Lecture 12
... We can directly observe the orbital motions of these stars. We can only see visual binaries if they are very near Earth. ...
... We can directly observe the orbital motions of these stars. We can only see visual binaries if they are very near Earth. ...
The Milky Way
... • If you know how luminous a star REALLY is and how bright it looks from Earth, you can determine how far away it must be to look that faint. • For any star in the sky, we KNOW: ...
... • If you know how luminous a star REALLY is and how bright it looks from Earth, you can determine how far away it must be to look that faint. • For any star in the sky, we KNOW: ...
STUDY GUIDE FOR CHAPTER 1
... A. They go through first red giant, helium burning in the core, and double shell burning phases. B. Then they go through a sequence of situations where the core is contracting and heating up when no fusion is going on inside it and then stops contracting when the next type of fusion begins. Meanwhil ...
... A. They go through first red giant, helium burning in the core, and double shell burning phases. B. Then they go through a sequence of situations where the core is contracting and heating up when no fusion is going on inside it and then stops contracting when the next type of fusion begins. Meanwhil ...
The Properties of Stars
... into helium in their cores. (50 billion years) When the core runs out of hydrogen, the push outward due to fusion decreases and gravity contracts the star causing fusion to begin in a shell of hydrogen surrounding the core. Shell-hydrogen burning takes place at a higher rate than hydrogen fusion did ...
... into helium in their cores. (50 billion years) When the core runs out of hydrogen, the push outward due to fusion decreases and gravity contracts the star causing fusion to begin in a shell of hydrogen surrounding the core. Shell-hydrogen burning takes place at a higher rate than hydrogen fusion did ...
Cosmic Distance Ladder
... • Reliable measurements, those with errors of 10% or less, can only be achieved at stellar distances of no more than about 100 pc. • Space-based telescopes are not limited by this effect and can accurately measure distances to objects beyond the limit of ground-based observations. • E.g. Hipparcos 0 ...
... • Reliable measurements, those with errors of 10% or less, can only be achieved at stellar distances of no more than about 100 pc. • Space-based telescopes are not limited by this effect and can accurately measure distances to objects beyond the limit of ground-based observations. • E.g. Hipparcos 0 ...
monkeyball_lifecycleofastar
... This phase is huge, our planet would be a grain of sand compared to a red supergiant. ...
... This phase is huge, our planet would be a grain of sand compared to a red supergiant. ...
The life of a Star (pages 468-471)
... 3. What happens when a star runs out of the fuels needed to produce energy? 4. What is a supernova? During this stage, what happens to the core of the star? When our Sun eventually swells into a red giant star, its outer layers will grow to be about 100 times its present size swallowing up Mercury ...
... 3. What happens when a star runs out of the fuels needed to produce energy? 4. What is a supernova? During this stage, what happens to the core of the star? When our Sun eventually swells into a red giant star, its outer layers will grow to be about 100 times its present size swallowing up Mercury ...
The Stars
... the main sequence. • Generally, the hotter the star, the more luminous it will be. • The main sequence is not a straight line but a band. ...
... the main sequence. • Generally, the hotter the star, the more luminous it will be. • The main sequence is not a straight line but a band. ...
The Young Astronomers Newsletter Volume 22 Number 3 February
... 2009 FD had been ranked among the top five objects in a list of the most dangerous objects, but new observations have now shown that it is far less likely to hit the Earth than had been feared. ...
... 2009 FD had been ranked among the top five objects in a list of the most dangerous objects, but new observations have now shown that it is far less likely to hit the Earth than had been feared. ...
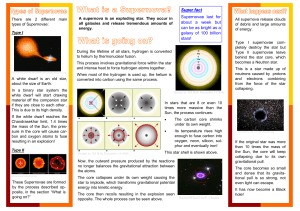
What is a supernova - University of Warwick
... As far back as AD184 in China astronomers have been able to observe and record supernovae. October 1604 was the last time a supernova in the Milky Way galaxy became visible on Earth . It was measured in detail by the German mathematician, Johannes Kepler, who noted that it was bright enough to see a ...
... As far back as AD184 in China astronomers have been able to observe and record supernovae. October 1604 was the last time a supernova in the Milky Way galaxy became visible on Earth . It was measured in detail by the German mathematician, Johannes Kepler, who noted that it was bright enough to see a ...
Stars - Science
... are red. Medium temperature stars are orange and yellow. The hottest stars are blue. ...
... are red. Medium temperature stars are orange and yellow. The hottest stars are blue. ...
Constellations Test Review
... 9. If Peter is sailing at night out at sea and measures that Polaris is 5 fists above the horizon, what is Peter’s latitude? ...
... 9. If Peter is sailing at night out at sea and measures that Polaris is 5 fists above the horizon, what is Peter’s latitude? ...
PDF version (two pages, including the full text)
... bit south of the point overhead is the second brightest star in the sky, Canopus. Rising in the southeast are the stars of the Southern Cross and the Pointers (Alpha and Beta Centauri). Alpha Centauri is a triple system, with two sun like stars orbiting each other every 80 years and a dim red dwarf ...
... bit south of the point overhead is the second brightest star in the sky, Canopus. Rising in the southeast are the stars of the Southern Cross and the Pointers (Alpha and Beta Centauri). Alpha Centauri is a triple system, with two sun like stars orbiting each other every 80 years and a dim red dwarf ...
Evolution of Stars and Galaxies
... Black hole If supernova core is 3 or more times as massive as Sun core will collapse Not even light can escape An event horizon anything crossing this will go (region nothing can escape) Other stars orbit around it as usual ...
... Black hole If supernova core is 3 or more times as massive as Sun core will collapse Not even light can escape An event horizon anything crossing this will go (region nothing can escape) Other stars orbit around it as usual ...
Cygnus (constellation)

Cygnus /ˈsɪɡnəs/ is a northern constellation lying on the plane of the Milky Way, deriving its name from the Latinized Greek word for swan. The swan is one of the most recognizable constellations of the northern summer and autumn, it features a prominent asterism known as the Northern Cross (in contrast to the Southern Cross). Cygnus was among the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations.Cygnus contains Deneb, one of the brightest stars in the night sky and one corner of the Summer Triangle, as well as some notable X-ray sources and the giant stellar association of Cygnus OB2. One of the stars of this association, NML Cygni, is one of the largest stars currently known. The constellation is also home to Cygnus X-1, a distant X-ray binary containing a supergiant and unseen massive companion that was the first object widely held to be a black hole. Many star systems in Cygnus have known planets as a result of the Kepler Mission observing one patch of the sky, the patch is the area around Cygnus. In addition, most of the eastern part of Cygnus is dominated by the Hercules–Corona Borealis Great Wall, a giant galaxy filament that is the largest known structure in the observable universe; covering most of the northern sky.


![2-2 wkst - Home [www.petoskeyschools.org]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/009700019_1-9e7a7c15444658cfc76a04a9cf1ba291-300x300.png)