mslien~1
... From above the Jeans criterion can be derived as M c M J where the Jeans mass MJ is given by the RHS of ...
... From above the Jeans criterion can be derived as M c M J where the Jeans mass MJ is given by the RHS of ...
HR Diagram and Life of a star
... temp This means that they are very large and can range in size from 100-1000 times the size of the sun GIANTS- large bright stars a bit smaller and fainter than Super giants Super giants in the Red temp range tend to be in their last stages of life. They are out of hydrogen and are now fusing Helium ...
... temp This means that they are very large and can range in size from 100-1000 times the size of the sun GIANTS- large bright stars a bit smaller and fainter than Super giants Super giants in the Red temp range tend to be in their last stages of life. They are out of hydrogen and are now fusing Helium ...
Stars
... size of the orbits yield the sum of the masses, while the relative distance of each star from the center of mass yields the ratio of the masses. •The ratio and sum provide each mass individually. ...
... size of the orbits yield the sum of the masses, while the relative distance of each star from the center of mass yields the ratio of the masses. •The ratio and sum provide each mass individually. ...
Astronomy 103 Exam 2 Review
... If black holes emit no light, how can we observe them? Which of the following observaLon methods is not valid? A. Ma=er pulled off a companion star emits a characterisLc X‐ ray spectrum as it falls toward the black hole. B. Companion stars suddenly disappear from view as they plunge into the bl ...
... If black holes emit no light, how can we observe them? Which of the following observaLon methods is not valid? A. Ma=er pulled off a companion star emits a characterisLc X‐ ray spectrum as it falls toward the black hole. B. Companion stars suddenly disappear from view as they plunge into the bl ...
stars - science1d
... the swan-shaped constellation known as Cygnus? 6. Is the star Aldebaran located east or west of Betelgeuse? 7. What is the name of the star cluster located midway between the constellations of Taurus and Perseus? 8. What large star seems to form the right foot of the constellation commonly referred ...
... the swan-shaped constellation known as Cygnus? 6. Is the star Aldebaran located east or west of Betelgeuse? 7. What is the name of the star cluster located midway between the constellations of Taurus and Perseus? 8. What large star seems to form the right foot of the constellation commonly referred ...
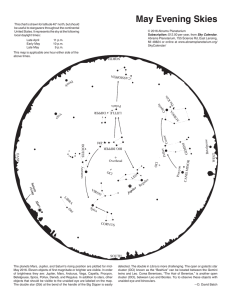
May Evening Skies
... The planets Mars, Jupiter, and Saturn's rising position are plotted for midMay 2016. Eleven objects of first magnitude or brighter are visible. In order of brightness they are: Jupiter, Mars, Arcturus, Vega, Capella, Procyon, Betelgeuse, Spica, Pollux, Deneb, and Regulus. In addition to stars, other ...
... The planets Mars, Jupiter, and Saturn's rising position are plotted for midMay 2016. Eleven objects of first magnitude or brighter are visible. In order of brightness they are: Jupiter, Mars, Arcturus, Vega, Capella, Procyon, Betelgeuse, Spica, Pollux, Deneb, and Regulus. In addition to stars, other ...
The Lives of Stars
... Astronomers speculate that stars form from gas and dust clouds called nebulae Gravity pulls the material togethe Accumulating gas increases temperature At 10,000,000 degrees nuclear fusion begins (transformation of hydrogen into helium) ...
... Astronomers speculate that stars form from gas and dust clouds called nebulae Gravity pulls the material togethe Accumulating gas increases temperature At 10,000,000 degrees nuclear fusion begins (transformation of hydrogen into helium) ...
Stars
... The center of our galaxy is also a copious source of x-rays and appears to be extremely massive. Stars in the Milky Way orbit around an unseen central object. Analysis of the orbital velocities of the stars about the center of the galaxy (using Kepler’s 3rd law) imply a mass of 2.6106 solar masses ...
... The center of our galaxy is also a copious source of x-rays and appears to be extremely massive. Stars in the Milky Way orbit around an unseen central object. Analysis of the orbital velocities of the stars about the center of the galaxy (using Kepler’s 3rd law) imply a mass of 2.6106 solar masses ...
Life Cycles of Stars
... megatons/second • Let’s relate that to human scales. What would that be at one kilometer distance? • 90 x 1015 tons/(150 x 106km)2 = 4 tons • Picture a truckload of explosives a km away giving off a one-second burst of heat and light to rival the Sun ...
... megatons/second • Let’s relate that to human scales. What would that be at one kilometer distance? • 90 x 1015 tons/(150 x 106km)2 = 4 tons • Picture a truckload of explosives a km away giving off a one-second burst of heat and light to rival the Sun ...
10 relativity, black holes_
... How can we see something that emits no light? Look for binary systems Make sure candidate is not a neutron star! ...
... How can we see something that emits no light? Look for binary systems Make sure candidate is not a neutron star! ...
AST121 Introduction to Astronomy
... activity has increased significantly. The Sun attains its expected sunspot maximum in the year 2000. These images are captured using Fe IX-X 171 Å emission showing the solar corona at a temperature of about 1.3 million K. Many more sunspots, solar flares, and coronal mass ejections occur during the ...
