PHYS3380_102615_bw
... Proplyds - disks of dust and gas surrounding newly formed stars. - of the five stars - all pre main sequence - in this field which spans about 0.14 light years, four appear to have associated proplyds - three bright ones and one dark one seen in silhouette against the bright nebula. - more complete ...
... Proplyds - disks of dust and gas surrounding newly formed stars. - of the five stars - all pre main sequence - in this field which spans about 0.14 light years, four appear to have associated proplyds - three bright ones and one dark one seen in silhouette against the bright nebula. - more complete ...
Test 2, November 14, 2016 - Physics@Brock
... 30. Star S is twice as luminous as star U, but its brightness is a half that of U. The distance that of U. of S is (a) twice (b) four times (c) one half (d) one quarter 31. A blue star has colder surface than a red star. (a) True. (b) False. 32. To determine the radius (R) of a star we need its (a) ...
... 30. Star S is twice as luminous as star U, but its brightness is a half that of U. The distance that of U. of S is (a) twice (b) four times (c) one half (d) one quarter 31. A blue star has colder surface than a red star. (a) True. (b) False. 32. To determine the radius (R) of a star we need its (a) ...
neutron star - Livonia Public Schools
... All stars, regardless of their size, eventually run out of fuel and collapse due to gravity. Death of Low-Mass Stars • Stars less than one-half the mass of the sun never evolve to the red giant stage but remain in the stable main-sequence stage until they consume all their hydrogen fuel and coll ...
... All stars, regardless of their size, eventually run out of fuel and collapse due to gravity. Death of Low-Mass Stars • Stars less than one-half the mass of the sun never evolve to the red giant stage but remain in the stable main-sequence stage until they consume all their hydrogen fuel and coll ...
Cluster and Association Members
... are physically related groups of stars held together by mutual gravitational attraction. Therefore, they populate a limited region of space, which is typically much smaller than their distance from the Sun, so that the members are all approximately at the same distance. They are believed to originat ...
... are physically related groups of stars held together by mutual gravitational attraction. Therefore, they populate a limited region of space, which is typically much smaller than their distance from the Sun, so that the members are all approximately at the same distance. They are believed to originat ...
The Stars - University of Redlands
... are each binary stars. But they were too close to be directly imaged - until 2 May 1996, when the NPOI produced the first image of Mizar A. That image was the highest angular resolution image ever made in optical astronomy. Since then, the NPOI has observed Mizar A in 23 different positions over hal ...
... are each binary stars. But they were too close to be directly imaged - until 2 May 1996, when the NPOI produced the first image of Mizar A. That image was the highest angular resolution image ever made in optical astronomy. Since then, the NPOI has observed Mizar A in 23 different positions over hal ...
PDF version (two pages, including the full text)
... Second-brightest among Leo’s stars is Denebola (‘tail of the lion’), well to the east (right, for an observer facing north) of the ‘question mark’. According to Egyptian legend, the sun was in Leo immediately after the Creation, near Denebola. On a more scientific note, Denebola is about 36 light ye ...
... Second-brightest among Leo’s stars is Denebola (‘tail of the lion’), well to the east (right, for an observer facing north) of the ‘question mark’. According to Egyptian legend, the sun was in Leo immediately after the Creation, near Denebola. On a more scientific note, Denebola is about 36 light ye ...
- National Optical Astronomy Observatory
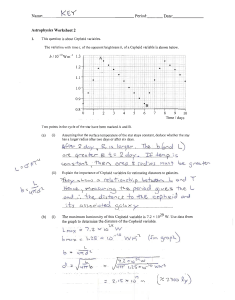
... Figure 1: (X=color index (b-v), Y=Brightness (v)) According to the graph, the tip of the main sequence appears to lie around NGC 1496-1. This star’s color index is approximately 0.062, classifying it as a spectral type A star. Based on this observation, the age of the cluster is estimated to be no ...
... Figure 1: (X=color index (b-v), Y=Brightness (v)) According to the graph, the tip of the main sequence appears to lie around NGC 1496-1. This star’s color index is approximately 0.062, classifying it as a spectral type A star. Based on this observation, the age of the cluster is estimated to be no ...
How the universe works – Answer Key Star dust is the building
... You could fit a million earths inside the sun. Our sun is over a million km in diameter. The largest star ever discovered is a billion times larger than our sun. Each star is a one of a kind but they all start off in the same way, as clouds of dust and gas called nebulas. Each nebula is a star nurse ...
... You could fit a million earths inside the sun. Our sun is over a million km in diameter. The largest star ever discovered is a billion times larger than our sun. Each star is a one of a kind but they all start off in the same way, as clouds of dust and gas called nebulas. Each nebula is a star nurse ...
Teacher Subject Title Concept Context Tek/SE Verb
... Engage – Stars in the Night Sky. Construct a KLEW Chart in the class science notebook: What do you see when you look up at the sky? Does the sky look the same during the day as it does at night? Other than the Moon, what do we see in the night sky? What do you know about stars? Misconceptions: stude ...
