Semester 1 Earth Science Gallery Review
... 5. What temperature is Sirius B? 6. This star is a red Giant. 7. What temperature is Bernard’s Star? 8. Which star is the dimmest (least bright) on the chart? 9. What category is the hottest star on the chart? 10. What color are the coolest stars? 11. What category of stars is hot but not very lumin ...
... 5. What temperature is Sirius B? 6. This star is a red Giant. 7. What temperature is Bernard’s Star? 8. Which star is the dimmest (least bright) on the chart? 9. What category is the hottest star on the chart? 10. What color are the coolest stars? 11. What category of stars is hot but not very lumin ...
Star Cycle2013
... A black hole is an extremely massive remnant from which light can not escape. “Black holes are where God divided by zero” Stephen Wright ...
... A black hole is an extremely massive remnant from which light can not escape. “Black holes are where God divided by zero” Stephen Wright ...
How Far Can You See?
... next nearest star either. It’s actually a triple system: three stars orbiting each other. The closest of the three, called Proxima Centauri, is a tiny, 4.2-lightyear-distant red ember, visible only through telescopes. But it might not be the record holder either. It’s possible that extremely dim sta ...
... next nearest star either. It’s actually a triple system: three stars orbiting each other. The closest of the three, called Proxima Centauri, is a tiny, 4.2-lightyear-distant red ember, visible only through telescopes. But it might not be the record holder either. It’s possible that extremely dim sta ...
Document
... • Gravitational tides pull matter off big low density objects towards small high density objects. ...
... • Gravitational tides pull matter off big low density objects towards small high density objects. ...
Stellar Evolution - Harnett County High Schools Wiki
... radiation that from Earth appears to blink on and off as the star spins, like the beam of light from a turning lighthouse. This "pulsing" appearance gives some neutron stars the name pulsars. ...
... radiation that from Earth appears to blink on and off as the star spins, like the beam of light from a turning lighthouse. This "pulsing" appearance gives some neutron stars the name pulsars. ...
Inverse Square Law
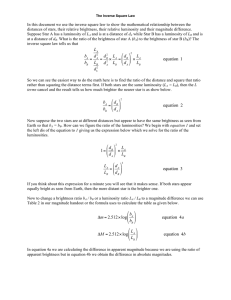
... distances of stars, their relative brightness, their relative luminosity and their magnitude difference. Suppose Star A has a luminosity of LA and is at a distance of dA while Star B has a luminosity of LB and is at a distance of dB. What is the ratio of the brightness of star A (bA) to the brightne ...
... distances of stars, their relative brightness, their relative luminosity and their magnitude difference. Suppose Star A has a luminosity of LA and is at a distance of dA while Star B has a luminosity of LB and is at a distance of dB. What is the ratio of the brightness of star A (bA) to the brightne ...
review
... • The fastest pulsars, called millisecond pulsars, have periods of about 1/1000 second. The reason they pulse so much faster than (for example) the Crab and Vela pulsars is that they • A. were formed from much more massive stars than were the Crab and Vela pulsars, and were spun up more as their cor ...
... • The fastest pulsars, called millisecond pulsars, have periods of about 1/1000 second. The reason they pulse so much faster than (for example) the Crab and Vela pulsars is that they • A. were formed from much more massive stars than were the Crab and Vela pulsars, and were spun up more as their cor ...
Objectives
... • Less massive stars burn cooler and therefore can last longer • Our Sun will fuse hydrogen for about 10 billion years • Once a star’s Hydrogen supply runs out, fusion stops and the core begins to contract • At this time, the outer layers of hydrogen fuse at an incredible rate and the star expands t ...
... • Less massive stars burn cooler and therefore can last longer • Our Sun will fuse hydrogen for about 10 billion years • Once a star’s Hydrogen supply runs out, fusion stops and the core begins to contract • At this time, the outer layers of hydrogen fuse at an incredible rate and the star expands t ...
Astronomy Fall 2013 Final Exam History of Astronomy Know: speed
... light on earth you see a flash of light like a light house. 7. What produces a Type II supernova? Supermassive (greater than 12 solar masses) cloud starts fusing elements until it makes an iron core- then it recoils and explodes 8.Almost half of all known millisecond pulsars are found in what type o ...
... light on earth you see a flash of light like a light house. 7. What produces a Type II supernova? Supermassive (greater than 12 solar masses) cloud starts fusing elements until it makes an iron core- then it recoils and explodes 8.Almost half of all known millisecond pulsars are found in what type o ...
read in advance to speed your work
... stars in Orion (Table II). Plot the MV values (MV again is simply absolute magnitude, M, with the subscript indicating that the magnitude is measured in the visual part of the spectrum) against the spectral classification for the first 8 stars in Table II. Make carefully positioned round points just ...
