Semester 1 Final Review Powerpoint
... compound CO2. This compound is considered a molecule because it contains one carbon atom and two oxygen atoms (both are non-metals). ...
... compound CO2. This compound is considered a molecule because it contains one carbon atom and two oxygen atoms (both are non-metals). ...
Redox - Plusnet
... O is -2, except in OF2 Group 7 are -1, except with O or F Group 1 metals are +1 Group 2 metals are +2 H is +1, except in hydrides, e.g. NaH Al is +3 The total for an ion is its charge (e.g. -1 for CN-) More electronegative atoms get negative numbers The total for a compound is 0, even in O2, Cl2 etc ...
... O is -2, except in OF2 Group 7 are -1, except with O or F Group 1 metals are +1 Group 2 metals are +2 H is +1, except in hydrides, e.g. NaH Al is +3 The total for an ion is its charge (e.g. -1 for CN-) More electronegative atoms get negative numbers The total for a compound is 0, even in O2, Cl2 etc ...
CHEM1405 2012-J-2 June 2012 • What is the ground state electron
... opposite spins, ensuring that no two electrons have the same set of quantum numbers. Aufbau principle: lowest energy orbitals fill first. Hund’s rule: electrons in degenerate orbitals (i.e. orbitals with same energy) have the maximum number of parallel spins to minimise electron / electron repulsion ...
... opposite spins, ensuring that no two electrons have the same set of quantum numbers. Aufbau principle: lowest energy orbitals fill first. Hund’s rule: electrons in degenerate orbitals (i.e. orbitals with same energy) have the maximum number of parallel spins to minimise electron / electron repulsion ...
Chapter 2
... Solute particles are larger than in a solution and scatter light; do not settle out. ...
... Solute particles are larger than in a solution and scatter light; do not settle out. ...
Time-dependent current-density-functional theory for metals
... ranging from the infrared to the far vacuum ultraviolet, and the energy-loss determinations of electrons traversing solid samples. Despite the apparent disparity between the two phenomena, they are in fact closely related. ...
... ranging from the infrared to the far vacuum ultraviolet, and the energy-loss determinations of electrons traversing solid samples. Despite the apparent disparity between the two phenomena, they are in fact closely related. ...
Compounds Power point
... That atoms are made up of Protons, Neutrons, and Electrons The identity of an atom is determined by the number of protons in the nucleus ...
... That atoms are made up of Protons, Neutrons, and Electrons The identity of an atom is determined by the number of protons in the nucleus ...
Chemistry 212 Name:
... Each halogen is obtained by oxidation of the halide ion to the halogen in a molten salt, except fluorine. None of the halogens is particularly abundant in nature, however all are easily accessible in concentrated forms rendering this point moot. All halogens have high electron affinities and ionizat ...
... Each halogen is obtained by oxidation of the halide ion to the halogen in a molten salt, except fluorine. None of the halogens is particularly abundant in nature, however all are easily accessible in concentrated forms rendering this point moot. All halogens have high electron affinities and ionizat ...
PPT - gserianne.com
... • number of protons in the nucleus of one atom • each element has a unique atomic number • equals the number of electrons in the atom in an electrically neutral, i.e., uncharged, atom Written as a subscript to the left of the element's symbol. ...
... • number of protons in the nucleus of one atom • each element has a unique atomic number • equals the number of electrons in the atom in an electrically neutral, i.e., uncharged, atom Written as a subscript to the left of the element's symbol. ...
Final Preparation
... 68. Balance the equation below and determine the number of moles of oxygen required to completely burn 5.00 moles of propane. ____C3H8 + ____O2 ____CO2 + ____H2O A. 5.00 B. 10.0 C. 15.0 D. 25.0 69. What is mutarotation? A. The conversion of a D-monosaccharide into an L-monosaccharide. B. The convers ...
... 68. Balance the equation below and determine the number of moles of oxygen required to completely burn 5.00 moles of propane. ____C3H8 + ____O2 ____CO2 + ____H2O A. 5.00 B. 10.0 C. 15.0 D. 25.0 69. What is mutarotation? A. The conversion of a D-monosaccharide into an L-monosaccharide. B. The convers ...
CHM_101_ASSIGNMENT_COPY_1_2
... Calculate the pressure equilibrium constant Kp for the reaction at this temperature. What is the partial pressure of chlorine in the vessel? 5. Write the expressions for the concentration equilibrium constant Kc and pressure equilibrium constant Kp for the following reactions: a) ...
... Calculate the pressure equilibrium constant Kp for the reaction at this temperature. What is the partial pressure of chlorine in the vessel? 5. Write the expressions for the concentration equilibrium constant Kc and pressure equilibrium constant Kp for the following reactions: a) ...
valence electrons
... • Consists of the elements symbol, which represents the innermost electrons too, and the valence electrons surrounding it. • Example: Lithium has 3 electrons but only 1 valence----Li • The number of valence electrons determines how many and what this atom (or ion) can bond to in order to make a mole ...
... • Consists of the elements symbol, which represents the innermost electrons too, and the valence electrons surrounding it. • Example: Lithium has 3 electrons but only 1 valence----Li • The number of valence electrons determines how many and what this atom (or ion) can bond to in order to make a mole ...
