chapter5
... (a) Principal Energy levels (sometimes called shells) -The energy levels of electrons are labeled by principal quantum numbers (n), which are integers starting at n = 1, 2, 3, 4, and so on. (b) Energy sublevels - For each principal energy level there may be several orbitals with different shapes tha ...
... (a) Principal Energy levels (sometimes called shells) -The energy levels of electrons are labeled by principal quantum numbers (n), which are integers starting at n = 1, 2, 3, 4, and so on. (b) Energy sublevels - For each principal energy level there may be several orbitals with different shapes tha ...
Element Symbol
... mixed and cannot be visibly distinguished. The particles of the substances are so small that they cannot be easily seen. 11. Another name for a homogeneous mixture is a solution. ...
... mixed and cannot be visibly distinguished. The particles of the substances are so small that they cannot be easily seen. 11. Another name for a homogeneous mixture is a solution. ...
Microbial Metabolism
... Modes of E Conservation-ATP • Fermentation: in which redox reaction ocurs WITHOUT a terminal electron acceptor (couple oxiation with subsequent reduction of an organic ...
... Modes of E Conservation-ATP • Fermentation: in which redox reaction ocurs WITHOUT a terminal electron acceptor (couple oxiation with subsequent reduction of an organic ...
What You Need To Know for the Chemistry Regents Exam
... Ionic substances have high melting and boiling points, form crystals, dissolve in water (dissociation), and conduct electricity in solution and as a liquid. Covalent or molecular substances have lower melting and boiling points, do not conduct electricity. Polar substances are dissolved only b ...
... Ionic substances have high melting and boiling points, form crystals, dissolve in water (dissociation), and conduct electricity in solution and as a liquid. Covalent or molecular substances have lower melting and boiling points, do not conduct electricity. Polar substances are dissolved only b ...
Chemistry Honors Unit 2 Study Guide Atomic Theory Mr. Brown Use
... Law of Definite Proportions/Composition = Chemical compounds always contain the same elements in exactly the same proportions by mass regardless of the amount or source of the sample. EX. NaCl always contain 39.34% by mass of Na and 60.66% by mass of Cl. Law of Multiple Proportions = If two or more ...
... Law of Definite Proportions/Composition = Chemical compounds always contain the same elements in exactly the same proportions by mass regardless of the amount or source of the sample. EX. NaCl always contain 39.34% by mass of Na and 60.66% by mass of Cl. Law of Multiple Proportions = If two or more ...
Need
... Ionic substances have high melting and boiling points, form crystals, dissolve in water (dissociation), and conduct electricity in solution and as a liquid. Covalent or molecular substances have lower melting and boiling points, do not conduct electricity. Polar substances are dissolved only b ...
... Ionic substances have high melting and boiling points, form crystals, dissolve in water (dissociation), and conduct electricity in solution and as a liquid. Covalent or molecular substances have lower melting and boiling points, do not conduct electricity. Polar substances are dissolved only b ...
final exam practice test - Clayton State University
... 35. Consider the following atoms and ions: Na, Na+, Mg, Mg+2, O, O2-, F, F- Which ones of the following groups includes only isoelectronic species? a.) Na, Mg, O, F b.) Na, Na+, Mg, Mg+2 c.) O, O-2, F, F-1 d.) Na+, Mg+2, O-2, Fe.) none of these 36. Arrange the following set of ions in order of incr ...
... 35. Consider the following atoms and ions: Na, Na+, Mg, Mg+2, O, O2-, F, F- Which ones of the following groups includes only isoelectronic species? a.) Na, Mg, O, F b.) Na, Na+, Mg, Mg+2 c.) O, O-2, F, F-1 d.) Na+, Mg+2, O-2, Fe.) none of these 36. Arrange the following set of ions in order of incr ...
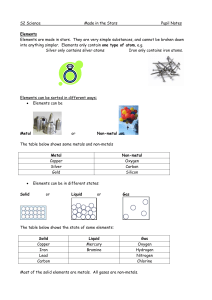
Made in the Stars Notes
... at room temperature except for mercury, which is a liquid. Non-metal solids are usually brittle (they break easily). Non-metals can be solids, liquids or gases at room temperature. Non-metals usually have low melting and boiling points. They are poor conductors of electricity. The exception is graph ...
... at room temperature except for mercury, which is a liquid. Non-metal solids are usually brittle (they break easily). Non-metals can be solids, liquids or gases at room temperature. Non-metals usually have low melting and boiling points. They are poor conductors of electricity. The exception is graph ...
