Chapter 4 Spectroscopy
... produces continuous spectrum • Low-density hot gas produces emission spectrum • Continuous spectrum incident on cool, thin gas produces absorption spectrum ...
... produces continuous spectrum • Low-density hot gas produces emission spectrum • Continuous spectrum incident on cool, thin gas produces absorption spectrum ...
R E V I E W -- P R A C T I C E E X A
... 79. The periodic law states that: a. The physical/chemical properties of the elements are periodic functions of their atomic number b. no two electrons with the same spin can be found in the same place at the same time. c. Electrons exhibit properties of both particles and waves. d. The chemical pro ...
... 79. The periodic law states that: a. The physical/chemical properties of the elements are periodic functions of their atomic number b. no two electrons with the same spin can be found in the same place at the same time. c. Electrons exhibit properties of both particles and waves. d. The chemical pro ...
The Basics - I`m a faculty member, and I need web space. What
... • Now all that is left to balance is the oxygen. There are 2 O on the reactant side and 7 on the product side. Our only source of oxygen is the O2. Any whole number we place in front of the O2 will result in an even number of atoms. The only way to balance the equation is to use a coefficient of 7/2 ...
... • Now all that is left to balance is the oxygen. There are 2 O on the reactant side and 7 on the product side. Our only source of oxygen is the O2. Any whole number we place in front of the O2 will result in an even number of atoms. The only way to balance the equation is to use a coefficient of 7/2 ...
1 - Cobb Learning
... the octet rule? (How many valence electrons do those atoms want to have?) A. 2 B. 18 C. 32 D. 8 11. What causes elements to bond? A. atomic number B. valence electrons C. atomic mass D. neutrons 12. From an element’s location on the periodic table, you can predict… A. its properties B. its chemical ...
... the octet rule? (How many valence electrons do those atoms want to have?) A. 2 B. 18 C. 32 D. 8 11. What causes elements to bond? A. atomic number B. valence electrons C. atomic mass D. neutrons 12. From an element’s location on the periodic table, you can predict… A. its properties B. its chemical ...
Dalton`s Atomic Theory
... c. The atoms of different elements differ in fundamental ways (e.g., different masses, different chemical behavior). d. Compounds form when atoms of different elements join together in simple whole number ratios. Thus, a given compound always contains the same relative number and types of atoms. e. ...
... c. The atoms of different elements differ in fundamental ways (e.g., different masses, different chemical behavior). d. Compounds form when atoms of different elements join together in simple whole number ratios. Thus, a given compound always contains the same relative number and types of atoms. e. ...
Summer Work
... 3. The number of protons in one atom of an element determines the atom’s __________________ , and the number of electrons determines ___________________ of an element. 4. The atomic number tells you the number of ______________________ in one atom of an element. It also tells you the number of _____ ...
... 3. The number of protons in one atom of an element determines the atom’s __________________ , and the number of electrons determines ___________________ of an element. 4. The atomic number tells you the number of ______________________ in one atom of an element. It also tells you the number of _____ ...
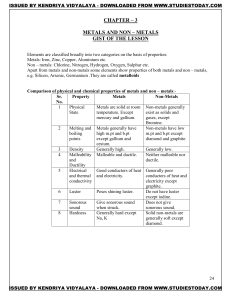
METALS AND NON – METALS Concepts
... Metals: Iron, Zinc, Copper, Aluminium etc. Non – metals: Chlorine, Nitrogen, Hydrogen, Oxygen, Sulphur etc. Apart from metals and non-metals some elements show properties of both metals and non – metals, e.g. Silicon, Arsenic, Germanium .They are called metalloids Comparison of physical and chemical ...
... Metals: Iron, Zinc, Copper, Aluminium etc. Non – metals: Chlorine, Nitrogen, Hydrogen, Oxygen, Sulphur etc. Apart from metals and non-metals some elements show properties of both metals and non – metals, e.g. Silicon, Arsenic, Germanium .They are called metalloids Comparison of physical and chemical ...