... stars in Orion (Table II). Plot the MV values (MV again is simply absolute magnitude, M, with the subscript indicating that the magnitude is measured in the visual part of the spectrum) against the spectral classification for the first 8 stars in Table II. Make carefully positioned round points just ...
ASTRONOMY 1102 1
... in chapters 27, 28, 29 anmd 30 of Astronomy: from the Earth to the Universe. The test will consist as usual of two parts: multiple choice questions and problems. I give below an example of what the test will look like and a couple of examples of questions and problems. Review class notes: do not mem ...
... in chapters 27, 28, 29 anmd 30 of Astronomy: from the Earth to the Universe. The test will consist as usual of two parts: multiple choice questions and problems. I give below an example of what the test will look like and a couple of examples of questions and problems. Review class notes: do not mem ...
parallax in arc seconds
... member of a triple star system called the Alpha Centauri System. Proxima Centauri has the largest known stellar parallax at 0.76”. ...
... member of a triple star system called the Alpha Centauri System. Proxima Centauri has the largest known stellar parallax at 0.76”. ...
Chapter 15 (Star Lives)
... 1. Explain in terms of its role in stellar evolution why iron is much more common than any other heavy element. 2. With one exception, which are more common on the periodic table, odd or even numbered elements? Relate this to the red giant stage of stellar evolution. 3. If practically every star mus ...
... 1. Explain in terms of its role in stellar evolution why iron is much more common than any other heavy element. 2. With one exception, which are more common on the periodic table, odd or even numbered elements? Relate this to the red giant stage of stellar evolution. 3. If practically every star mus ...
CST Prep- 8th Grade Astronomy
... 17. How are the inner planets different from the outer planets? 18. Describe the difference between a solar eclipse and a lunar eclipse. 19. Describe the current theory of how Earth’s moon formed. 20. What causes phases of the moon? 21. What characteristics of Earth’s moon supports the current theor ...
... 17. How are the inner planets different from the outer planets? 18. Describe the difference between a solar eclipse and a lunar eclipse. 19. Describe the current theory of how Earth’s moon formed. 20. What causes phases of the moon? 21. What characteristics of Earth’s moon supports the current theor ...
Unit 60 to 79
... a. Have a companion star (be a member of a binary) b. Exceed its Chandrasekhar limit c. Have begun life as a high-mass star d. Continue the fusion cycle until its core is completely composed of iron 7) Which of the following events will not leave any remnant? a. Type I supernova b. Type II supernova ...
... a. Have a companion star (be a member of a binary) b. Exceed its Chandrasekhar limit c. Have begun life as a high-mass star d. Continue the fusion cycle until its core is completely composed of iron 7) Which of the following events will not leave any remnant? a. Type I supernova b. Type II supernova ...
The Galactic Super Star Cluster Westerlund 1
... times the mass of Orion. Therefore, we would have expected diffuse emission with L x = 3x10 35 erg s-1, which is five times more flux than we observe. We suggest that the IMF is nonstandard, as is often claimed for young, massive star clusters. ...
... times the mass of Orion. Therefore, we would have expected diffuse emission with L x = 3x10 35 erg s-1, which is five times more flux than we observe. We suggest that the IMF is nonstandard, as is often claimed for young, massive star clusters. ...
Cygnus (constellation)

Cygnus /ˈsɪɡnəs/ is a northern constellation lying on the plane of the Milky Way, deriving its name from the Latinized Greek word for swan. The swan is one of the most recognizable constellations of the northern summer and autumn, it features a prominent asterism known as the Northern Cross (in contrast to the Southern Cross). Cygnus was among the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations.Cygnus contains Deneb, one of the brightest stars in the night sky and one corner of the Summer Triangle, as well as some notable X-ray sources and the giant stellar association of Cygnus OB2. One of the stars of this association, NML Cygni, is one of the largest stars currently known. The constellation is also home to Cygnus X-1, a distant X-ray binary containing a supergiant and unseen massive companion that was the first object widely held to be a black hole. Many star systems in Cygnus have known planets as a result of the Kepler Mission observing one patch of the sky, the patch is the area around Cygnus. In addition, most of the eastern part of Cygnus is dominated by the Hercules–Corona Borealis Great Wall, a giant galaxy filament that is the largest known structure in the observable universe; covering most of the northern sky.