Final Review Answers
... 1) Define the following terms: (Look up) a) valence electrons b) octet rule c) malleable d) ductile 2) Differentiate between ionic, covalent, and metallic bonding in terms of electron location and types of atoms combined. Ionic - M/NM, e- donated; Covalent - NM, e- shared; Metallic - M, valence e- m ...
... 1) Define the following terms: (Look up) a) valence electrons b) octet rule c) malleable d) ductile 2) Differentiate between ionic, covalent, and metallic bonding in terms of electron location and types of atoms combined. Ionic - M/NM, e- donated; Covalent - NM, e- shared; Metallic - M, valence e- m ...
Group IV Elements
... Si, Ge, Sn,Pb Si most abundant element in Nature afdter O Ge, Sn, Pb are rare elements Sn,Pb have been known since long time, because they can be just melted out of their minerals Ge was discovered after its existance has been predicted. It is purified from coal and zinc ore concentrates ...
... Si, Ge, Sn,Pb Si most abundant element in Nature afdter O Ge, Sn, Pb are rare elements Sn,Pb have been known since long time, because they can be just melted out of their minerals Ge was discovered after its existance has been predicted. It is purified from coal and zinc ore concentrates ...
1. Which of the following statements best describes the
... Gas particles are packed closely together, but have some ability to move. ...
... Gas particles are packed closely together, but have some ability to move. ...
Labs - newtunings.com
... 5.2i When a bond is broken, energy is absorbed. When a bond is formed, energy is released. 5.2j Electronegativity indicates how strongly an atom of an element attracts electrons in a chemical bond. Electronegativity values are assigned according to arbitrary scales. 5.2k The electronegativity differ ...
... 5.2i When a bond is broken, energy is absorbed. When a bond is formed, energy is released. 5.2j Electronegativity indicates how strongly an atom of an element attracts electrons in a chemical bond. Electronegativity values are assigned according to arbitrary scales. 5.2k The electronegativity differ ...
Chem vocab quiz definitons
... Liquid is the state of matter that is described as having a definite volume but an indefinite shape. Gas is the state of matter that is described as having no definite shape, or volume. Solid is the state of matter that is described as having a definite shape and volume. Viscosity is a property of l ...
... Liquid is the state of matter that is described as having a definite volume but an indefinite shape. Gas is the state of matter that is described as having no definite shape, or volume. Solid is the state of matter that is described as having a definite shape and volume. Viscosity is a property of l ...
2 - grade11chemistry
... • Absences for an evaluation will result in a mark of ZERO unless arrangements have been made with your teacher prior to the evaluation. • Do NOT expect to show up the next day with a note of any kind and be able to write the test/quiz. • Projects/assignments are due on the given due dates. If there ...
... • Absences for an evaluation will result in a mark of ZERO unless arrangements have been made with your teacher prior to the evaluation. • Do NOT expect to show up the next day with a note of any kind and be able to write the test/quiz. • Projects/assignments are due on the given due dates. If there ...
Regents_Chem_Core_for_review
... increases. When an atom loses one or more electrons, it becomes a positive ion and its radius decreases. (5.2c) IV.7 When a bond is broken, energy is absorbed. When a bond is formed, energy is released. (5.2i) IV.8 Atoms attain a stable valence electron configuration by bonding with other atoms. Nob ...
... increases. When an atom loses one or more electrons, it becomes a positive ion and its radius decreases. (5.2c) IV.7 When a bond is broken, energy is absorbed. When a bond is formed, energy is released. (5.2i) IV.8 Atoms attain a stable valence electron configuration by bonding with other atoms. Nob ...
Section 13: Optical properties of solids
... Since a photon of visible light has a wavelength of order 5000 Å, the photon wave vector q is typically of order 105 cm-1. Typical Brillouin zone dimensions, on the other hand, are of order kF ~ 108 cm-1. Thus the term q in (23) can shift the wave vector k by only a fraction of a percent of the dime ...
... Since a photon of visible light has a wavelength of order 5000 Å, the photon wave vector q is typically of order 105 cm-1. Typical Brillouin zone dimensions, on the other hand, are of order kF ~ 108 cm-1. Thus the term q in (23) can shift the wave vector k by only a fraction of a percent of the dime ...
Arts and Sciences Program Chemistry Department Chemistry Placement Test
... Calculate the mass of the air contained in a room that measures 2.50 m 5.50 m 3.00 m (density of air = 1.29 g/dm3 at 25C). ...
... Calculate the mass of the air contained in a room that measures 2.50 m 5.50 m 3.00 m (density of air = 1.29 g/dm3 at 25C). ...
