chapters 1-4
... Atom – smallest building block; molecule – combination of two or more atoms. Can be an element or compound. ...
... Atom – smallest building block; molecule – combination of two or more atoms. Can be an element or compound. ...
Solute
... Solid – definite volume and shape; particles packed in fixed positions. Liquid – definite volume but indefinite shape; particles close together but not in fixed positions Gas – neither definite volume nor definite shape; particles are at great distances from one another Plasma – high temperature, io ...
... Solid – definite volume and shape; particles packed in fixed positions. Liquid – definite volume but indefinite shape; particles close together but not in fixed positions Gas – neither definite volume nor definite shape; particles are at great distances from one another Plasma – high temperature, io ...
Biology\Ch 2 Chemistry
... Colloids, or colloidal suspensions, don’t settle out even if not stirred. Ex: milk ...
... Colloids, or colloidal suspensions, don’t settle out even if not stirred. Ex: milk ...
(null): 110.ReactionsIntro
... 1) Electrons cannot be created or destroyed, only rearranged 2) Old bonds are broken and new bonds are made … 3) So, new substance must be made (chem change) 4) Ex: Zn + HCl ZnCl2 + H2 a) label each chemical with bond type (metallic, covalent, ionic, covalent) b) Have to break e.g. metallic zinc b ...
... 1) Electrons cannot be created or destroyed, only rearranged 2) Old bonds are broken and new bonds are made … 3) So, new substance must be made (chem change) 4) Ex: Zn + HCl ZnCl2 + H2 a) label each chemical with bond type (metallic, covalent, ionic, covalent) b) Have to break e.g. metallic zinc b ...
Final
... Trends – list elements, ions, ionic compounds, or covalent bonds in order of increasing or decreasing atomic radii ion radii (isoelectronic series) ionization energy lattice energy bond strength bond length Develop Lewis dot structures for: compounds with central atom having only an octet compounds ...
... Trends – list elements, ions, ionic compounds, or covalent bonds in order of increasing or decreasing atomic radii ion radii (isoelectronic series) ionization energy lattice energy bond strength bond length Develop Lewis dot structures for: compounds with central atom having only an octet compounds ...
Reactions of common metals and properties of
... 2 Na Æ 2 Na+ + 2 e2 H+ + 2 e- Æ H2(g) The two half-reactions combined can be written as: 2 Na + 2 H+ Æ 2 Na+ + H2(g) Atoms of the alkali metals are easily excited; even the flame of a Bunsen burner can excite their valence electrons. As the electrons jump back to lower energy levels, they give chara ...
... 2 Na Æ 2 Na+ + 2 e2 H+ + 2 e- Æ H2(g) The two half-reactions combined can be written as: 2 Na + 2 H+ Æ 2 Na+ + H2(g) Atoms of the alkali metals are easily excited; even the flame of a Bunsen burner can excite their valence electrons. As the electrons jump back to lower energy levels, they give chara ...
Chemistry Final Exam Study Guide_S2014
... 2. Convert the following numbers into or out of scientific notation. a. 548,000 b. 0.0000770 c. 1.200 × 10-3 d. 9.25 × 107 3. Osmium is the densest element with a density of 22.57 g/cm3. Find the mass of a 56.2 cm3 sample of osmium. 4. Perform the following SI prefix conversions. a. 65.2 mm = ? cm b ...
... 2. Convert the following numbers into or out of scientific notation. a. 548,000 b. 0.0000770 c. 1.200 × 10-3 d. 9.25 × 107 3. Osmium is the densest element with a density of 22.57 g/cm3. Find the mass of a 56.2 cm3 sample of osmium. 4. Perform the following SI prefix conversions. a. 65.2 mm = ? cm b ...
Naming Ionic Compounds
... ** this is just like you learned for molecular compounds except you are not worried about the numbers of an element examples: NaCl – sodium chloride CaCl2 – calcium chloride Mg3N2 – magnesium nitride PbO – lead oxide ...
... ** this is just like you learned for molecular compounds except you are not worried about the numbers of an element examples: NaCl – sodium chloride CaCl2 – calcium chloride Mg3N2 – magnesium nitride PbO – lead oxide ...
