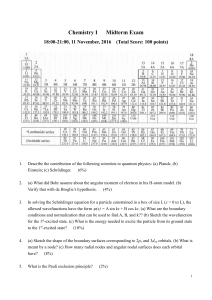
Chemistry I Midterm Exam
... In solving the Schrödinger equation for a particle constrained in a box of size L (x = 0 to L), the allowed wavefunctions have the form (x) = A sin kx + B cos kx. (a) What are the boundary conditions and normalization that can be used to find A, B, and k?? (b) Sketch the wavefunction for the 1st-ex ...
... In solving the Schrödinger equation for a particle constrained in a box of size L (x = 0 to L), the allowed wavefunctions have the form (x) = A sin kx + B cos kx. (a) What are the boundary conditions and normalization that can be used to find A, B, and k?? (b) Sketch the wavefunction for the 1st-ex ...
Quantum Mechanical Model
... Two lobes along the z axis and a belt centered in the xy plane – dz2 ...
... Two lobes along the z axis and a belt centered in the xy plane – dz2 ...
Document
... Coupling of electronic and nuclear motion – Hund’s cases • Coupling between various angular momentum vectors – Gyroscopic forces disturb orbital motion of electrons – Internal magnetic fields from the rotation of nuclei couple with the electron spin ...
... Coupling of electronic and nuclear motion – Hund’s cases • Coupling between various angular momentum vectors – Gyroscopic forces disturb orbital motion of electrons – Internal magnetic fields from the rotation of nuclei couple with the electron spin ...
Quantum Model Worksheet
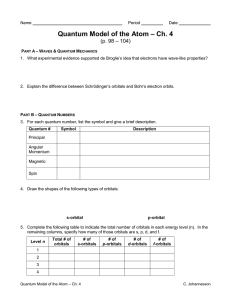
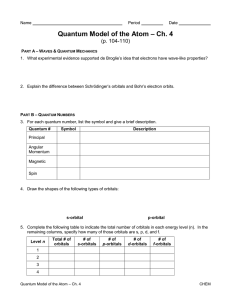
... PART A – WAVES & QUANTUM MECHANICS 1. What experimental evidence supported de Broglie’s idea that electrons have wave-like properties? ...
... PART A – WAVES & QUANTUM MECHANICS 1. What experimental evidence supported de Broglie’s idea that electrons have wave-like properties? ...
Quantum Model Worksheet
... PART A – WAVES & QUANTUM MECHANICS 1. What experimental evidence supported de Broglie’s idea that electrons have wave-like properties? ...
... PART A – WAVES & QUANTUM MECHANICS 1. What experimental evidence supported de Broglie’s idea that electrons have wave-like properties? ...
Energy levels of various orbitals MEMORIZE ! 1s < 2s < 2p < 3s < 3p
... Probability of finding an electron depends only on the distance of the electron from the nucleus Differences among s orbitals in different shells are: - size increases in successively higher shells - electron distribution in outer s oribtals have region of max. probability separated by a node (a sur ...
... Probability of finding an electron depends only on the distance of the electron from the nucleus Differences among s orbitals in different shells are: - size increases in successively higher shells - electron distribution in outer s oribtals have region of max. probability separated by a node (a sur ...
PowerPoint
... The volume around the nucleus where the electron appears 90-95% of the time The Pauli principle No two electrons in an atom may have identical sets of four quantum numbers ...
... The volume around the nucleus where the electron appears 90-95% of the time The Pauli principle No two electrons in an atom may have identical sets of four quantum numbers ...
The Quantum Mechanical Picture of the Atom
... Orbital The volume around the nucleus where the electron appears 90-95% of the time The Pauli principle No two electrons in an atom may have identical sets of four quantum numbers ...
... Orbital The volume around the nucleus where the electron appears 90-95% of the time The Pauli principle No two electrons in an atom may have identical sets of four quantum numbers ...
Atomic Orbitals and quantum numbers
... •Therefore, on any given energy level, there can be up to 1s orbital, 3p orbitals, 5d orbitals, and 7f orbitals. ...
