Kinetics & Equilibrium
... THE ENERGY OF THE PROCESS MUST DECREASE AND THE UNIVERSE MUST BECOME MORE RANDOM!!!! ...
... THE ENERGY OF THE PROCESS MUST DECREASE AND THE UNIVERSE MUST BECOME MORE RANDOM!!!! ...
Reaction Rate Reading Packet
... For the same mass, many small particles have a greater total surface area than one large particle. For example, steel wool has a larger surface area than a block of steel of the same mass. This allows oxygen molecules to collide with many more iron atoms per unit of time. The more surface contact be ...
... For the same mass, many small particles have a greater total surface area than one large particle. For example, steel wool has a larger surface area than a block of steel of the same mass. This allows oxygen molecules to collide with many more iron atoms per unit of time. The more surface contact be ...
Slide 1 - MrCard.Org
... • Change activation rate by adding catalyst • Allows need for less energy to make reaction happen • Catalyst not considered part of reaction • In humans have enzymes to allow reaction to occur at a lower temperature ...
... • Change activation rate by adding catalyst • Allows need for less energy to make reaction happen • Catalyst not considered part of reaction • In humans have enzymes to allow reaction to occur at a lower temperature ...
Problem Set: Empirical and Molecular Formulas
... 6. Titanium (IV) oxide, TiO2, is used as a pigment in paints and as a whitening and coating agent for paper. It can be made by reacting O2 with TiCl4. TiCl4 + O2 TiO2 + 2 Cl2 (already balanced) a) If 4.5 mol of TiCl4 react with 3.5 mol O2, identify both the limiting and excess reactants. b) How ma ...
... 6. Titanium (IV) oxide, TiO2, is used as a pigment in paints and as a whitening and coating agent for paper. It can be made by reacting O2 with TiCl4. TiCl4 + O2 TiO2 + 2 Cl2 (already balanced) a) If 4.5 mol of TiCl4 react with 3.5 mol O2, identify both the limiting and excess reactants. b) How ma ...
Ch. 6: Chemical Reactions Study Guide
... A synthesis reaction is a reaction between at least two compounds in which a new, more complex compound is formed. The product of the synthesis reaction between sodium and chlorine gas is sodium chloride. In a decomposition reaction, the reactants are broken down into other substances. Most of the e ...
... A synthesis reaction is a reaction between at least two compounds in which a new, more complex compound is formed. The product of the synthesis reaction between sodium and chlorine gas is sodium chloride. In a decomposition reaction, the reactants are broken down into other substances. Most of the e ...
The Nature of Chemical Reactions
... How many nitrate molecules are in the product side? The reactant side? ...
... How many nitrate molecules are in the product side? The reactant side? ...
Exam 2-f06 - Clayton State University
... 8.) The equilibrium constant, Kc for the following gas phase reaction is 0.50 at 600°C. A mixture of HCHO, H and CO is introduced into a flask at 600°C. After a short time, analysis of a small amount of the reaction mixture shows the concentration to be [HCHO] = 1.5M, [H2] = 1.2 M and [CO] = 1.0M. W ...
... 8.) The equilibrium constant, Kc for the following gas phase reaction is 0.50 at 600°C. A mixture of HCHO, H and CO is introduced into a flask at 600°C. After a short time, analysis of a small amount of the reaction mixture shows the concentration to be [HCHO] = 1.5M, [H2] = 1.2 M and [CO] = 1.0M. W ...
Toluenediamine
... The direct dinitration of toluene could be achieved using a large excess of fuming nitric acid in the presence of the solvents CCl4 and acetic anhydride and the catalyst “claycop”, an acidic montmorillonite clay impregnated with anhydrous cupric nitrate. The yield after 4 h at 25C was 95%, and the ...
... The direct dinitration of toluene could be achieved using a large excess of fuming nitric acid in the presence of the solvents CCl4 and acetic anhydride and the catalyst “claycop”, an acidic montmorillonite clay impregnated with anhydrous cupric nitrate. The yield after 4 h at 25C was 95%, and the ...
PHT-224 Lectures 7
... - resistant to corrosion - sterilizable - can be shaped into rigid, semi rigid or collapsible containers ...
... - resistant to corrosion - sterilizable - can be shaped into rigid, semi rigid or collapsible containers ...