Things to Know to Pass the Chemistry Regents
... *Tables T and B 69. Combined gas law on Table T *If given STP, given temp and pressure (Table A) 70. Pressure and volume indirect, P up, V down (PVC pipe) 71. Temperature and pressure direct, T up, P up 72. Temperature and volume direct, T up, V up 73. Gases most ideal at high temp and low pressure ...
... *Tables T and B 69. Combined gas law on Table T *If given STP, given temp and pressure (Table A) 70. Pressure and volume indirect, P up, V down (PVC pipe) 71. Temperature and pressure direct, T up, P up 72. Temperature and volume direct, T up, V up 73. Gases most ideal at high temp and low pressure ...
Chemical Nomenclature (ionic compounds)
... d) The charge of the ion is always written as a superscript, above and to the right of the symbol for the element. i.e. Na+1 , F-1, Ca+2 e) The number of atoms of an element in a compound is written as a SUBSCRIPT, below and to the right of the symbol for the element. (ones, “1” are not used, but ar ...
... d) The charge of the ion is always written as a superscript, above and to the right of the symbol for the element. i.e. Na+1 , F-1, Ca+2 e) The number of atoms of an element in a compound is written as a SUBSCRIPT, below and to the right of the symbol for the element. (ones, “1” are not used, but ar ...
Chemistry Midterm Review 2006
... 13. What is the difference between a nonpolar covalent bond and a polar covalent bond? 14. What are the characteristics of a covalent and ionic compound? 15. Define chemical bond. What is a lone pair of electrons? 16. What is the difference between a single, double, and triple bond? 17. Draw Lewis d ...
... 13. What is the difference between a nonpolar covalent bond and a polar covalent bond? 14. What are the characteristics of a covalent and ionic compound? 15. Define chemical bond. What is a lone pair of electrons? 16. What is the difference between a single, double, and triple bond? 17. Draw Lewis d ...
CP Chemistry Final Exam Review Sheet
... 50. What is the octet rule? The octet rule states that atoms will gain, lose, or share electrons in order to get a full octet (8 e-) in the valence (outermost) shell of an atom. 51. An ion is a particle with an electrical charge created by the transfer (loss or gaining) of electrons. 52. What is a c ...
... 50. What is the octet rule? The octet rule states that atoms will gain, lose, or share electrons in order to get a full octet (8 e-) in the valence (outermost) shell of an atom. 51. An ion is a particle with an electrical charge created by the transfer (loss or gaining) of electrons. 52. What is a c ...
Physical Science - Edgemead High School
... through a conductor colliding with the particles of which the conductor (metal) is made and transferring kinetic energy. State and explain factors that affect the resistance of a given material i.e. temperature, length and thickness. Explain why a battery in a circuit goes flat eventually by ref ...
... through a conductor colliding with the particles of which the conductor (metal) is made and transferring kinetic energy. State and explain factors that affect the resistance of a given material i.e. temperature, length and thickness. Explain why a battery in a circuit goes flat eventually by ref ...
Resource for Final Exam Prep
... Photoelectric effect kinetic energy of ejected electron Uncertainty principle you can estimate accurately the position and the momentum of an electron at the same time Quantum numbers (n, l, ml, ms), what do they each define? Value of l for s, p, d and f orbitals Energies of different level depe ...
... Photoelectric effect kinetic energy of ejected electron Uncertainty principle you can estimate accurately the position and the momentum of an electron at the same time Quantum numbers (n, l, ml, ms), what do they each define? Value of l for s, p, d and f orbitals Energies of different level depe ...
final exam review packet
... Know Bohr’s model and how electrons behave, excite/ground state, atomic spectra Know quantum model: orbitals, sublevels, energy levels, # electrons Know the EMR spectrum, relative energy, wavelength and frequency Know relationship between energy, wavelength and frequency Be able to write electron co ...
... Know Bohr’s model and how electrons behave, excite/ground state, atomic spectra Know quantum model: orbitals, sublevels, energy levels, # electrons Know the EMR spectrum, relative energy, wavelength and frequency Know relationship between energy, wavelength and frequency Be able to write electron co ...
- gst boces
... *Tables T and B 69. Combined gas law on Table T *If given STP, given temp and pressure (Table A) 70. Pressure and volume indirect, P up, V down (PVC pipe) 71. Temperature and pressure direct, T up, P up 72. Temperature and volume direct, T up, V up 73. Gases most ideal at high temp and low pressure ...
... *Tables T and B 69. Combined gas law on Table T *If given STP, given temp and pressure (Table A) 70. Pressure and volume indirect, P up, V down (PVC pipe) 71. Temperature and pressure direct, T up, P up 72. Temperature and volume direct, T up, V up 73. Gases most ideal at high temp and low pressure ...
Chemistry Final Exam Review 2006-2007
... 23. List in order of strength of the following IMF : dipole-dipole forces, London Dispersion forces, and hydrogen bonding 24. Identify which ones have dipole-dipole forces? PBr3, N2, CF4, HBr, H2O 25. Identify which ones have London dispersion forces? , N2, CF4, HBr, SO2 26. Identify which ones have ...
