and green is ___________________. 8. This region is _____________ light years across! 9. Hubble even showed a star about to die! As a sta ...
RED “O Big Red
... Kara reset the star reader. Where had she heard that unusual name before? then she remembered—aldebaran (all-deB-er-on) was one of the brightest stars in earth’s sky. soon the Stella was bathed in red light. “this star is enormous!” manolo shouted. “it’s 44 times wider than the sun, but its temperat ...
... Kara reset the star reader. Where had she heard that unusual name before? then she remembered—aldebaran (all-deB-er-on) was one of the brightest stars in earth’s sky. soon the Stella was bathed in red light. “this star is enormous!” manolo shouted. “it’s 44 times wider than the sun, but its temperat ...
Lesson 3 Power Notes Outline
... Some supergiants are so massive that their cores are unable to stop collapsing under the force of gravity. ...
... Some supergiants are so massive that their cores are unable to stop collapsing under the force of gravity. ...
Classification_of_Stars_By_Luminosity
... He called the brightest stars in the sky first magnitude and the dimmest visible to the naked eye sixth magnitude. Stars of intermediate brightness were given intermediate values. ...
... He called the brightest stars in the sky first magnitude and the dimmest visible to the naked eye sixth magnitude. Stars of intermediate brightness were given intermediate values. ...
Orion - Starry Starry Night!
... Visible : Jan, Feb, Mar, Apr, Dec Winter - Spring Canis Major contains Sirius, the brightest star in the night sky, known as the "dog star". It is bright because of its proximity to our Solar System. In contrast, the other bright stars of the constellation are stars of great distance and high lumino ...
... Visible : Jan, Feb, Mar, Apr, Dec Winter - Spring Canis Major contains Sirius, the brightest star in the night sky, known as the "dog star". It is bright because of its proximity to our Solar System. In contrast, the other bright stars of the constellation are stars of great distance and high lumino ...
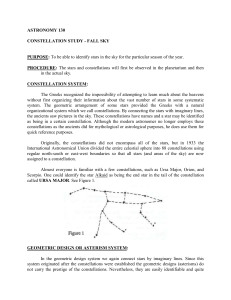
Laboratory Procedure (Word Format)
... might indicate? There will be several telescopes set up on the observing deck. Observe the following objects and make a sketch of what you observe. Beta Cygnus (Alberio), Epsilon Lyra, M-57, M-13, and any of the planets that are visible. Record on your drawing of the constellations the location of a ...
... might indicate? There will be several telescopes set up on the observing deck. Observe the following objects and make a sketch of what you observe. Beta Cygnus (Alberio), Epsilon Lyra, M-57, M-13, and any of the planets that are visible. Record on your drawing of the constellations the location of a ...
Volume 20 Number 4 March 2012 - Forsyth Astronomical Society
... fastest winds generated by supermassive black holes, objects millions or billions of times more massive. Also, this is nearly 10 times faster than any seen from a black hole resulting from the collapse of an extremely massive star (stellar-mass black hole). ...
... fastest winds generated by supermassive black holes, objects millions or billions of times more massive. Also, this is nearly 10 times faster than any seen from a black hole resulting from the collapse of an extremely massive star (stellar-mass black hole). ...
ecliptic. - Valhalla High School
... So, 360° = 24 h R.A., 15° = 1 h R.A., and 1° = 4 min R.A. Right ascension increases from west to east (note that we are looking at the exterior of the celestial sphere in the above picture). ...
... So, 360° = 24 h R.A., 15° = 1 h R.A., and 1° = 4 min R.A. Right ascension increases from west to east (note that we are looking at the exterior of the celestial sphere in the above picture). ...
Measuring the Stars
... The spectroscopic parallax calculation can be misleading if the star is not on the main sequence. The width of spectral lines can be used to define luminosity classes: ...
... The spectroscopic parallax calculation can be misleading if the star is not on the main sequence. The width of spectral lines can be used to define luminosity classes: ...
Star Questions 2008 - Fort Thomas Independent Schools
... accumulates more matter than it had when it was on the main sequence, causing the core to grow to a size greater than 1.4 solar masses. ...
... accumulates more matter than it had when it was on the main sequence, causing the core to grow to a size greater than 1.4 solar masses. ...
The Star
... above the entrance was now a fused stump, but even the first long-range photographs told us that here was the work of intelligence. A little later we detected the continent-wide pattern of radioactivity that had been buried in the rock. Even if the pylon above the Vault had been destroyed, this woul ...
... above the entrance was now a fused stump, but even the first long-range photographs told us that here was the work of intelligence. A little later we detected the continent-wide pattern of radioactivity that had been buried in the rock. Even if the pylon above the Vault had been destroyed, this woul ...
File
... Cosmic wreckage from the detonation of a massive star is the subject of this official first image from NASA's Chandra X-ray Observatory. ...
... Cosmic wreckage from the detonation of a massive star is the subject of this official first image from NASA's Chandra X-ray Observatory. ...
Mr. Scharff
... Introduction. The Hertzsprung-Russell diagram is actually a graph that illustrates the relationship that exists between the average surface temperature of stars and their absolute magnitude, which is how bright they would appear to be if they were al the same distance away. Rather than speak of the ...
... Introduction. The Hertzsprung-Russell diagram is actually a graph that illustrates the relationship that exists between the average surface temperature of stars and their absolute magnitude, which is how bright they would appear to be if they were al the same distance away. Rather than speak of the ...
Thursday October 1 - Montana State University
... we can find its distance. • A star of known luminosity is called a standard candle. • More on this later... ...
... we can find its distance. • A star of known luminosity is called a standard candle. • More on this later... ...
Cygnus (constellation)

Cygnus /ˈsɪɡnəs/ is a northern constellation lying on the plane of the Milky Way, deriving its name from the Latinized Greek word for swan. The swan is one of the most recognizable constellations of the northern summer and autumn, it features a prominent asterism known as the Northern Cross (in contrast to the Southern Cross). Cygnus was among the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations.Cygnus contains Deneb, one of the brightest stars in the night sky and one corner of the Summer Triangle, as well as some notable X-ray sources and the giant stellar association of Cygnus OB2. One of the stars of this association, NML Cygni, is one of the largest stars currently known. The constellation is also home to Cygnus X-1, a distant X-ray binary containing a supergiant and unseen massive companion that was the first object widely held to be a black hole. Many star systems in Cygnus have known planets as a result of the Kepler Mission observing one patch of the sky, the patch is the area around Cygnus. In addition, most of the eastern part of Cygnus is dominated by the Hercules–Corona Borealis Great Wall, a giant galaxy filament that is the largest known structure in the observable universe; covering most of the northern sky.