8hrdiagram1s
... If you know the luminosity and you measure the flux you can find the distance (F = L/4pd2) Called spectroscopic parallax ...
... If you know the luminosity and you measure the flux you can find the distance (F = L/4pd2) Called spectroscopic parallax ...
PHYS 200 - Understanding the Universe
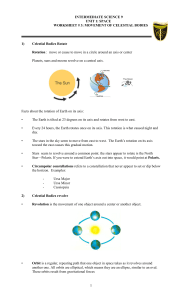
... • Report on: what makes up the solar system, what is the physical difference between planets and stars, whether stars live forever, and what makes up our Milky Way Galaxy. • Comprehend that cosmic bodies are always in motion relative to each other. That for example the relative motion of the Earth, ...
... • Report on: what makes up the solar system, what is the physical difference between planets and stars, whether stars live forever, and what makes up our Milky Way Galaxy. • Comprehend that cosmic bodies are always in motion relative to each other. That for example the relative motion of the Earth, ...
Reach for the Stars B
... 4. What will eventually cause the dust and gas in this DSO to dissipate? 5. Which DSO, a very bright radio source, is depicted in Image [3]? 6. Why might this DSO not have been visible in the past? 7. Which DSO, a massive star-forming region, is depicted in Image [4]? 8. [T10] What is the common nic ...
... 4. What will eventually cause the dust and gas in this DSO to dissipate? 5. Which DSO, a very bright radio source, is depicted in Image [3]? 6. Why might this DSO not have been visible in the past? 7. Which DSO, a massive star-forming region, is depicted in Image [4]? 8. [T10] What is the common nic ...
Slide 1
... Besides the usual stars, clusters of stars, galaxies, and clusters and super- clusters of galaxies, the universe contains a number of other interesting objects. Among these are stars known as red giants, white dwarfs, neutron stars, black holes and exploding stars called novae and supernovae. In ad ...
... Besides the usual stars, clusters of stars, galaxies, and clusters and super- clusters of galaxies, the universe contains a number of other interesting objects. Among these are stars known as red giants, white dwarfs, neutron stars, black holes and exploding stars called novae and supernovae. In ad ...
The Life of a Star - Department of Physics and Astronomy
... • When the central temperature of a red giant reaches about 100 million K, helium fusion begins in the core • This process, also called the triple alpha process, converts helium to carbon and oxygen ...
... • When the central temperature of a red giant reaches about 100 million K, helium fusion begins in the core • This process, also called the triple alpha process, converts helium to carbon and oxygen ...
Testing Your Sky
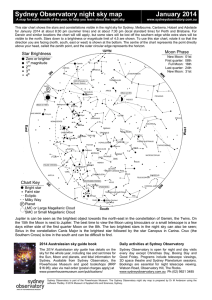
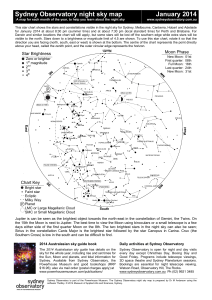
... There is another factor that must be kept in mind when it comes to viewing the heavens the transparency of the atmosphere. Even if the sky is totally dark, unless the sky permits the starlight to travel through it you won't be able to see the heavens very well. This is akin to viewing the sky throug ...
... There is another factor that must be kept in mind when it comes to viewing the heavens the transparency of the atmosphere. Even if the sky is totally dark, unless the sky permits the starlight to travel through it you won't be able to see the heavens very well. This is akin to viewing the sky throug ...
The Night Sky This Month - Usk Astronomical Society
... before reaching Pleiades. The asterism is known as the Hyades, and is the nearest open cluster to us. The brightest star in the constellation, the red giant star Aldebaran, is prominent in the vee and is described as the right eye of the bull, even though its name means the ‘follower’ of the Pleiade ...
... before reaching Pleiades. The asterism is known as the Hyades, and is the nearest open cluster to us. The brightest star in the constellation, the red giant star Aldebaran, is prominent in the vee and is described as the right eye of the bull, even though its name means the ‘follower’ of the Pleiade ...
File - Mr. Fifield`s Corner
... As the earth revolves around the Sun, it appears that the sun is moving against the background stars. the Sun follows the same path through the sky every day. We call this path the ecliptic. Along this path lie the 12 zodiacal constellations ...
... As the earth revolves around the Sun, it appears that the sun is moving against the background stars. the Sun follows the same path through the sky every day. We call this path the ecliptic. Along this path lie the 12 zodiacal constellations ...