... •Therefore, on any given energy level, there can be up to 1s orbital, 3p orbitals, 5d orbitals, and 7f orbitals. ...
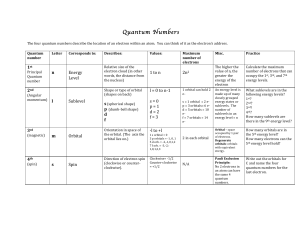
Quantum Numbers Handout File
... The!higher!the! value!of!n,!the! greater!the! energy!of!the! electron! ...
... The!higher!the! value!of!n,!the! greater!the! energy!of!the! electron! ...
Exam and Study Notes
... o The Aufbau Principle (electrons start from the lowest energy) “The building up principle” The Aufbau Principle states that the to fill the 3d subshell, the 4s subshell must have 2 electrons in the subshell first o Pauli Exclusion Principle(Opposite spins) No two electron can have the same sp ...
... o The Aufbau Principle (electrons start from the lowest energy) “The building up principle” The Aufbau Principle states that the to fill the 3d subshell, the 4s subshell must have 2 electrons in the subshell first o Pauli Exclusion Principle(Opposite spins) No two electron can have the same sp ...
The Modern Atomic Model
... •Energy levels contain electrons. •Electrons travel around the nucleus. •Different orbitals varied by different quantum (energy). •Gaps between energy levels were not equal. ...
... •Energy levels contain electrons. •Electrons travel around the nucleus. •Different orbitals varied by different quantum (energy). •Gaps between energy levels were not equal. ...
Tutorial 7
... Energy of the transition from the first energy level to the third energy level in a hydrogen atom. ...
... Energy of the transition from the first energy level to the third energy level in a hydrogen atom. ...
Energy levels of various orbitals MEMORIZE ! 1s < 2s < 2p < 3s < 3p
... Energy levels of various orbitals For hydrogen, energy level depend only on n For multielectron atoms (all others) - energy levels depend on both n and l A diagram which shows the orbital energy levels for both is shown below. ...
... Energy levels of various orbitals For hydrogen, energy level depend only on n For multielectron atoms (all others) - energy levels depend on both n and l A diagram which shows the orbital energy levels for both is shown below. ...
Hybridization of atomic orbitals In general VSEPR predicts the
... Hybridization of atomic orbitals In general VSEPR predicts the shape of molecules and ions accurately CH4 : tetrahedral Four equal bonds with equal HCH angles A covalent bond is formed by sharing two electrons by two atoms Imagine an orbital (containing 1 electron) from one atom overlaps with an orb ...
... Hybridization of atomic orbitals In general VSEPR predicts the shape of molecules and ions accurately CH4 : tetrahedral Four equal bonds with equal HCH angles A covalent bond is formed by sharing two electrons by two atoms Imagine an orbital (containing 1 electron) from one atom overlaps with an orb ...
4 Arrangement of Electrons
... o Discuss the dual wave-particle nature of light o Discuss the significance of the photoelectric effect and the line-emission spectrum of hydrogen to the development of the atomic model o Describe the Bohr model of the hydrogen atom o Discuss Louis de Broglie’s role in the development of the quantum ...
... o Discuss the dual wave-particle nature of light o Discuss the significance of the photoelectric effect and the line-emission spectrum of hydrogen to the development of the atomic model o Describe the Bohr model of the hydrogen atom o Discuss Louis de Broglie’s role in the development of the quantum ...
Molecular orbital

In chemistry, a molecular orbital (or MO) is a mathematical function describing the wave-like behavior of an electron in a molecule. This function can be used to calculate chemical and physical properties such as the probability of finding an electron in any specific region. The term orbital was introduced by Robert S. Mulliken in 1932 as an abbreviation for one-electron orbital wave function. At an elementary level, it is used to describe the region of space in which the function has a significant amplitude. Molecular orbitals are usually constructed by combining atomic orbitals or hybrid orbitals from each atom of the molecule, or other molecular orbitals from groups of atoms. They can be quantitatively calculated using the Hartree–Fock or self-consistent field (SCF) methods.