File
... Name: _______________________________________________________________________ Period: ____ 11.2: Types of Chemical Reactions Part A: Completion Directions: Each blank can be completed with a term, short phrase, or number. It is possible to __1__ the products of some chemical ...
... Name: _______________________________________________________________________ Period: ____ 11.2: Types of Chemical Reactions Part A: Completion Directions: Each blank can be completed with a term, short phrase, or number. It is possible to __1__ the products of some chemical ...
8th Grade Ch. 7 Chemical Reactions Study guide
... ____ 25. Chemical reactions usually speed up at ____ temperatures. A. Celsius B. lower C. higher D. absolute ____ 26. Catalysts ____ the activation energy needed to start a chemical reaction. A. inhibit B. increase C. reduce D. balance ____ 27. To check that an equation is balanced, count the number ...
... ____ 25. Chemical reactions usually speed up at ____ temperatures. A. Celsius B. lower C. higher D. absolute ____ 26. Catalysts ____ the activation energy needed to start a chemical reaction. A. inhibit B. increase C. reduce D. balance ____ 27. To check that an equation is balanced, count the number ...
unit 4 review sheet
... the sum of these coefficients? g. When “c” is correctly balanced using the smallest whole number coefficients, what is the coefficient for HCl? h. When “d” is correctly balanced using the smallest whole number coefficients, what is the sum of these coefficients? i. When “e” is correctly balanced usi ...
... the sum of these coefficients? g. When “c” is correctly balanced using the smallest whole number coefficients, what is the coefficient for HCl? h. When “d” is correctly balanced using the smallest whole number coefficients, what is the sum of these coefficients? i. When “e” is correctly balanced usi ...
Chemical Synthesis Using Earth-Abundant Metal
... (i.e., Pd, Pt, Ru, Rh, Ir, Ag and Au). The problem with precious metals is that they are expensive, steadily rarefying, and are generally non-renewable. Catalysts made from these metals can also be harmful to humans and to the environment. ...
... (i.e., Pd, Pt, Ru, Rh, Ir, Ag and Au). The problem with precious metals is that they are expensive, steadily rarefying, and are generally non-renewable. Catalysts made from these metals can also be harmful to humans and to the environment. ...
Ch. 2 The Chemistry of Life
... - Catalyst – a substance that _________ up the _______ of a chemical reaction - Enzymes - ___________ that act as ________________ catalysts o _______________ speed up _______________ reactions that take place in ______ - ___________ are specific, they _____________ only __ chemical reaction - _____ ...
... - Catalyst – a substance that _________ up the _______ of a chemical reaction - Enzymes - ___________ that act as ________________ catalysts o _______________ speed up _______________ reactions that take place in ______ - ___________ are specific, they _____________ only __ chemical reaction - _____ ...
Test 4
... 1. Suppose you have 1.00L of an aqueous buffer containing 55.0 mmol of acetic acid (pKa=4.67) and 45 mmol acetate Calculate the pH of this buffer. ...
... 1. Suppose you have 1.00L of an aqueous buffer containing 55.0 mmol of acetic acid (pKa=4.67) and 45 mmol acetate Calculate the pH of this buffer. ...
Presentation - Chem Rxns - stpats-sch3u-sem1-2013
... A reaction doesn’t occur unless the particles collide with a certain minimum energy called the activation energy of the reaction Activation energy is the minimum energy required before a reaction can occur.You can show this on an energy profile for the reaction. For a simple over-all exothermic reac ...
... A reaction doesn’t occur unless the particles collide with a certain minimum energy called the activation energy of the reaction Activation energy is the minimum energy required before a reaction can occur.You can show this on an energy profile for the reaction. For a simple over-all exothermic reac ...
Document
... energy into its surroundings The energy released by forming products is GREATER than the energy required to break the reactant’s bonds It’s surroundings would feel hot, because heat (energy) is being released. ...
... energy into its surroundings The energy released by forming products is GREATER than the energy required to break the reactant’s bonds It’s surroundings would feel hot, because heat (energy) is being released. ...
Lecture 8
... of reaction with respect to reactants A and B. - Orders of reaction depend on the mechanism and are not necessarily equal to the stoichiometric coefficients a and b. The rate constant depends on the mechanism and especially on the energy barrier or activation energy associated with the reaction path ...
... of reaction with respect to reactants A and B. - Orders of reaction depend on the mechanism and are not necessarily equal to the stoichiometric coefficients a and b. The rate constant depends on the mechanism and especially on the energy barrier or activation energy associated with the reaction path ...
