Writing Chemical Equations
... • 2 Al atoms react with 3 Br2 molecules – Amounts in moles of species ...
... • 2 Al atoms react with 3 Br2 molecules – Amounts in moles of species ...
Rate of Reaction
... Rate of Reaction Rates of reactions are usually expressed in units of moles per liter per unit time. If we know the chemical equation for a reaction, its rate can be determined by following the change in concentration of any product or reactant that can be detected quantitatively. r = ∆ concentratio ...
... Rate of Reaction Rates of reactions are usually expressed in units of moles per liter per unit time. If we know the chemical equation for a reaction, its rate can be determined by following the change in concentration of any product or reactant that can be detected quantitatively. r = ∆ concentratio ...
Document
... A. because proteins (enzymes) are made of chiral subunits they usually react with only one stereoisomer of a molecule. B. because proteins (enzymes) are not made of chiral subunits they react with all stereoisomers of a molecule. C. because proteins (enzymes) are made of chiral subunits they react w ...
... A. because proteins (enzymes) are made of chiral subunits they usually react with only one stereoisomer of a molecule. B. because proteins (enzymes) are not made of chiral subunits they react with all stereoisomers of a molecule. C. because proteins (enzymes) are made of chiral subunits they react w ...
The Sabatier Principle Illustrated by Catalytic H2
... between binding the reagents to the surface and not binding any of the reaction intermediates too strong relative to the product. The principle explains why a so-called volcano curve is most often obtained when plotting catalytic activity versus surface reactivity. It is important to note the distin ...
... between binding the reagents to the surface and not binding any of the reaction intermediates too strong relative to the product. The principle explains why a so-called volcano curve is most often obtained when plotting catalytic activity versus surface reactivity. It is important to note the distin ...
Factors Affecting the Rate of a Chemical Reaction
... 1. Increasing the surface area gives a faster reaction because more particles are ‘exposed’ to the other reactant. 2. Increasing the concentration increases the rate of reaction because there are more collisions between the reactant particles. 3. Increasing the temperature increases the rate of reac ...
... 1. Increasing the surface area gives a faster reaction because more particles are ‘exposed’ to the other reactant. 2. Increasing the concentration increases the rate of reaction because there are more collisions between the reactant particles. 3. Increasing the temperature increases the rate of reac ...
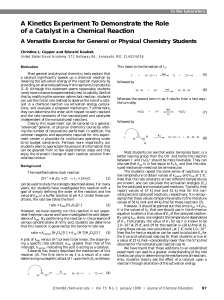
JCE0198 p0087 A Kinetics Experiment To Demonstrate the Role of
... better leaving group than the OH{ and hence the reaction between I{ and H3O 2+ should be more favorable. They can also see that kcat is in fact equal to K1 kH and that the catalyzed mechanism need not be termolecular. The students repeat the same series of reactions at a low temperature to obtain va ...
... better leaving group than the OH{ and hence the reaction between I{ and H3O 2+ should be more favorable. They can also see that kcat is in fact equal to K1 kH and that the catalyzed mechanism need not be termolecular. The students repeat the same series of reactions at a low temperature to obtain va ...
Enthalpy diagram relating the change for a reaction to enthalpies of
... 1. Physical state of the reactants: when reactants are in different phases for example when a solid reacts with a liquid the reaction is limited to the area of contact. Reactions involving solids will proceed faster if the surface area of the solid is increased. 2. Concentration of the reactants: as ...
... 1. Physical state of the reactants: when reactants are in different phases for example when a solid reacts with a liquid the reaction is limited to the area of contact. Reactions involving solids will proceed faster if the surface area of the solid is increased. 2. Concentration of the reactants: as ...
CHEMICAL REACTIONS
... __ Na2S + __ AgNO3 _ NaNO3 + _ Ag2S ___ Mg + ___ HCl ___ H2 + ___ MgCl2 ...
... __ Na2S + __ AgNO3 _ NaNO3 + _ Ag2S ___ Mg + ___ HCl ___ H2 + ___ MgCl2 ...
2 - Glow Blogs
... follows first-order kinetics with respect to both iodine and hydrogen. When this reaction was studied at different temperatures, the data shown in the table below were obtained. The data could be used to determine the activation energy for the forward reaction. Temperature/K ...
