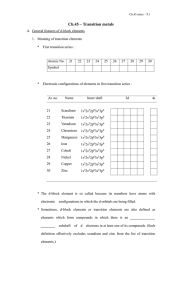
Chemistry 8.2
... • There are several ways to classify chemical reactions. • The classification scheme described in this section provides an introduction to five basic types of reactions: • synthesis or combination or composition ...
... • There are several ways to classify chemical reactions. • The classification scheme described in this section provides an introduction to five basic types of reactions: • synthesis or combination or composition ...
Advanced Higher Chemistry Resource Guide
... Advanced Higher Chemistry Resources Guide This resource guide has been produced in response to requests from staff who attended the NQ Sciences events at Hampden Stadium in December 2013. Those attending felt it would be useful to have a document which helped them navigate to the most relevant resou ...
... Advanced Higher Chemistry Resources Guide This resource guide has been produced in response to requests from staff who attended the NQ Sciences events at Hampden Stadium in December 2013. Those attending felt it would be useful to have a document which helped them navigate to the most relevant resou ...
Audit Schedule
... intermediate values may produce slightly different results from those in the text. 2. Don’t underestimate the importance of density. It is a simple concept, but one that will be important for many problems later in the course, so be sure to remember it. 3. Most of the unit conversions you will do in ...
... intermediate values may produce slightly different results from those in the text. 2. Don’t underestimate the importance of density. It is a simple concept, but one that will be important for many problems later in the course, so be sure to remember it. 3. Most of the unit conversions you will do in ...
Energetics - chemistryatdulwich
... size of ion: the smaller the ion , the larger the electrostatic attraction and the more energy is needed to sublime the ions. charge of the ion: the larger the charge, the greater the electrostatic attraction. The smaller the ionic radius and the greater the charge of the ion the greater the charg ...
... size of ion: the smaller the ion , the larger the electrostatic attraction and the more energy is needed to sublime the ions. charge of the ion: the larger the charge, the greater the electrostatic attraction. The smaller the ionic radius and the greater the charge of the ion the greater the charg ...
19_Worked_Examples
... Plan We expect ΔS to be positive if there is an increase in temperature, increase in volume, or increase in number of gas particles. The question states that the temperature is constant, and so we need to concern ourselves only with volume and number of particles. Solve (a) Evaporation involves a la ...
... Plan We expect ΔS to be positive if there is an increase in temperature, increase in volume, or increase in number of gas particles. The question states that the temperature is constant, and so we need to concern ourselves only with volume and number of particles. Solve (a) Evaporation involves a la ...
Net ionic equation
... A base is a substance that forms OH- ion when added to water (Arrhenius definition). A strong soluble base is a soluble hydroxide compound that completely dissociates when added to water. An insoluble base is an insoluble hydroxide compound. There are also a few substances that act as weak bases in ...
... A base is a substance that forms OH- ion when added to water (Arrhenius definition). A strong soluble base is a soluble hydroxide compound that completely dissociates when added to water. An insoluble base is an insoluble hydroxide compound. There are also a few substances that act as weak bases in ...
mc_ch08 - MrBrownsChem1LCHS
... • List three observations that suggest that a chemical reaction has taken place. • List three requirements for a correctly written chemical equation. • Write a word equation and a formula equation for a given chemical reaction. • Balance a formula equation by inspection. ...
... • List three observations that suggest that a chemical reaction has taken place. • List three requirements for a correctly written chemical equation. • Write a word equation and a formula equation for a given chemical reaction. • Balance a formula equation by inspection. ...
Chemical Thermodynamics - Winona State University
... • A gas is less ordered than a liquid that is less ordered than a solid. • Any process that increases the number of gas molecules leads to an increase in entropy. • When NO(g) reacts with O2(g) to form NO2(g), the total number of gas molecules decreases, and the entropy decreases. HyperChem ...
... • A gas is less ordered than a liquid that is less ordered than a solid. • Any process that increases the number of gas molecules leads to an increase in entropy. • When NO(g) reacts with O2(g) to form NO2(g), the total number of gas molecules decreases, and the entropy decreases. HyperChem ...
Principles of Reactivity: Chemical Equilibria
... the equilibrium constant for the new equation (Knew) is the old equilibrium constant (Kold) raised to the power of the multiplication factor. The equilibrium constants for a reaction and its reverse are the reciprocals of each other. When two or more chemical equations are added to produce a net equ ...
... the equilibrium constant for the new equation (Knew) is the old equilibrium constant (Kold) raised to the power of the multiplication factor. The equilibrium constants for a reaction and its reverse are the reciprocals of each other. When two or more chemical equations are added to produce a net equ ...
Topic 15 Energetics - slider-dpchemistry-11
... The degree of covalent character is usually expressed as the difference between experimental and theoretical lattice enthalpy values divided the experimental value. For example the experimental value for AgCl(s) is –905 kJ mol‾1. The theoretical value is –770 kJ mol‾1. The difference is therefore 13 ...
... The degree of covalent character is usually expressed as the difference between experimental and theoretical lattice enthalpy values divided the experimental value. For example the experimental value for AgCl(s) is –905 kJ mol‾1. The theoretical value is –770 kJ mol‾1. The difference is therefore 13 ...
Chapter 19 Chemical Thermodynamics
... Plan: The sign of ΔS will be positive if there is an increase in temperature, an increase in the volume in which the molecules move, or an increase in the number of gas particles in the reaction. The question states that the temperature is constant. Thus, we need to evaluate each equation with the o ...
... Plan: The sign of ΔS will be positive if there is an increase in temperature, an increase in the volume in which the molecules move, or an increase in the number of gas particles in the reaction. The question states that the temperature is constant. Thus, we need to evaluate each equation with the o ...
1. What energy changes occur when chemical bonds are formed
... The reaction is spontaneous at low temperatures but becomes non-spontaneous at high temperatures. ...
... The reaction is spontaneous at low temperatures but becomes non-spontaneous at high temperatures. ...
Thermodynamics ppt
... q < 0 ⇒ exothermic ⇒ heat is flowing out of the system to the surroundings w > 0 ⇒ work is being done on the system by the surroundings when a gas is getting compressed by an external pressure w < 0 ⇒ the system is doing work on the surroundings when a gas is expanding against an external pressure ∆ ...
... q < 0 ⇒ exothermic ⇒ heat is flowing out of the system to the surroundings w > 0 ⇒ work is being done on the system by the surroundings when a gas is getting compressed by an external pressure w < 0 ⇒ the system is doing work on the surroundings when a gas is expanding against an external pressure ∆ ...
Catalysis

Catalysis is the increase in the rate of a chemical reaction due to the participation of an additional substance called a catalyst. With a catalyst, reactions occur faster and require less activation energy. Because catalysts are not consumed in the catalyzed reaction, they can continue to catalyze the reaction of further quantities of reactant. Often only tiny amounts are required.