18 - cloudfront.net
... Notice that the activation energy barrier for the catalyzed reaction is lower than that of the uncatalyzed reaction. With a lower activation-energy barrier, more reactants have the energy to form products within a given time. For instance, the rate of the combination reaction of hydrogen and oxygen ...
... Notice that the activation energy barrier for the catalyzed reaction is lower than that of the uncatalyzed reaction. With a lower activation-energy barrier, more reactants have the energy to form products within a given time. For instance, the rate of the combination reaction of hydrogen and oxygen ...
classification of chemical reactions
... energy is needed to keep the reaction going energy is shown on________________________________________ Reactants + heat energy products ...
... energy is needed to keep the reaction going energy is shown on________________________________________ Reactants + heat energy products ...
Chemical Reactions
... Synthesis Reactions • A synthesis reaction is a reaction in which two or more substances react to form a single substance • The reactants may be either elements or compounds • The product synthesized is always a compound ...
... Synthesis Reactions • A synthesis reaction is a reaction in which two or more substances react to form a single substance • The reactants may be either elements or compounds • The product synthesized is always a compound ...
Collision Theory
... • Before atoms/molecules/ions can react, they must first collide • An effective collision between two species puts enough energy to break key bonds • The activation energy (Ea) is the minimum energy that must be supplied by collisions to trigger a reaction • A certain fraction of all molecules in a ...
... • Before atoms/molecules/ions can react, they must first collide • An effective collision between two species puts enough energy to break key bonds • The activation energy (Ea) is the minimum energy that must be supplied by collisions to trigger a reaction • A certain fraction of all molecules in a ...
Catalysis
... 4. Enzyme catalysed reactions are much more sensitive to catalytic poisons such as HCN, H2S, CS2 etc. The inhibitors interact with the active functional groups present on the enzyme surface and often reduce or completely destroy the catalytic activity of the enzymes 5. The activity of certain enzym ...
... 4. Enzyme catalysed reactions are much more sensitive to catalytic poisons such as HCN, H2S, CS2 etc. The inhibitors interact with the active functional groups present on the enzyme surface and often reduce or completely destroy the catalytic activity of the enzymes 5. The activity of certain enzym ...
Chemical Reactions
... 3. THINK VISUALLY The graphs below show the amount of energy present during two chemical reactions. One of the reactions is an energy-absorbing reaction, the other is an energy-releasing reaction. Label the type of reaction for each, label the energy level for the reactants and products, then draw a ...
... 3. THINK VISUALLY The graphs below show the amount of energy present during two chemical reactions. One of the reactions is an energy-absorbing reaction, the other is an energy-releasing reaction. Label the type of reaction for each, label the energy level for the reactants and products, then draw a ...
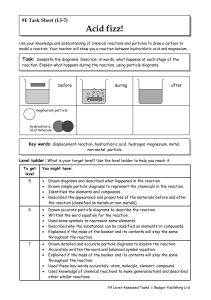
Year 9 Homework Task 9E-5 Reactions 5-7
... Use your knowledge and understanding of chemical reactions and particles to draw a cartoon to model a reaction. Your teacher will show you a reaction between hydrochloric acid and magnesium. ...
... Use your knowledge and understanding of chemical reactions and particles to draw a cartoon to model a reaction. Your teacher will show you a reaction between hydrochloric acid and magnesium. ...
Lesson 6
... Turn to page 28 of the textbook and read "The Changes That Occur." 4. The substances present before a reaction are called the ________________. 5. The substances present after a reaction are called the _________________. 6. List the three main indicators that a chemical reaction has occurred. 7. Are ...
... Turn to page 28 of the textbook and read "The Changes That Occur." 4. The substances present before a reaction are called the ________________. 5. The substances present after a reaction are called the _________________. 6. List the three main indicators that a chemical reaction has occurred. 7. Are ...
RTF
... Write reversible reactions for each of the following situations (be sure to balance your equations): a. ...
... Write reversible reactions for each of the following situations (be sure to balance your equations): a. ...
Catalysis

Catalysis is the increase in the rate of a chemical reaction due to the participation of an additional substance called a catalyst. With a catalyst, reactions occur faster and require less activation energy. Because catalysts are not consumed in the catalyzed reaction, they can continue to catalyze the reaction of further quantities of reactant. Often only tiny amounts are required.