Chapter-2-Human-Chemistry
... needed to disrupt and rearrange the stable electron configuration 2.Concentration and Temperature are main factors in influencing chemical reactions ...
... needed to disrupt and rearrange the stable electron configuration 2.Concentration and Temperature are main factors in influencing chemical reactions ...
File
... water (dissociation), and conduct electricity in solution and as a liquid. Covalent or molecular substances have lower melting and boiling points, do not conduct electricity. Polar substances are dissolved only by another polar substance. Non-polar substances are dissolved only by other non-pola ...
... water (dissociation), and conduct electricity in solution and as a liquid. Covalent or molecular substances have lower melting and boiling points, do not conduct electricity. Polar substances are dissolved only by another polar substance. Non-polar substances are dissolved only by other non-pola ...
What You Need To Know for the Chemistry Regents
... water (dissociation), and conduct electricity in solution and as a liquid. Covalent or molecular substances have lower melting and boiling points, do not conduct electricity. Polar substances are dissolved only by another polar substance. Non-polar substances are dissolved only by other non-pola ...
... water (dissociation), and conduct electricity in solution and as a liquid. Covalent or molecular substances have lower melting and boiling points, do not conduct electricity. Polar substances are dissolved only by another polar substance. Non-polar substances are dissolved only by other non-pola ...
File
... cloud and the probability model, wave/particle duality of electrons revisited, relate electron configurations of atoms to the Bohr and electron cloud models, describe the concepts of excited and ground state of electrons in atoms (electromagnetic radiation is given off as photons), emission spectrum ...
... cloud and the probability model, wave/particle duality of electrons revisited, relate electron configurations of atoms to the Bohr and electron cloud models, describe the concepts of excited and ground state of electrons in atoms (electromagnetic radiation is given off as photons), emission spectrum ...
Section 3.6
... 16. (a) Dimes were shipped out of the country because it is illegal to deface or alter Canadian currency in Canada. (b) These metals have very different magnetic properties, which could be used to separate them. (c) A magnet should separate these coins easily, because nickel is ferromagnetic (strong ...
... 16. (a) Dimes were shipped out of the country because it is illegal to deface or alter Canadian currency in Canada. (b) These metals have very different magnetic properties, which could be used to separate them. (c) A magnet should separate these coins easily, because nickel is ferromagnetic (strong ...
Bio 102 Lecture - chapter 2 The Chemical Basis of Life
... If 3 or less electrons in the outer most shell – Tendency to donate electrons. If 5 or more electrons in the outer most shell – Tendency to receive electrons. A ‘chemical bond’ the force of attraction between atoms to attain stability. ...
... If 3 or less electrons in the outer most shell – Tendency to donate electrons. If 5 or more electrons in the outer most shell – Tendency to receive electrons. A ‘chemical bond’ the force of attraction between atoms to attain stability. ...
∙ ∙B x
... 1. Draw the structural formula of water showing its shape. 2. What are the electronegativites of oxygen and hydrogen? 3. Are the bonding electrons shared equally between oxygen and hydrogen? 4. Where is the highest probability of finding them? 5. Is there an even distribution of bonding electrons in ...
... 1. Draw the structural formula of water showing its shape. 2. What are the electronegativites of oxygen and hydrogen? 3. Are the bonding electrons shared equally between oxygen and hydrogen? 4. Where is the highest probability of finding them? 5. Is there an even distribution of bonding electrons in ...
NYS Regents Chemistry June 21, 2002
... 1: II. PERIODIC TABLE\1. Properties of Elements\A. Metals\1. Metals - (32) 2: II. PERIODIC TABLE\2. Valence Electrons\A. Electron / Ionic Configuration\2. Ionic Configuration - (10, 30) 2: II. PERIODIC TABLE\4. Properties of Periods\C. Electronegativity\1. Electronegativity - (11, 13) 1: II. PERIODI ...
... 1: II. PERIODIC TABLE\1. Properties of Elements\A. Metals\1. Metals - (32) 2: II. PERIODIC TABLE\2. Valence Electrons\A. Electron / Ionic Configuration\2. Ionic Configuration - (10, 30) 2: II. PERIODIC TABLE\4. Properties of Periods\C. Electronegativity\1. Electronegativity - (11, 13) 1: II. PERIODI ...
