Thermodynamics: Entropy, Free Energy and the Direction of
... (a) 1mol of SO2(g) or 1mol of SO3(g) (b) 1mol of CO2(s) or 1mol of CO2(g) (c) 3mol of oxygen gas (O2) or 2mol of ozone gas (O3) (d) 1mol of KBr(s) or 1mol of KBr(aq) (e) Seawater in midwinter at 20C or in midsummer at 230C (f) 1mol of CF4(g) or 1mol of CCl4(g) PLAN: In general less ordered systems h ...
... (a) 1mol of SO2(g) or 1mol of SO3(g) (b) 1mol of CO2(s) or 1mol of CO2(g) (c) 3mol of oxygen gas (O2) or 2mol of ozone gas (O3) (d) 1mol of KBr(s) or 1mol of KBr(aq) (e) Seawater in midwinter at 20C or in midsummer at 230C (f) 1mol of CF4(g) or 1mol of CCl4(g) PLAN: In general less ordered systems h ...
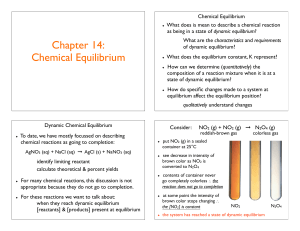
Chapter 14: Chemical Equilibrium
... Effect of Changing Pressure on Equilibrium Position There are 3 ways to change the pressure of a chemical reaction system: 1.! add or remove a gas phase reactant or product recall that Preactant or Pproduct are related (through PV=nRT) to molar concentration ...
... Effect of Changing Pressure on Equilibrium Position There are 3 ways to change the pressure of a chemical reaction system: 1.! add or remove a gas phase reactant or product recall that Preactant or Pproduct are related (through PV=nRT) to molar concentration ...
1. Consider the thermochemistry of C
... that the amount of water produced is negligible. To calculate this, take the number of moles of (NH2)2Co produced from part a and divide this by the volume, in L. For all exams, the concentration is 0.112 M c) How many grams of NH3 and CO2 remain at the end of the reaction? By definition, the limiti ...
... that the amount of water produced is negligible. To calculate this, take the number of moles of (NH2)2Co produced from part a and divide this by the volume, in L. For all exams, the concentration is 0.112 M c) How many grams of NH3 and CO2 remain at the end of the reaction? By definition, the limiti ...
Thermodynamics and Equilibrium
... – This inequality implies that for a reaction to be spontaneous, H-TS must be negative. – If H-TS is positive, the reverse reaction is spontaneous. If H-TS=0, the reaction is at equilibrium Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company.All rights reserved. ...
... – This inequality implies that for a reaction to be spontaneous, H-TS must be negative. – If H-TS is positive, the reverse reaction is spontaneous. If H-TS=0, the reaction is at equilibrium Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company.All rights reserved. ...
enthalpy 2
... oxygen under standard conditions, all reactants in their standard states. The enthalpies of combustion can be determined using a calorimeter which is explained below; it uses the symbol c. ...
... oxygen under standard conditions, all reactants in their standard states. The enthalpies of combustion can be determined using a calorimeter which is explained below; it uses the symbol c. ...
380 KB / 39 pages
... cylinder containing a red solution of dilute ammonia to which has been added a few drops of phenol red acid-base indicator solution, bubbles of gas are rapidly evolved, a white fog forms above the solution, and, after a short time, the solution in the cylinder turns yellow. A number of physical and ...
... cylinder containing a red solution of dilute ammonia to which has been added a few drops of phenol red acid-base indicator solution, bubbles of gas are rapidly evolved, a white fog forms above the solution, and, after a short time, the solution in the cylinder turns yellow. A number of physical and ...
Reaction Rates
... Collision orientation and the activated complex Why do most collisions fail to produce products? What other factors must be considered? Figure 4a and b show one possible answer to this question. These illustrations indicate that in order for a collision to lead to a reaction, the carbon atom in a CO ...
... Collision orientation and the activated complex Why do most collisions fail to produce products? What other factors must be considered? Figure 4a and b show one possible answer to this question. These illustrations indicate that in order for a collision to lead to a reaction, the carbon atom in a CO ...
File
... products, but the amount of matter present at the end of the ______________________________________________________________ reaction is the same as it was at the beginning of the reaction. ______________________________________________________________ ...
... products, but the amount of matter present at the end of the ______________________________________________________________ reaction is the same as it was at the beginning of the reaction. ______________________________________________________________ ...
DEPARTMENT OF CHEMISTRY, CFS, IIUM
... the amount of matter is called an intensive property. A characteristic that can be observed without producing new kinds of matter is called a physical property. A characteristic that depends on how a kind of matter changes suring interactions with other kinds of matter is called chemical property. M ...
... the amount of matter is called an intensive property. A characteristic that can be observed without producing new kinds of matter is called a physical property. A characteristic that depends on how a kind of matter changes suring interactions with other kinds of matter is called chemical property. M ...
Chapter 5HW_Ans
... a) Oxidized: gain of protons (hydrogen is also reduction) b) reduced c) redox reactions go together as one species losses (electrons or hydrogen in oxidation or gains oxygen) and concomitantly the other species gains (electrons or hydrogen) in reduction. ...
... a) Oxidized: gain of protons (hydrogen is also reduction) b) reduced c) redox reactions go together as one species losses (electrons or hydrogen in oxidation or gains oxygen) and concomitantly the other species gains (electrons or hydrogen) in reduction. ...
15.0 EquilibriumIHS2014
... increasing the container volume. Then the equilibrium shifts to the left (the side with more moles of gas) • At B, the temperature is increased. Then the equilibrium shifts to left. • At C, C2H6(g) is added to the system. Then the equilibrium shifts to the left. • At D, no shift in equilibrium posit ...
... increasing the container volume. Then the equilibrium shifts to the left (the side with more moles of gas) • At B, the temperature is increased. Then the equilibrium shifts to left. • At C, C2H6(g) is added to the system. Then the equilibrium shifts to the left. • At D, no shift in equilibrium posit ...
P. Mignon, J. Steyaert, R. Loris, P. Geerlings, and S. Loverix, J. Biol
... been shown to take part in catalysis (5). Both the His-40 and Glu-58 side chains are in the direct vicinity of the 2⬘-nucleophile. pH dependence studies have shown Glu-58 to be unprotonated and His-40 to be protonated at the onset of catalysis, proving that Glu-58 is the catalytic base accepting a p ...
... been shown to take part in catalysis (5). Both the His-40 and Glu-58 side chains are in the direct vicinity of the 2⬘-nucleophile. pH dependence studies have shown Glu-58 to be unprotonated and His-40 to be protonated at the onset of catalysis, proving that Glu-58 is the catalytic base accepting a p ...
Catalysis

Catalysis is the increase in the rate of a chemical reaction due to the participation of an additional substance called a catalyst. With a catalyst, reactions occur faster and require less activation energy. Because catalysts are not consumed in the catalyzed reaction, they can continue to catalyze the reaction of further quantities of reactant. Often only tiny amounts are required.