Campbell Biology, 10e (Reece) Chapter 2 The Chemical Context of
... B) the number of protons in the element C) the number of protons plus neutrons in the element D) the number of protons plus electrons in the element 6) In what way are elements in the same column of the periodic table the same? They have the same number of _____. A) protons B) electrons when neutral ...
... B) the number of protons in the element C) the number of protons plus neutrons in the element D) the number of protons plus electrons in the element 6) In what way are elements in the same column of the periodic table the same? They have the same number of _____. A) protons B) electrons when neutral ...
CHEMISTRY IM 06 SYLLABUS
... Intermolecular forces: permanent dipole-permanent dipole; van der Waals’ forces (also known as induced dipole-induced dipole forces) and hydrogen bonds. ...
... Intermolecular forces: permanent dipole-permanent dipole; van der Waals’ forces (also known as induced dipole-induced dipole forces) and hydrogen bonds. ...
Seminario Tunable electronic properties of self
... between the deposited species and the inorganic surface, as well as on morphological and structural aspects. One possible strategy to further steer the structural and electronic properties at interfaces is to use molecular mixtures such as donor-acceptor molecular pairs, since the introduction of th ...
... between the deposited species and the inorganic surface, as well as on morphological and structural aspects. One possible strategy to further steer the structural and electronic properties at interfaces is to use molecular mixtures such as donor-acceptor molecular pairs, since the introduction of th ...
CHEMISTRY IM 06 SYLLABUS
... Intermolecular forces: permanent dipole-permanent dipole; van der Waals’ forces (also known as induced dipole-induced dipole forces) and hydrogen bonds. ...
... Intermolecular forces: permanent dipole-permanent dipole; van der Waals’ forces (also known as induced dipole-induced dipole forces) and hydrogen bonds. ...
Document
... The noble gases are unreactive in chemical reactions In 1916, Gilbert Lewis used this fact to explain why atoms form certain kinds of ions and molecules The Octet Rule: in forming compounds, atoms tend to achieve a noble gas configuration; 8 in the outer level is stable l Each noble gas (except He, ...
... The noble gases are unreactive in chemical reactions In 1916, Gilbert Lewis used this fact to explain why atoms form certain kinds of ions and molecules The Octet Rule: in forming compounds, atoms tend to achieve a noble gas configuration; 8 in the outer level is stable l Each noble gas (except He, ...
Document
... Four electron pairs around an atom assume tetrahedral arrangement. When there are not enough electrons for single bonds the molecule forms multiple bonds and the structure differs. VSEPR theory treats each multiple bond as a single electron group, because it occupies roughly the same region of space ...
... Four electron pairs around an atom assume tetrahedral arrangement. When there are not enough electrons for single bonds the molecule forms multiple bonds and the structure differs. VSEPR theory treats each multiple bond as a single electron group, because it occupies roughly the same region of space ...
Key Concept 1: An atom is the smallest unit of an element that
... Key Concept 7: Electrons are located outside of the nucleus and arranged by energy levels in the electron cloud. There are a certain number of electrons that each energy level can hold. ...
... Key Concept 7: Electrons are located outside of the nucleus and arranged by energy levels in the electron cloud. There are a certain number of electrons that each energy level can hold. ...
key concepts of matter
... Key Concept 1: An element can be identified by its atomic number, or the number of protons located in its nucleus. Key Concept 2: Electrons are located outside of the nucleus and arranged by energy levels in the electron cloud. There are a certain number of electrons that each energy level can hold. ...
... Key Concept 1: An element can be identified by its atomic number, or the number of protons located in its nucleus. Key Concept 2: Electrons are located outside of the nucleus and arranged by energy levels in the electron cloud. There are a certain number of electrons that each energy level can hold. ...
Packet
... 28. Hugh was born 6.391875 X 103 days ago. How old (in years, with 1yr= 365.25 days) is Hugh? ...
... 28. Hugh was born 6.391875 X 103 days ago. How old (in years, with 1yr= 365.25 days) is Hugh? ...
Unit Two Objectives
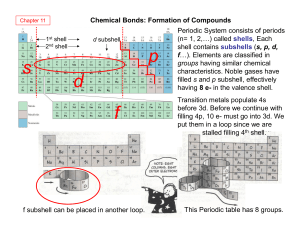
... 1. The Periodic Table: What is the Periodic Law? The Periodic Law states that when the elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic number, there is a periodic repetition of their chemical and physical properties. a. The horizontal rows are called the periods. There are seven periods. Going a ...
... 1. The Periodic Table: What is the Periodic Law? The Periodic Law states that when the elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic number, there is a periodic repetition of their chemical and physical properties. a. The horizontal rows are called the periods. There are seven periods. Going a ...
SEMESTER 1 EXAM Prblms/Short Ans
... Would the ionization energy be higher in area “A” or area “C”? Explain your answer: 12.If the pairs of atoms below bonded, predict whether the bond would be ionic or covalent by placing an upper case “C” or “I” after the pair. (SR # 3, p. 177) ...
... Would the ionization energy be higher in area “A” or area “C”? Explain your answer: 12.If the pairs of atoms below bonded, predict whether the bond would be ionic or covalent by placing an upper case “C” or “I” after the pair. (SR # 3, p. 177) ...
3 molecules
... • Compound held together electrostatically • Very strong forces hold the lattice together, so ionic cmpd’s have very high melting points ...
... • Compound held together electrostatically • Very strong forces hold the lattice together, so ionic cmpd’s have very high melting points ...