200 Ways to Pass the Chemistry - Home 15-16
... 94. Atoms are most stable when they have 8 valence electrons (an octet) (except H & He) and tend to form ions to obtain such a configuration of electrons. Which of the following atoms forms a stable ion that does not have an octet structure? Li F Na Cl 95. Covalent bonds non-metal with non-metal for ...
... 94. Atoms are most stable when they have 8 valence electrons (an octet) (except H & He) and tend to form ions to obtain such a configuration of electrons. Which of the following atoms forms a stable ion that does not have an octet structure? Li F Na Cl 95. Covalent bonds non-metal with non-metal for ...
Honors Mid-Term Review Sheet
... 27. What is the mass of 180.3 cm3 of lead if the density is 11.4 g/cm3? 28. What is the density of 325g of a substance with a volume of 492mL? 29. Define accuracy and precision. 30. Complete the following calculations with the correct number of significant figures: a. 1.23kg + 4.082kg b. 16.04s – 5 ...
... 27. What is the mass of 180.3 cm3 of lead if the density is 11.4 g/cm3? 28. What is the density of 325g of a substance with a volume of 492mL? 29. Define accuracy and precision. 30. Complete the following calculations with the correct number of significant figures: a. 1.23kg + 4.082kg b. 16.04s – 5 ...
All That Matters - Teach-n-Learn-Chem
... One of the many ways scientist classify substances is by the periodic table. The periodic table is a chart showing the elements in order by increasing atomic number and grouped by their similar qualities. Russian chemist Dimitri Mendeleev is believed to be the first to place the elements in order by ...
... One of the many ways scientist classify substances is by the periodic table. The periodic table is a chart showing the elements in order by increasing atomic number and grouped by their similar qualities. Russian chemist Dimitri Mendeleev is believed to be the first to place the elements in order by ...
Review topics-blog
... which mostly increases from left to right across a row of the periodic table but decreases from top to bottom down a group. We will discuss why, as well we will discuss other trends like atomic size, ionic size, and electron affinity trends. These trends can help us understand simple bonding tren ...
... which mostly increases from left to right across a row of the periodic table but decreases from top to bottom down a group. We will discuss why, as well we will discuss other trends like atomic size, ionic size, and electron affinity trends. These trends can help us understand simple bonding tren ...
Stoichiometry - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... illustrate and explain the formation of ionic, covalent, and metallic bonds determine the distribution of electrons in the major energy levels for the first thirtyeighth elements and for ions in groups 1, 2, 3, 15, 16, and 17 state the octet rule predict the ionic charge for ions in the main ...
... illustrate and explain the formation of ionic, covalent, and metallic bonds determine the distribution of electrons in the major energy levels for the first thirtyeighth elements and for ions in groups 1, 2, 3, 15, 16, and 17 state the octet rule predict the ionic charge for ions in the main ...
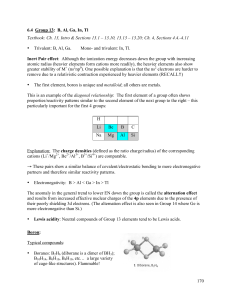
Group II Elements - Innovative Education.org
... The two electrons of the Be2+ ion occupy the first energy level only so the ion is very small. Ions such as this, small and highly charged, have a high charge density and the charge density of the Be2+ ion is very high indeed. As a consequence of this the properties of beryllium and its compounds ar ...
... The two electrons of the Be2+ ion occupy the first energy level only so the ion is very small. Ions such as this, small and highly charged, have a high charge density and the charge density of the Be2+ ion is very high indeed. As a consequence of this the properties of beryllium and its compounds ar ...
Chem Regents 2015 A Few Things
... In BOTH types of cell the same types of reaction occur at the same electrode: ANode — OXidation ...
... In BOTH types of cell the same types of reaction occur at the same electrode: ANode — OXidation ...
Chemistry -- Oxidation
... most compounds. Exceptions are O2 (where O = 0) and peroxides, such as H2O2 or Na2O2, where O = -1. • For other elements, you can usually use If no other rules apply, assume ON is the same as the charge taken on in an ionic compound (“the charge it would like to be) ...
... most compounds. Exceptions are O2 (where O = 0) and peroxides, such as H2O2 or Na2O2, where O = -1. • For other elements, you can usually use If no other rules apply, assume ON is the same as the charge taken on in an ionic compound (“the charge it would like to be) ...