∙ ∙B x
... 1. Draw the structural formula of water showing its shape. 2. What are the electronegativites of oxygen and hydrogen? 3. Are the bonding electrons shared equally between oxygen and hydrogen? 4. Where is the highest probability of finding them? 5. Is there an even distribution of bonding electrons in ...
... 1. Draw the structural formula of water showing its shape. 2. What are the electronegativites of oxygen and hydrogen? 3. Are the bonding electrons shared equally between oxygen and hydrogen? 4. Where is the highest probability of finding them? 5. Is there an even distribution of bonding electrons in ...
1st Semester Practice Test
... a. a pure substance that cannot be broken down into simpler, stable substances. b. a substance, made of two or more atoms that are chemically bonded, that can be broken down into simpler, stable substances. c. the smallest unit of matter that maintains its chemical identity. d. any substance ...
... a. a pure substance that cannot be broken down into simpler, stable substances. b. a substance, made of two or more atoms that are chemically bonded, that can be broken down into simpler, stable substances. c. the smallest unit of matter that maintains its chemical identity. d. any substance ...
Chemistry - StudyTime NZ
... From this informa>on, we can tell that Magnesium has three electron shells, the last of which contains 2 electrons. We can assume that the first two electron shells are full with 2 electrons and 8 ...
... From this informa>on, we can tell that Magnesium has three electron shells, the last of which contains 2 electrons. We can assume that the first two electron shells are full with 2 electrons and 8 ...
Tutorial 1
... 8. Identify the following as elements or compounds: NH3, N2, S8, NO, CO, CO2, H2, SO2 9. Give three number of protons and electrons in each of the following common ions: Na +, Ca2+, Al3+, Fe2+, I-, F-, S2-, O2-, N3-, K+, Mg2+, Fe3+, Br-, Mn2+, C4-, and Cu2+ 10. Define molecular formula and empirical ...
... 8. Identify the following as elements or compounds: NH3, N2, S8, NO, CO, CO2, H2, SO2 9. Give three number of protons and electrons in each of the following common ions: Na +, Ca2+, Al3+, Fe2+, I-, F-, S2-, O2-, N3-, K+, Mg2+, Fe3+, Br-, Mn2+, C4-, and Cu2+ 10. Define molecular formula and empirical ...
Chapter 9. Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories
... molecule. • They do not explain why a chemical bond forms. • How can quantum mechanics be used to account for molecular shape? What are the orbitals that are involved in bonding? • We use valence-bond theory. • A covalent bond forms when the orbitals on two atoms overlap. • The shared region of spac ...
... molecule. • They do not explain why a chemical bond forms. • How can quantum mechanics be used to account for molecular shape? What are the orbitals that are involved in bonding? • We use valence-bond theory. • A covalent bond forms when the orbitals on two atoms overlap. • The shared region of spac ...
Physics 361 Principles of Modern Physics
... inhabit. This gives the electrons some wiggle room in order to accelerate. Compare to a classical charged particle in an electric field. As the particle experiences a force, the energy state of the particle changes. If there are no energy states available for the particle to inhabit – it can’t accel ...
... inhabit. This gives the electrons some wiggle room in order to accelerate. Compare to a classical charged particle in an electric field. As the particle experiences a force, the energy state of the particle changes. If there are no energy states available for the particle to inhabit – it can’t accel ...
cell molecules
... commonly involved in chemical reactions are known as functional groups. • Functional groups are attachments that replace one or more hydrogen atoms to the carbon skeleton of the hydrocarbon. ...
... commonly involved in chemical reactions are known as functional groups. • Functional groups are attachments that replace one or more hydrogen atoms to the carbon skeleton of the hydrocarbon. ...
Chemistry Reference Table Review
... 83. What are two properties of most nonmetals? (1) high ionization energy and poor electrical conductivity (2) high ionization energy and good electrical conductivity (3) low ionization energy and poor electrical conductivity (4) low ionization energy and good electrical conductivity 84. Based on Ta ...
... 83. What are two properties of most nonmetals? (1) high ionization energy and poor electrical conductivity (2) high ionization energy and good electrical conductivity (3) low ionization energy and poor electrical conductivity (4) low ionization energy and good electrical conductivity 84. Based on Ta ...
CHM 101 - Academic Computer Center
... high, positive or slightly negative low, positive or slightly negative high, very negative None of these is generally correct. ...
... high, positive or slightly negative low, positive or slightly negative high, very negative None of these is generally correct. ...