FIREWORKS EMC summary notes
... In a chemical reaction a new substance is always formed. Most chemical changes are not easily reversed; they are irreversible. In a physical change no new substance is formed. Melting and evaporation are examples of physical changes. Physical changes are usually reversible. You can tell that a react ...
... In a chemical reaction a new substance is always formed. Most chemical changes are not easily reversed; they are irreversible. In a physical change no new substance is formed. Melting and evaporation are examples of physical changes. Physical changes are usually reversible. You can tell that a react ...
Semester 2 Final Exam
... 54. Which of the following describes the bonds in a molecule of ethyne, C2H2? (A) 1 double bond, 2 single bonds. (B) 1 triple bond, 2 single bonds. (C) 2 double bonds, 1 single bond. (D) 3 single bonds. 55. The total number of dots drawn in the Lewis structure of nitrogen, N2, is (A) 5 (B) 10 (C) 14 ...
... 54. Which of the following describes the bonds in a molecule of ethyne, C2H2? (A) 1 double bond, 2 single bonds. (B) 1 triple bond, 2 single bonds. (C) 2 double bonds, 1 single bond. (D) 3 single bonds. 55. The total number of dots drawn in the Lewis structure of nitrogen, N2, is (A) 5 (B) 10 (C) 14 ...
CHEM 120 WEEK 11 LECTURES (INORGANIC WEEK 2) Dr. MD
... Contains only metals, apart from boron. Boron is also the only element which does not form a stable trication (B3+) again will have too high a charge density to be stable. Why do the other elements form tri-cations (M3+ )? Soln. √ Because they have the valence electronic configuration ns2np1 and ...
... Contains only metals, apart from boron. Boron is also the only element which does not form a stable trication (B3+) again will have too high a charge density to be stable. Why do the other elements form tri-cations (M3+ )? Soln. √ Because they have the valence electronic configuration ns2np1 and ...
Review Packet
... 28. Hugh was born 6.391875 X 103 days ago. How old (in years, with 1yr= 365.25 days) is Hugh? ...
... 28. Hugh was born 6.391875 X 103 days ago. How old (in years, with 1yr= 365.25 days) is Hugh? ...
CHEMISTRY: MIDTERM EXAM REVIEW SPRING 2013 Multiple
... ____ 27. What must be done to be certain that a chemical change has taken place? a. Demonstrate that a release of energy occurred after the change. b. Check for the production of bubbles before and after the change. c. Check the composition of the sample before and after the change. d. Demonstrate t ...
... ____ 27. What must be done to be certain that a chemical change has taken place? a. Demonstrate that a release of energy occurred after the change. b. Check for the production of bubbles before and after the change. c. Check the composition of the sample before and after the change. d. Demonstrate t ...
Name_____________________________________ Chemistry
... An example of a chemical change is a. sanding wood. c. milk going sour. b. melting ice. d. vaporizing gasoline. ____ 12. A physical change occurs when a a. peach spoils. c. bracelet turns your wrist green. b. copper bowl tarnishes. d. glue gun melts a glue stick. ____ 13. The state of matter in whic ...
... An example of a chemical change is a. sanding wood. c. milk going sour. b. melting ice. d. vaporizing gasoline. ____ 12. A physical change occurs when a a. peach spoils. c. bracelet turns your wrist green. b. copper bowl tarnishes. d. glue gun melts a glue stick. ____ 13. The state of matter in whic ...
Atoms, compounds and elements - Mrs. Tes de Luna`s Science Class
... ◦ The first part of his theory states that all matter is made of atoms, which are indivisible. ◦ The second part of the theory says all atoms of a given element are identical in mass and properties. ◦ The third part says compounds are combinations of two or more different types of atoms. ◦ The fourt ...
... ◦ The first part of his theory states that all matter is made of atoms, which are indivisible. ◦ The second part of the theory says all atoms of a given element are identical in mass and properties. ◦ The third part says compounds are combinations of two or more different types of atoms. ◦ The fourt ...
Unit 1 Review, pages 138–145
... (b) A periodic trend is a pattern in properties of elements that we observe as we move across a period on the periodic table. 33. The contribution to the periodic table made by Dobereiner was his early attempt to classify small groups of elements according to their properties. 34. If an atom has hig ...