... 23. List in order of strength of the following IMF : dipole-dipole forces, London Dispersion forces, and hydrogen bonding 24. Identify which ones have dipole-dipole forces? PBr3, N2, CF4, HBr, H2O 25. Identify which ones have London dispersion forces? , N2, CF4, HBr, SO2 26. Identify which ones have ...
C. Adding acid shifts the equilibrium to the right
... Chm.1.2.1 Compare (qualitatively) the relative strengths of ionic, covalent, and metallic bonds. Chm.1.2.2 Infer the type of bond and chemical formula formed between atoms. Chm.1.2.3 Compare inter- and intra- particle forces. Chm.1.2.4 Interpret the name and formula of compounds using IUPAC conventi ...
... Chm.1.2.1 Compare (qualitatively) the relative strengths of ionic, covalent, and metallic bonds. Chm.1.2.2 Infer the type of bond and chemical formula formed between atoms. Chm.1.2.3 Compare inter- and intra- particle forces. Chm.1.2.4 Interpret the name and formula of compounds using IUPAC conventi ...
3.091 – Introduction to Solid State Chemistry Lecture Notes No
... by electronic rearrangements must be in a lower energy state than the atoms were prior to interaction, prior to bond formation. Since atoms of each of the elements have different electronic structures, the variety of possible chemical bonds (differing from each other in at least some small way) is c ...
... by electronic rearrangements must be in a lower energy state than the atoms were prior to interaction, prior to bond formation. Since atoms of each of the elements have different electronic structures, the variety of possible chemical bonds (differing from each other in at least some small way) is c ...
Chemistry of Life
... • To do work or cause change • ____________________________: Energy is not created or destroyed it only changes forms • _______________(exothermic)- releasing of energy • _______________(endothermic)-absorption of energy • Activation energy: Energy needed to start the reaction • ____________: someth ...
... • To do work or cause change • ____________________________: Energy is not created or destroyed it only changes forms • _______________(exothermic)- releasing of energy • _______________(endothermic)-absorption of energy • Activation energy: Energy needed to start the reaction • ____________: someth ...
Chemical Bonding
... A bonding molecular orbital places a high electron charge density between the two nuclei. This reduces the repulsions between the positively charged nuclei, lowering the energy and increasing the stability of the molecule. An anti-bonding molecular orbital places a low electron charge density betwee ...
... A bonding molecular orbital places a high electron charge density between the two nuclei. This reduces the repulsions between the positively charged nuclei, lowering the energy and increasing the stability of the molecule. An anti-bonding molecular orbital places a low electron charge density betwee ...
Chemistry Mid-Term Review Sheet
... 48. What are the following groups called: Group 1, 2, 3 – 12, 17, and 18? 49. List the properties of metals, nonmetals, and metalloids. 50. What does each row on the periodic table represent? 51. How did Mendeleev arrange his periodic table? 52. How is the modern periodic table arranged? 53. What de ...
... 48. What are the following groups called: Group 1, 2, 3 – 12, 17, and 18? 49. List the properties of metals, nonmetals, and metalloids. 50. What does each row on the periodic table represent? 51. How did Mendeleev arrange his periodic table? 52. How is the modern periodic table arranged? 53. What de ...
Unit Description - Honors Chemistry
... Explain the origin of the atomic emission spectrum of an element, using Bohr’s hydrogen spectrum (5.1) Describe the quantum mechanical model of the atom (5.2) Describe Heisenberg’s Uncertainty Principle (5.2) Distinguish between an orbit and an orbital (5.2) Distinguish among principal ene ...
... Explain the origin of the atomic emission spectrum of an element, using Bohr’s hydrogen spectrum (5.1) Describe the quantum mechanical model of the atom (5.2) Describe Heisenberg’s Uncertainty Principle (5.2) Distinguish between an orbit and an orbital (5.2) Distinguish among principal ene ...
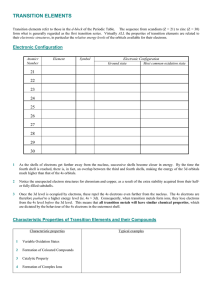
TRANSITION ELEMENTS
... Formation of Coloured Compounds Most of the compounds and complexes of transition elements are coloured. The colour of these compounds can often be related to incompletely filled d-orbitals in the transition metal ion. The outer electronic orbitals of transition metal ions have only small energy dif ...
... Formation of Coloured Compounds Most of the compounds and complexes of transition elements are coloured. The colour of these compounds can often be related to incompletely filled d-orbitals in the transition metal ion. The outer electronic orbitals of transition metal ions have only small energy dif ...