CHEMISTRY IM 06 SYLLABUS 1
... The Examination consists of one three-hour paper. The paper will be divided into three sections: Section A will contain between eight and ten compulsory questions of the fill-in type requiring short answers; Section B will consist of between four and sixcompulsory structured questions; Section C wil ...
... The Examination consists of one three-hour paper. The paper will be divided into three sections: Section A will contain between eight and ten compulsory questions of the fill-in type requiring short answers; Section B will consist of between four and sixcompulsory structured questions; Section C wil ...
Matter - Moodle
... help to ___________________and ______________________ substances • Characteristic Properties are the _______________or _____________________ characteristics the substance is known for Example: • Helium is light and non-flammable so it is good for _____________________ element A substance that cannot ...
... help to ___________________and ______________________ substances • Characteristic Properties are the _______________or _____________________ characteristics the substance is known for Example: • Helium is light and non-flammable so it is good for _____________________ element A substance that cannot ...
Midterm Review Answers
... Questions 52-53nrefer to the following types of energy A) Activation energy B) Free energy C) Ionization energy D) Kinetic energy E) Lattice energy 52. The energy required to convert a ground-state atom in the gas phase to a gaseous positive ion. C 53. The energy released when gas phase ions bond t ...
... Questions 52-53nrefer to the following types of energy A) Activation energy B) Free energy C) Ionization energy D) Kinetic energy E) Lattice energy 52. The energy required to convert a ground-state atom in the gas phase to a gaseous positive ion. C 53. The energy released when gas phase ions bond t ...
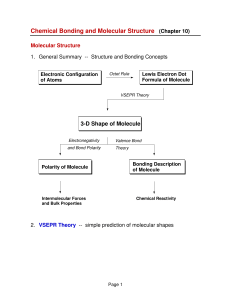
3-D Shape of Molecule
... 2. Molecular Orbitals for simple diatomic molecules (H2 and He2) in H2 the 1s atomic orbitals on the two H atoms are combined into: a bonding MO -- σ1s and an antibonding MO -- σ*1s MO energy level diagram for H2 (only the bonding MO is filled): ...
... 2. Molecular Orbitals for simple diatomic molecules (H2 and He2) in H2 the 1s atomic orbitals on the two H atoms are combined into: a bonding MO -- σ1s and an antibonding MO -- σ*1s MO energy level diagram for H2 (only the bonding MO is filled): ...
Chemistry Fall-2016 Final
... AA. any metal in Group 2A of the periodic table; generally harder, denser, stronger, and have higher melting points than alkali metals ...
... AA. any metal in Group 2A of the periodic table; generally harder, denser, stronger, and have higher melting points than alkali metals ...
Chemistry Midterm Review 2006
... 13. Which of the following compounds are ionic? A. H2O b. Na2O c. CO2 d. CaS, e. SO2 f. CaCO3. 14. What is the difference between a nonpolar covalent bond and a polar covalent bond? 15. What are the properties of a covalent and ionic compound in terms of state of matter, ability to conduct electric ...
... 13. Which of the following compounds are ionic? A. H2O b. Na2O c. CO2 d. CaS, e. SO2 f. CaCO3. 14. What is the difference between a nonpolar covalent bond and a polar covalent bond? 15. What are the properties of a covalent and ionic compound in terms of state of matter, ability to conduct electric ...
Fall Semester Review Packet
... 9. Describe how the current periodic table is arranged by comparing groups, periods and properties of the elements. 10. Explain the difference between a molecule (covalent compound) and an ionic compound. Include the interaction between valence electrons and the types of bonds for each. 11. There ar ...
... 9. Describe how the current periodic table is arranged by comparing groups, periods and properties of the elements. 10. Explain the difference between a molecule (covalent compound) and an ionic compound. Include the interaction between valence electrons and the types of bonds for each. 11. There ar ...
Class 1
... place confidence in the estimate of τ, and hence we are justified in doubting the estimate of 〈 〉, as we indicated earlier. Estimating τ: ...
