Stars, Constellations, and Quasars
... and archaeological evidence such as Stonehenge points to these early studies of astronomy. Ancient cultures also developed elaborate mythologies around stars and constellations and gave them names, some of which are still in use today. ...
... and archaeological evidence such as Stonehenge points to these early studies of astronomy. Ancient cultures also developed elaborate mythologies around stars and constellations and gave them names, some of which are still in use today. ...
The Electromagnetic Spectrum
... • Without telescopes you cannot objects with magnitudes over 6. ...
... • Without telescopes you cannot objects with magnitudes over 6. ...
Zairamink_Lifecycle of a Star
... about 1.5 solar masses and less than 5 times the mass of the sun. If you have some where around that mass then after the super nova the protons and electrons of atoms are forced together into neutrons. When neutron stars form, they maintain the momentum of the entire star, but now they're just a few ...
... about 1.5 solar masses and less than 5 times the mass of the sun. If you have some where around that mass then after the super nova the protons and electrons of atoms are forced together into neutrons. When neutron stars form, they maintain the momentum of the entire star, but now they're just a few ...
Document
... Aquarii is an example of this class. Amplitudes and light-curve shapes generally vary and periods are in the range of 35–1200 days.. • * SRB: Spectral-type (M, C, S or Me, Ce, Se) giants with poorly defined periodicity (mean cycles in the range of 20 to 2300 days) or with alternating intervals of pe ...
... Aquarii is an example of this class. Amplitudes and light-curve shapes generally vary and periods are in the range of 35–1200 days.. • * SRB: Spectral-type (M, C, S or Me, Ce, Se) giants with poorly defined periodicity (mean cycles in the range of 20 to 2300 days) or with alternating intervals of pe ...
Teacher`s Guide The Solar Empire: A Star is Born
... different masses evolve—solar mass stars, such as the sun; low-mass stars 0.8 or less than the sun’s mass; and higher-mass stars.) ...
... different masses evolve—solar mass stars, such as the sun; low-mass stars 0.8 or less than the sun’s mass; and higher-mass stars.) ...
Here you can get a Science reprint
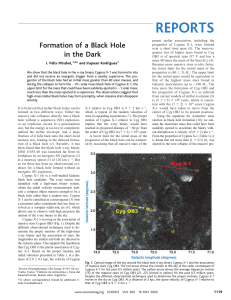
... X-1 was not through a Type II SN, where hydrogen envelopes are blown away and the ejected masses are in the range of 10 to 50 MJ (12), much greater than the upper limit for the mass that could have been suddenly ejected in Cygnus X-1. Alternatively, the core collapse could have occurred in a progeni ...
... X-1 was not through a Type II SN, where hydrogen envelopes are blown away and the ejected masses are in the range of 10 to 50 MJ (12), much greater than the upper limit for the mass that could have been suddenly ejected in Cygnus X-1. Alternatively, the core collapse could have occurred in a progeni ...
New Braunfels Astronomy Club
... Just to the northwest of Castor’s foot. About 2° southeast of δ, the waist of Pollux ...
... Just to the northwest of Castor’s foot. About 2° southeast of δ, the waist of Pollux ...
That is an irrelevant question, Ms Gajda, there was no
... 15. Thinking critically – why might a cooler star appear to be brighter than a hotter star? That cooler star could be bigger than the hotter star therefore it would appear brighter from Earth. The cooler star could also be closer than the hotter star. 16. Out of which material do stars begin to form ...
... 15. Thinking critically – why might a cooler star appear to be brighter than a hotter star? That cooler star could be bigger than the hotter star therefore it would appear brighter from Earth. The cooler star could also be closer than the hotter star. 16. Out of which material do stars begin to form ...
Star in a Box Worksheet - Beginning with solutions
... 1. What stages of their lives are the two stars in? Deneb is between the main sequence and the Hertzsprung Gap. Betelgeuse is between the Hertzsprung Gap and core helium burning. 2. How long does each star have to live? D eneb has about 1 million years left to live and Betelgeuse has about 400 th ...
... 1. What stages of their lives are the two stars in? Deneb is between the main sequence and the Hertzsprung Gap. Betelgeuse is between the Hertzsprung Gap and core helium burning. 2. How long does each star have to live? D eneb has about 1 million years left to live and Betelgeuse has about 400 th ...