... activity has increased significantly. The Sun attains its expected sunspot maximum in the year 2000. These images are captured using Fe IX-X 171 Å emission showing the solar corona at a temperature of about 1.3 million K. Many more sunspots, solar flares, and coronal mass ejections occur during the ...
Parallax - High Point University
... activity has increased significantly. The Sun attains its expected sunspot maximum in the year 2000. These images are captured using Fe IX-X 171 Å emission showing the solar corona at a temperature of about 1.3 million K. Many more sunspots, solar flares, and coronal mass ejections occur during the ...
... activity has increased significantly. The Sun attains its expected sunspot maximum in the year 2000. These images are captured using Fe IX-X 171 Å emission showing the solar corona at a temperature of about 1.3 million K. Many more sunspots, solar flares, and coronal mass ejections occur during the ...
Reading Preview
... A star’s ________ gives clues about the star’s temperature. The coolest stars appear ________. The hottest stars appear ________. Very large stars are called ________ stars or ____________ stars. Our sun is a medium sized ________. Most stars are ________ than the sun. White dwarf stars are abou ...
... A star’s ________ gives clues about the star’s temperature. The coolest stars appear ________. The hottest stars appear ________. Very large stars are called ________ stars or ____________ stars. Our sun is a medium sized ________. Most stars are ________ than the sun. White dwarf stars are abou ...
Skymapper and Kepler K2: Finding the Origin of Hot Gas Giants
... determine which stars are young. • Data/pretty images prior to May 1 would really help the proposal for K2 targets! • This is standard “fast” survey data. ...
... determine which stars are young. • Data/pretty images prior to May 1 would really help the proposal for K2 targets! • This is standard “fast” survey data. ...
Presentation for perspective graduate students 2006
... Colors and spectral types measure a star’s temperature The Hertzsprung-Russell (H-R) diagram is a graph plotting luminosity vs temperature • Most stars belong to the main sequence. Other important classes are giants, supergiants and white dwarfs. • Spectral typing can be used to determine distances ...
... Colors and spectral types measure a star’s temperature The Hertzsprung-Russell (H-R) diagram is a graph plotting luminosity vs temperature • Most stars belong to the main sequence. Other important classes are giants, supergiants and white dwarfs. • Spectral typing can be used to determine distances ...
$doc.title
... 2a. Mark and label the Sun (spectral type=G2V, MV = 4.83, B-‐V=+0.66) and the star Vega (spectral type: A0V, MV = 0.5, B-‐V=0.0) in the HR diagram. [Assume the tick marks on the lower horizontal ...
... 2a. Mark and label the Sun (spectral type=G2V, MV = 4.83, B-‐V=+0.66) and the star Vega (spectral type: A0V, MV = 0.5, B-‐V=0.0) in the HR diagram. [Assume the tick marks on the lower horizontal ...
Astronomy 1 – Winter 2011
... Colors and spectral types measure a star’s temperature The Hertzsprung-Russell (H-R) diagram is a graph plotting luminosity vs temperature • Most stars belong to the main sequence. Other important classes are giants, supergiants and white dwarfs. • Spectral typing can be used to determine distance ...
... Colors and spectral types measure a star’s temperature The Hertzsprung-Russell (H-R) diagram is a graph plotting luminosity vs temperature • Most stars belong to the main sequence. Other important classes are giants, supergiants and white dwarfs. • Spectral typing can be used to determine distance ...
Mon Oct 22, 2012 MOON IN CAPRICORNUS The moon is waxing
... The moon is in its waxing gibbous phase, and has entered a part of the sky known as “the sea.” A large part of the sky has been designated as such because of all the watery constellations found there. In the zodiac there is Capricornus the Sea Goat, followed to the east by Aquarius, the water carrie ...
... The moon is in its waxing gibbous phase, and has entered a part of the sky known as “the sea.” A large part of the sky has been designated as such because of all the watery constellations found there. In the zodiac there is Capricornus the Sea Goat, followed to the east by Aquarius, the water carrie ...
Lecture 2+3 - University of Texas Astronomy Home Page
... As we move away from the photosphere (solar surface) temperature suddenly start to go up again…. Corona at T=10^6 K emits most of Sun’s X-rays ...
... As we move away from the photosphere (solar surface) temperature suddenly start to go up again…. Corona at T=10^6 K emits most of Sun’s X-rays ...
Cygnus (constellation)

Cygnus /ˈsɪɡnəs/ is a northern constellation lying on the plane of the Milky Way, deriving its name from the Latinized Greek word for swan. The swan is one of the most recognizable constellations of the northern summer and autumn, it features a prominent asterism known as the Northern Cross (in contrast to the Southern Cross). Cygnus was among the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations.Cygnus contains Deneb, one of the brightest stars in the night sky and one corner of the Summer Triangle, as well as some notable X-ray sources and the giant stellar association of Cygnus OB2. One of the stars of this association, NML Cygni, is one of the largest stars currently known. The constellation is also home to Cygnus X-1, a distant X-ray binary containing a supergiant and unseen massive companion that was the first object widely held to be a black hole. Many star systems in Cygnus have known planets as a result of the Kepler Mission observing one patch of the sky, the patch is the area around Cygnus. In addition, most of the eastern part of Cygnus is dominated by the Hercules–Corona Borealis Great Wall, a giant galaxy filament that is the largest known structure in the observable universe; covering most of the northern sky.