... place confidence in the estimate of τ, and hence we are justified in doubting the estimate of 〈 〉, as we indicated earlier. Estimating τ: ...
100 years of work function - Materials Science -
... The term “work function” (WF) was coined about 1923 for the work expressed in eV which is necessary to get electron out of metal. Prior to that time it was defined as the work necessary to get electron out of metal, or work done when electron escapes from a metal. Over the last 100 years this fundam ...
... The term “work function” (WF) was coined about 1923 for the work expressed in eV which is necessary to get electron out of metal. Prior to that time it was defined as the work necessary to get electron out of metal, or work done when electron escapes from a metal. Over the last 100 years this fundam ...
Chapter 4 Chemical Foundations: Elements, Atoms, and Ions
... • Atoms of a given element are different from those of any other element. – Carbon atoms have different chemical and physical properties than sulfur atoms. ...
... • Atoms of a given element are different from those of any other element. – Carbon atoms have different chemical and physical properties than sulfur atoms. ...
Worksheet 4 - Periodic Trends A number of physical and chemical
... When an electron is removed from an atom the repulsion between the remaining electrons decreases. The nuclear charge remains constant, so more energy is required to remove another electron from the positively charged ion. This means that, I1 < I2 < I3 < ..., for any given atom. Going down a group t ...
... When an electron is removed from an atom the repulsion between the remaining electrons decreases. The nuclear charge remains constant, so more energy is required to remove another electron from the positively charged ion. This means that, I1 < I2 < I3 < ..., for any given atom. Going down a group t ...
Fall Exam 1
... A. chlorine and oxygen C. tin and lead B. calcium and scandium D. sulfur and arsenic 26. Gallium has an average atomic mass of 69.72 amu. Gallium exists as two naturally occurring isotopes, 69Ga and 71Ga with a natural abundance of 39.89% and an atomic mass of 70.92 amu. What is the atomic mass of 6 ...
... A. chlorine and oxygen C. tin and lead B. calcium and scandium D. sulfur and arsenic 26. Gallium has an average atomic mass of 69.72 amu. Gallium exists as two naturally occurring isotopes, 69Ga and 71Ga with a natural abundance of 39.89% and an atomic mass of 70.92 amu. What is the atomic mass of 6 ...
velocity components and the magnetic fields are in the transverse
... field varies as eikuz and the radiation field as ei(kz-wt), we find that the v´B term varies as ei((ku+k)z-wt). Hence it has a phase velocity that is less than the speed of light in vacuum. Therefore an electron beam can move synchronous with this ponderomotive force. The corresponding radiation fie ...
... field varies as eikuz and the radiation field as ei(kz-wt), we find that the v´B term varies as ei((ku+k)z-wt). Hence it has a phase velocity that is less than the speed of light in vacuum. Therefore an electron beam can move synchronous with this ponderomotive force. The corresponding radiation fie ...
electron configuration
... Filling Patterns of Atomic Orbitals • Atomic Orbitals are filled from lowest energy to highest energy • Full/half full atomic orbitals – Adding electrons until all orbitals are full is a lower energy state (usually) – Paired electrons are higher energy than unpaired (Hund’s Rule) – Half full orbita ...
... Filling Patterns of Atomic Orbitals • Atomic Orbitals are filled from lowest energy to highest energy • Full/half full atomic orbitals – Adding electrons until all orbitals are full is a lower energy state (usually) – Paired electrons are higher energy than unpaired (Hund’s Rule) – Half full orbita ...
Elements Elements (cont.) Elements (cont.)
... • J.J. Thomson investigated a beam called a cathode ray. ray • He determined that the ray was made of tiny negatively charged particles we now call electrons. ...
... • J.J. Thomson investigated a beam called a cathode ray. ray • He determined that the ray was made of tiny negatively charged particles we now call electrons. ...