Bonding - Berkeley City College
... •The 'd+' and 'd-' symbols indicate partial positive and negative charges. •The arrow indicates the "pull" of electrons off the hydrogen and towards the more electronegative atom. ...
... •The 'd+' and 'd-' symbols indicate partial positive and negative charges. •The arrow indicates the "pull" of electrons off the hydrogen and towards the more electronegative atom. ...
Chapter 2 - My Teacher Site
... • Atoms with incomplete valence shells can interact with other atoms in such a way that completes their valence shell, either by: • Sharing valence electrons • Transferring valence electrons • These interactions usually result in atoms staying close together, held by attractions called chemical bon ...
... • Atoms with incomplete valence shells can interact with other atoms in such a way that completes their valence shell, either by: • Sharing valence electrons • Transferring valence electrons • These interactions usually result in atoms staying close together, held by attractions called chemical bon ...
radiation physics
... 1. Positive Charge – atoms lose an electron A positively charged object has a deficiency of electrons 2. Negative Charge – atoms gain an electron A negatively charged object has an excess of electrons *A charged body has an electric field surrounding it. II. Electrification – a process where electro ...
... 1. Positive Charge – atoms lose an electron A positively charged object has a deficiency of electrons 2. Negative Charge – atoms gain an electron A negatively charged object has an excess of electrons *A charged body has an electric field surrounding it. II. Electrification – a process where electro ...
FREE Sample Here
... 1. List several differences between ionic and covalent bonds. Ionic bonds occur when ions of opposite charge are mutually attracted. Acids and bases are examples of ionic compounds. Covalent bonds are strong chemical bonds that occur when atoms share electrons. Methane and sugar are examples of cova ...
... 1. List several differences between ionic and covalent bonds. Ionic bonds occur when ions of opposite charge are mutually attracted. Acids and bases are examples of ionic compounds. Covalent bonds are strong chemical bonds that occur when atoms share electrons. Methane and sugar are examples of cova ...
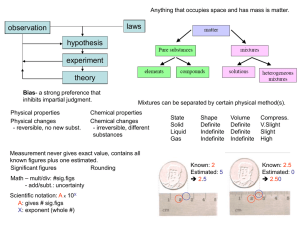
SEPARATION OF MATTER - Los Angeles City College
... • Physical properties: characteristics of a material which may be determined without altering the composition of the material; bp (boiling point), mp, color, density etc., no change in the chemical identity occurs. • Chemical properties: characteristics of a material which involves altering the comp ...
... • Physical properties: characteristics of a material which may be determined without altering the composition of the material; bp (boiling point), mp, color, density etc., no change in the chemical identity occurs. • Chemical properties: characteristics of a material which involves altering the comp ...
Analysis of a Matter
... • Physical properties: characteristics of a material which may be determined without altering the composition of the material; bp (boiling point), mp, color, density etc., no change in the chemical identity occurs. • Chemical properties: characteristics of a material which involves altering the comp ...
... • Physical properties: characteristics of a material which may be determined without altering the composition of the material; bp (boiling point), mp, color, density etc., no change in the chemical identity occurs. • Chemical properties: characteristics of a material which involves altering the comp ...
Sections 6.4 - 6.5
... Mg and Cu; in ship building as HYDRONALIUM, alloyed with 3-12 % Mg – with disastrous consequences in the BC SeaCat Ferry building program and the Falkland War: Al/Mg + n O2(g) → Al2O3 + MgO + lots of heat ! in water: Al/Mg + n H2O(l) → Al2O3 + MgO + n H2(g) ! …, i.e. Mg and Al burn underwater once i ...
... Mg and Cu; in ship building as HYDRONALIUM, alloyed with 3-12 % Mg – with disastrous consequences in the BC SeaCat Ferry building program and the Falkland War: Al/Mg + n O2(g) → Al2O3 + MgO + lots of heat ! in water: Al/Mg + n H2O(l) → Al2O3 + MgO + n H2(g) ! …, i.e. Mg and Al burn underwater once i ...
H 2 O
... • Volume – Temperature Relationship – At constant pressure, the volume is directly proportional to temperature ...
... • Volume – Temperature Relationship – At constant pressure, the volume is directly proportional to temperature ...