Document
... Bond formation involves the electrons (e-) in the outermost (valence) shell. A complete outer shell consists of 8 valence electrons (except H and He which have 2) Destruction of a bond corresponds to a release of energy. Generally double or triple bond energies are higher than for single bonds. ...
... Bond formation involves the electrons (e-) in the outermost (valence) shell. A complete outer shell consists of 8 valence electrons (except H and He which have 2) Destruction of a bond corresponds to a release of energy. Generally double or triple bond energies are higher than for single bonds. ...
CHEMISTRY
... (3) It is independent of temperature (4) It is highly specific 2. The dissociation constant of an acid HA is 1 x 10-5. The pH of 0.1 molar solution of the acid will be: ...
... (3) It is independent of temperature (4) It is highly specific 2. The dissociation constant of an acid HA is 1 x 10-5. The pH of 0.1 molar solution of the acid will be: ...
Begin Chemical Equations Practice
... • In a chemical reaction, the materials to the left of the arrow are the reactants. Reactants are consumed in the reaction. • The arrow is like an equal sign in math. It can be read “react to produce” or “produces” or “forms”. • The materials to the right of the arrow are the products. They form as ...
... • In a chemical reaction, the materials to the left of the arrow are the reactants. Reactants are consumed in the reaction. • The arrow is like an equal sign in math. It can be read “react to produce” or “produces” or “forms”. • The materials to the right of the arrow are the products. They form as ...
California Chemistry Standards Test
... Gases and Their Properties-(6) 1. pressure and movement of molecules 2. diffusion of gases 3. gas laws and problems 4. real vs ideal gases 5. STP 6. convert between C and K 7. absolute zero (0 K) Acids & Bases-(5) 1. properties of acids & bases and salt solutions 2. acids-hydrogen-ion donating 3. ba ...
... Gases and Their Properties-(6) 1. pressure and movement of molecules 2. diffusion of gases 3. gas laws and problems 4. real vs ideal gases 5. STP 6. convert between C and K 7. absolute zero (0 K) Acids & Bases-(5) 1. properties of acids & bases and salt solutions 2. acids-hydrogen-ion donating 3. ba ...
THE SUN: Fusion, Fission and Combustion
... present in the bonds between atoms. Reactants start at a higher energy level than products. ...
... present in the bonds between atoms. Reactants start at a higher energy level than products. ...
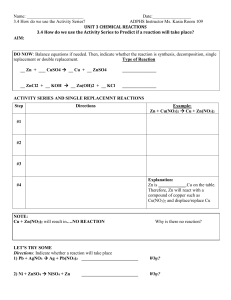
3.4 How do we use the Activity Series
... F2 + 2NaCl Cl2 + 2NaF 1. What is the most reactive nonmetal according to the table?___________________________________ 2. ______________________will react with anything below it 3. Will the above reaction take place?_____________________________________________________ 4. Will the reverse reaction ...
... F2 + 2NaCl Cl2 + 2NaF 1. What is the most reactive nonmetal according to the table?___________________________________ 2. ______________________will react with anything below it 3. Will the above reaction take place?_____________________________________________________ 4. Will the reverse reaction ...
REACTION DYNAMICS
... What information can infra-red chemiluminescence provide on the energetics and/or dynamics of a chemical reaction? What other experimental methods can be used to obtain similar information? ...
... What information can infra-red chemiluminescence provide on the energetics and/or dynamics of a chemical reaction? What other experimental methods can be used to obtain similar information? ...
IB Chemistry Brakke ECA - Topic 15 T15D12
... The absolute entropy values, S, at 238 K for N2(g), H2(g) and NH3(g) are 192, 131 and 193 J K ο ο respectively. Calculate ∆S for the reaction and explain the sign of ∆S . ...
... The absolute entropy values, S, at 238 K for N2(g), H2(g) and NH3(g) are 192, 131 and 193 J K ο ο respectively. Calculate ∆S for the reaction and explain the sign of ∆S . ...
Catalysis

Catalysis is the increase in the rate of a chemical reaction due to the participation of an additional substance called a catalyst. With a catalyst, reactions occur faster and require less activation energy. Because catalysts are not consumed in the catalyzed reaction, they can continue to catalyze the reaction of further quantities of reactant. Often only tiny amounts are required.