Gupta 2014 Credit: Google Images for the pictures Chapter 1
... Titration is a method to determine the molarity of unknown acid or base. In titration, an acid or base of unknown molarity is titrated against a standard solution (whose M is known) of acid or base.The end point in a titration is indicated by a color change by the indicator. Indicators are weak acid ...
... Titration is a method to determine the molarity of unknown acid or base. In titration, an acid or base of unknown molarity is titrated against a standard solution (whose M is known) of acid or base.The end point in a titration is indicated by a color change by the indicator. Indicators are weak acid ...
PAP Chemistry - Fall Final Review
... 10. How does mass number relate to number of protons when talking about isotopes? ...
... 10. How does mass number relate to number of protons when talking about isotopes? ...
The Periodic Table OL Page 1 of 2 G. Galvin Name: Periodic Table
... 2. Robert Boyle: Defn: An element is a substance that cannot be split into simpler substances by chemical means. History of the Periodic Table: 1. Mendeleev: Arranged the elements in order of increasing weight. Defn: Mendeleev’s Periodic Law: When elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic ...
... 2. Robert Boyle: Defn: An element is a substance that cannot be split into simpler substances by chemical means. History of the Periodic Table: 1. Mendeleev: Arranged the elements in order of increasing weight. Defn: Mendeleev’s Periodic Law: When elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic ...
Atomic Structure (history of atom)
... ATOMS of any one ELEMENT are different from those of any other element Atoms of different elements can physically mix together or chemically combine to form ...
... ATOMS of any one ELEMENT are different from those of any other element Atoms of different elements can physically mix together or chemically combine to form ...
AHSGE Review
... Groups are together because the elements in them have similar properties and react in the same manner. Across periods (left to right), atomic radius (size) decreases, ionization energy (ease of losing an electron) increases, and electronegativity (ability to attract electrons) increases. ...
... Groups are together because the elements in them have similar properties and react in the same manner. Across periods (left to right), atomic radius (size) decreases, ionization energy (ease of losing an electron) increases, and electronegativity (ability to attract electrons) increases. ...
THE CHEMICAL BASIS OF LIFE
... 11. Calcium (Ca) has an atomic number of 20; chlorine (Cl) has an atomic number of 17. a. The number of electrons in the outer shell of calcium is ______________. b. The number of electrons in the outer shell of chlorine is ______________. c. In a chemical reaction between these two atoms, _________ ...
... 11. Calcium (Ca) has an atomic number of 20; chlorine (Cl) has an atomic number of 17. a. The number of electrons in the outer shell of calcium is ______________. b. The number of electrons in the outer shell of chlorine is ______________. c. In a chemical reaction between these two atoms, _________ ...
Document
... 47) Applying Concepts: The elements shown in the diagram are ______. a) part of the same group b) part of the same period c) not related ...
... 47) Applying Concepts: The elements shown in the diagram are ______. a) part of the same group b) part of the same period c) not related ...
Answer key
... Protons and neutrons are found in the center of the atom, called the nucleus. The electrons move about in the electron cloud that surrounds the nucleus. 46. Which subatomic particle(s) defines the identity of the atom? Protons 47. Which subatomic particle(s) determines chemical properties? electrons ...
... Protons and neutrons are found in the center of the atom, called the nucleus. The electrons move about in the electron cloud that surrounds the nucleus. 46. Which subatomic particle(s) defines the identity of the atom? Protons 47. Which subatomic particle(s) determines chemical properties? electrons ...
File
... Protons and neutrons are found in the center of the atom, called the nucleus. The electrons move about in the electron cloud that surrounds the nucleus. 46. Which subatomic particle(s) defines the identity of the atom? Protons 47. Which subatomic particle(s) determines chemical properties? electrons ...
... Protons and neutrons are found in the center of the atom, called the nucleus. The electrons move about in the electron cloud that surrounds the nucleus. 46. Which subatomic particle(s) defines the identity of the atom? Protons 47. Which subatomic particle(s) determines chemical properties? electrons ...