No Slide Title
... Parallax: the apparent shift in the position of an object due to the movement of the observer. Remember looking at your finger through the left and then right eye? One parsec is the distance an object must be in order to have a parallax of one arc second. One parsec = 3.3 light years Alpha Centauri ...
... Parallax: the apparent shift in the position of an object due to the movement of the observer. Remember looking at your finger through the left and then right eye? One parsec is the distance an object must be in order to have a parallax of one arc second. One parsec = 3.3 light years Alpha Centauri ...
Astronomy and Space articles
... The Brightest Star in the Night Sky Since writing recently about the first star to become visible in the evenings, which at this time of the year is Sirius, I have had a few questions about that star, and why it is so bright. Sirius is a brilliant star, visible high in our northern evening sky. It i ...
... The Brightest Star in the Night Sky Since writing recently about the first star to become visible in the evenings, which at this time of the year is Sirius, I have had a few questions about that star, and why it is so bright. Sirius is a brilliant star, visible high in our northern evening sky. It i ...
Lecture 5
... Mass-Luminosity Relation for MainSequence Stars • Main sequence stars are stars like the Sun but with different masses • The mass-luminosity relation expresses a direct correlation between mass and luminosity for main-sequence stars • The greater the mass of a main-sequence star, the greater its lu ...
... Mass-Luminosity Relation for MainSequence Stars • Main sequence stars are stars like the Sun but with different masses • The mass-luminosity relation expresses a direct correlation between mass and luminosity for main-sequence stars • The greater the mass of a main-sequence star, the greater its lu ...
_____ 1. Which of the following statements is NOT true about stars
... ___________________ once it has used up all of its hydrogen. The center of the star will _________________ as the atmosphere begins to grow large. The mass of the star will determine if it will be a red giant or a supergiant. 11. What is the difference between a red giant and a supergiant? _________ ...
... ___________________ once it has used up all of its hydrogen. The center of the star will _________________ as the atmosphere begins to grow large. The mass of the star will determine if it will be a red giant or a supergiant. 11. What is the difference between a red giant and a supergiant? _________ ...
the stars
... distinguish colors: only the brightest stars are sufficiently luminous to show their real color. Looking at the sky with a binocular or a telescope we see that stars have colors and that these colors can be put in a sequence: from blue to white, yellow, orange and red. Astronomers use spectra to stu ...
... distinguish colors: only the brightest stars are sufficiently luminous to show their real color. Looking at the sky with a binocular or a telescope we see that stars have colors and that these colors can be put in a sequence: from blue to white, yellow, orange and red. Astronomers use spectra to stu ...
AST 112 – Activity #4 The Stellar Magnitude System
... necessary. Hint: Also refer to Table 4-1 above. (a) Is star J further than, closer to, or equal to 10 pc distant? ...
... necessary. Hint: Also refer to Table 4-1 above. (a) Is star J further than, closer to, or equal to 10 pc distant? ...
Homework 4
... 1. If a protostar is forming out of a cold molecular cloud, how can its luminosity be upto one hundred times as large as the luminosity of the star it will become? ...
... 1. If a protostar is forming out of a cold molecular cloud, how can its luminosity be upto one hundred times as large as the luminosity of the star it will become? ...
Cygnus (constellation)

Cygnus /ˈsɪɡnəs/ is a northern constellation lying on the plane of the Milky Way, deriving its name from the Latinized Greek word for swan. The swan is one of the most recognizable constellations of the northern summer and autumn, it features a prominent asterism known as the Northern Cross (in contrast to the Southern Cross). Cygnus was among the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations.Cygnus contains Deneb, one of the brightest stars in the night sky and one corner of the Summer Triangle, as well as some notable X-ray sources and the giant stellar association of Cygnus OB2. One of the stars of this association, NML Cygni, is one of the largest stars currently known. The constellation is also home to Cygnus X-1, a distant X-ray binary containing a supergiant and unseen massive companion that was the first object widely held to be a black hole. Many star systems in Cygnus have known planets as a result of the Kepler Mission observing one patch of the sky, the patch is the area around Cygnus. In addition, most of the eastern part of Cygnus is dominated by the Hercules–Corona Borealis Great Wall, a giant galaxy filament that is the largest known structure in the observable universe; covering most of the northern sky.