... Engage – Stars in the Night Sky. Construct a KLEW Chart in the class science notebook: What do you see when you look up at the sky? Does the sky look the same during the day as it does at night? Other than the Moon, what do we see in the night sky? What do you know about stars? Misconceptions: stude ...
Grade 6 Standard 4 - Murray School District
... C. Libra and Capricorn D. Taurus and Aries 6. When Earth is in this location, which constellation would not be visible at night? A. Gemini B. Scorpius C. Cancer D. Aries 7. Six months from now which constellation will be visible at night? A. Libra B. Aries C. Taurus D. Pisces 8. Which of the followi ...
... C. Libra and Capricorn D. Taurus and Aries 6. When Earth is in this location, which constellation would not be visible at night? A. Gemini B. Scorpius C. Cancer D. Aries 7. Six months from now which constellation will be visible at night? A. Libra B. Aries C. Taurus D. Pisces 8. Which of the followi ...
Stars Chapter 21
... • Spectroscope: Breaks light from a distant star into its characteristic color • SPECTRUM: the band of colors that forms as light passes through a prism • Used to see if galaxies are moving away or toward the earth ...
... • Spectroscope: Breaks light from a distant star into its characteristic color • SPECTRUM: the band of colors that forms as light passes through a prism • Used to see if galaxies are moving away or toward the earth ...
Lecture 13: The stars are suns
... Stars are fusion reactors like our sun, with similar physical properties. Spectroscopes, atomic theory, and especially measurements of stellar distances (1838) made it possible for astronomers to derive properties of stars and establish the Sun-stellar connection. • Physical properties of stars we w ...
... Stars are fusion reactors like our sun, with similar physical properties. Spectroscopes, atomic theory, and especially measurements of stellar distances (1838) made it possible for astronomers to derive properties of stars and establish the Sun-stellar connection. • Physical properties of stars we w ...
3 sr -1
... Brightest stars: ~1st magnitude Faintest stars (unaided eye): 6th magnitude More quantitative: ...
... Brightest stars: ~1st magnitude Faintest stars (unaided eye): 6th magnitude More quantitative: ...
Grade 9 Science – Unit 4 Space Quiz
... d. A display of shifting colours in the sky caused by solar particles colliding with matter in the upper atmosphere e. None of the above 5. Stars can be different colours, temperatures and luminosities. These different characteristics can be represented in a Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram. Where is our ...
... d. A display of shifting colours in the sky caused by solar particles colliding with matter in the upper atmosphere e. None of the above 5. Stars can be different colours, temperatures and luminosities. These different characteristics can be represented in a Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram. Where is our ...
EMR, Telescopes, Stars, Solar System study guide `14-15
... 9. The distance that light travels in a year is known as a _________________________. 10. The time it takes light from a star 100 light years away to reach Earth is ___________________. 11. Parallax is used to find the ____________________________ to nearby stars. 12. Astronomers use a _____________ ...
... 9. The distance that light travels in a year is known as a _________________________. 10. The time it takes light from a star 100 light years away to reach Earth is ___________________. 11. Parallax is used to find the ____________________________ to nearby stars. 12. Astronomers use a _____________ ...
6th Grade Science Chapter 19 Jeopardy Game
... b. Distant galaxies share many characteristics with early galaxies. c. Distant galaxies have not changed as much as close galaxies, so they are most similar to early galaxies. d. Because it takes a long time for light to travel through space, looking at distant galaxies shows what early galaxies loo ...
... b. Distant galaxies share many characteristics with early galaxies. c. Distant galaxies have not changed as much as close galaxies, so they are most similar to early galaxies. d. Because it takes a long time for light to travel through space, looking at distant galaxies shows what early galaxies loo ...
Cygnus (constellation)

Cygnus /ˈsɪɡnəs/ is a northern constellation lying on the plane of the Milky Way, deriving its name from the Latinized Greek word for swan. The swan is one of the most recognizable constellations of the northern summer and autumn, it features a prominent asterism known as the Northern Cross (in contrast to the Southern Cross). Cygnus was among the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations.Cygnus contains Deneb, one of the brightest stars in the night sky and one corner of the Summer Triangle, as well as some notable X-ray sources and the giant stellar association of Cygnus OB2. One of the stars of this association, NML Cygni, is one of the largest stars currently known. The constellation is also home to Cygnus X-1, a distant X-ray binary containing a supergiant and unseen massive companion that was the first object widely held to be a black hole. Many star systems in Cygnus have known planets as a result of the Kepler Mission observing one patch of the sky, the patch is the area around Cygnus. In addition, most of the eastern part of Cygnus is dominated by the Hercules–Corona Borealis Great Wall, a giant galaxy filament that is the largest known structure in the observable universe; covering most of the northern sky.