... (b) A periodic trend is a pattern in properties of elements that we observe as we move across a period on the periodic table. 33. The contribution to the periodic table made by Dobereiner was his early attempt to classify small groups of elements according to their properties. 34. If an atom has hig ...
Chapter 4 The Structure of Matter
... • 5. Formula unit is the smallest ratio of ions in ionic compounds • a. Na+1Cl-1 or Ca+2F2-1 • b. When melted or dissolved in H2O ionic compounds will conduct electricity because the ions are free to move. • c. As solids the ions are locked so tightly that they do not conduct electricity. ...
... • 5. Formula unit is the smallest ratio of ions in ionic compounds • a. Na+1Cl-1 or Ca+2F2-1 • b. When melted or dissolved in H2O ionic compounds will conduct electricity because the ions are free to move. • c. As solids the ions are locked so tightly that they do not conduct electricity. ...
Semester 1 Study Guide – Chemistry
... 13. The quantity of heat required to change the temperature of 1g of a substance by 1 oC is defined as a. A joule b. Specific heat capacity c. A calorie d. Density 14. The specific heat capacity of iron is 0.45J/goC. How many joules of energy are needed to warm 1.50g of iron from 20.00oC to 29.00oC ...
... 13. The quantity of heat required to change the temperature of 1g of a substance by 1 oC is defined as a. A joule b. Specific heat capacity c. A calorie d. Density 14. The specific heat capacity of iron is 0.45J/goC. How many joules of energy are needed to warm 1.50g of iron from 20.00oC to 29.00oC ...
Atoms, Ions and Molecules
... Oxygen atoms easily gain two electrons. In this case the oxygen ion has 8 protons and 10 electrons so the overall charge is 8 – 1 0 = –2. Remember that neutrons have no electric charge so ...
... Oxygen atoms easily gain two electrons. In this case the oxygen ion has 8 protons and 10 electrons so the overall charge is 8 – 1 0 = –2. Remember that neutrons have no electric charge so ...
Lecture 21 revised (Slides) October 12
... • The occupied shell with the highest value of n is called the valence shell. When atoms undergo chemical change electrons in the valence shell can be lost or shared with other atoms. The valence shell can also pick up electrons. Atoms with similar chemical properties often have the “same” valence s ...
... • The occupied shell with the highest value of n is called the valence shell. When atoms undergo chemical change electrons in the valence shell can be lost or shared with other atoms. The valence shell can also pick up electrons. Atoms with similar chemical properties often have the “same” valence s ...
K,7th Grade Test Review: Atoms and Chemical Reactions PART
... 1. __________ is the smallest unit of an element that is still that element. 2. __________ is a substance that cannot be broken down into similar substances by physical or chemical changes. 3. Protons and neutrons have a __________ of 1 unit. Electrons have almost none. 4. An atom with more protons ...
... 1. __________ is the smallest unit of an element that is still that element. 2. __________ is a substance that cannot be broken down into similar substances by physical or chemical changes. 3. Protons and neutrons have a __________ of 1 unit. Electrons have almost none. 4. An atom with more protons ...
Periodic Table, Bonding, Reactions, and Moles
... 8. Explain, in terms of valence electrons, why the bonding in magnesium oxide, MgO, is similar to the bonding in barium chloride, BaCl2. 9. Identify the type of bonding between the atoms in an oxygen molecule. ...
... 8. Explain, in terms of valence electrons, why the bonding in magnesium oxide, MgO, is similar to the bonding in barium chloride, BaCl2. 9. Identify the type of bonding between the atoms in an oxygen molecule. ...
1 st Nine Weeks Study Guide for Chemistry
... E. How do you tell an element from a compound? Element is one type of atom, a compound is two or more elements chemically combined. F. What are physical properties? Give at least five examples. Have to do with appearance, density, malleable, ductile. Boiling point G. What are chemical properties? Gi ...
... E. How do you tell an element from a compound? Element is one type of atom, a compound is two or more elements chemically combined. F. What are physical properties? Give at least five examples. Have to do with appearance, density, malleable, ductile. Boiling point G. What are chemical properties? Gi ...