The Sun - Hicksville Public Schools
... weeks or months. During this short interval, a supernova can radiate as much energy as the Sun would emit over 10 billion years. The explosion expels much or all of a star's material at high velocity, driving a shock wave into the surrounding interstellar medium, where it sweeps up an expanding shel ...
... weeks or months. During this short interval, a supernova can radiate as much energy as the Sun would emit over 10 billion years. The explosion expels much or all of a star's material at high velocity, driving a shock wave into the surrounding interstellar medium, where it sweeps up an expanding shel ...
Skills Worksheet
... astronomers can calculate the temperature of a star by measuring its color. The color of a star is determined by its chemical composition. Each element gives off a specific light pattern that varies with temperature. To calculate star temperatures, astronomers use a spectrophotometer—an instrument t ...
... astronomers can calculate the temperature of a star by measuring its color. The color of a star is determined by its chemical composition. Each element gives off a specific light pattern that varies with temperature. To calculate star temperatures, astronomers use a spectrophotometer—an instrument t ...
Topic E: Astrophysics E1 Introduction to the Universe.
... This means that depending on it’s location in it’s orbit, it will feel more or less pull from the Sun This pulls on the Earths axis of rotation and makes it wooble. This is technically called _______________. This means that the “North Star” won’t always be the north star. Period – _______ ...
... This means that depending on it’s location in it’s orbit, it will feel more or less pull from the Sun This pulls on the Earths axis of rotation and makes it wooble. This is technically called _______________. This means that the “North Star” won’t always be the north star. Period – _______ ...
stars - Chatt
... out of fuel. • When it “dies” it will become a white dwarf. • Our Sun is bigger than 95% of the stars in the Universe. • The Size Of Our World ...
... out of fuel. • When it “dies” it will become a white dwarf. • Our Sun is bigger than 95% of the stars in the Universe. • The Size Of Our World ...
November 2013 - Pomona Valley Amateur Astronomers
... that the Claremont Library Telescopes are doing well. The Riverside Astronomical Society is looking for Volunteers and a Board member for next May's RTMC. Lee Collins followed with his “What's Up” segment on Novas and Supernovas. Tycho Brahe saw a supernova that was brighter than Venus in 1572. Thir ...
... that the Claremont Library Telescopes are doing well. The Riverside Astronomical Society is looking for Volunteers and a Board member for next May's RTMC. Lee Collins followed with his “What's Up” segment on Novas and Supernovas. Tycho Brahe saw a supernova that was brighter than Venus in 1572. Thir ...
Introduction to the Earth
... distance measurement called the Light- year 1 light-year is the distance light travels in one ...
... distance measurement called the Light- year 1 light-year is the distance light travels in one ...
A tour of the solar system.
... Chamberlin (1900) – A star passed close to Sun, pulling away huge filaments of material. Problems: such events are extremely rare. Also material is so hot that it would dissipate into space and not accrete. ...
... Chamberlin (1900) – A star passed close to Sun, pulling away huge filaments of material. Problems: such events are extremely rare. Also material is so hot that it would dissipate into space and not accrete. ...
Star Formation
... fusion. They continue to cool, eventually becoming compact, dark, cold fragments of unburned matter • They are known as brown dwarfs ...
... fusion. They continue to cool, eventually becoming compact, dark, cold fragments of unburned matter • They are known as brown dwarfs ...
Cygnus (constellation)

Cygnus /ˈsɪɡnəs/ is a northern constellation lying on the plane of the Milky Way, deriving its name from the Latinized Greek word for swan. The swan is one of the most recognizable constellations of the northern summer and autumn, it features a prominent asterism known as the Northern Cross (in contrast to the Southern Cross). Cygnus was among the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations.Cygnus contains Deneb, one of the brightest stars in the night sky and one corner of the Summer Triangle, as well as some notable X-ray sources and the giant stellar association of Cygnus OB2. One of the stars of this association, NML Cygni, is one of the largest stars currently known. The constellation is also home to Cygnus X-1, a distant X-ray binary containing a supergiant and unseen massive companion that was the first object widely held to be a black hole. Many star systems in Cygnus have known planets as a result of the Kepler Mission observing one patch of the sky, the patch is the area around Cygnus. In addition, most of the eastern part of Cygnus is dominated by the Hercules–Corona Borealis Great Wall, a giant galaxy filament that is the largest known structure in the observable universe; covering most of the northern sky.