... follows first-order kinetics with respect to both iodine and hydrogen. When this reaction was studied at different temperatures, the data shown in the table below were obtained. The data could be used to determine the activation energy for the forward reaction. Temperature/K ...
UNIT 1 - StudyGuide.PK
... area under them, the maximum of the higher temperature curve will have a lower y-axis value. For a given Eact, there is a larger number of molecules with E ⇒ Eact at the higher temperature. Heterogeneous catalysts often work by weakening the bonds in the reactants by the process of adsorption. Homog ...
... area under them, the maximum of the higher temperature curve will have a lower y-axis value. For a given Eact, there is a larger number of molecules with E ⇒ Eact at the higher temperature. Heterogeneous catalysts often work by weakening the bonds in the reactants by the process of adsorption. Homog ...
Chapter 19 Reaction Rates And Equilibrium
... • Particles of reactants (ions, atoms, molecules) must collide in order for reactions to occur • An effective collision occurs when reactant particles approach each other: – at the proper angle – With enough Energy (Force) ...
... • Particles of reactants (ions, atoms, molecules) must collide in order for reactions to occur • An effective collision occurs when reactant particles approach each other: – at the proper angle – With enough Energy (Force) ...
Chemical reactions
... Reaction products = substances formed in a chemical reaction. They are written in the right term of the equation Because in a chemical reaction, the nature of atoms of the substances is not changed, the chemical equations are equalized so that the number of atoms of a certain element from the left t ...
... Reaction products = substances formed in a chemical reaction. They are written in the right term of the equation Because in a chemical reaction, the nature of atoms of the substances is not changed, the chemical equations are equalized so that the number of atoms of a certain element from the left t ...
CHEMICAL REACTION
... • COEFFICIENTS show ratio of substances • ENERGY and other conditions may also be shown • SUBSCRIPTS show other descriptive information ...
... • COEFFICIENTS show ratio of substances • ENERGY and other conditions may also be shown • SUBSCRIPTS show other descriptive information ...
Year 10 Chemistry Exam June 2011 Multiple Choice Section A
... Which of the following processes is an example of a chemical change? A magnesium ribbon is surrounded by bubbles when it is placed in hydrochloric acid solution B a mist forms when you breathe onto cold glass C ice melts as you hold it in the palm of your hand D a litre of water boils dry in a sauce ...
... Which of the following processes is an example of a chemical change? A magnesium ribbon is surrounded by bubbles when it is placed in hydrochloric acid solution B a mist forms when you breathe onto cold glass C ice melts as you hold it in the palm of your hand D a litre of water boils dry in a sauce ...
Chapter 11 Chemical Reactions
... (aq) after the formula = dissolved in water, an aqueous solution: NaCl(aq) is a salt water solution used after a product indicates a gas has been produced: H2↑ used after a product indicates a solid has been produced: PbI2↓ ...
... (aq) after the formula = dissolved in water, an aqueous solution: NaCl(aq) is a salt water solution used after a product indicates a gas has been produced: H2↑ used after a product indicates a solid has been produced: PbI2↓ ...
Nature of chemical reaction - Environmental-Chemistry
... To break down starch into smaller molecules ...
... To break down starch into smaller molecules ...
MS PowerPoint - Catalysis Eprints database
... appearing into the products Definition: a catalyst is a substance that increases the rate at which a chemical reaction approaches equilibrium without becoming itself permanently involved. Catalysis is a kinetic phenomenon. ...
... appearing into the products Definition: a catalyst is a substance that increases the rate at which a chemical reaction approaches equilibrium without becoming itself permanently involved. Catalysis is a kinetic phenomenon. ...
+ H 2 SO 4(aq) - Rothschild Science
... Reactivity of a metal makes a difference! If a metal is more reactive than the metal it is displacing a rxn will occur. If the metal is less reactive than the metal it is displacing, a rxn will not occur. ...
... Reactivity of a metal makes a difference! If a metal is more reactive than the metal it is displacing a rxn will occur. If the metal is less reactive than the metal it is displacing, a rxn will not occur. ...
Catalysis

Catalysis is the increase in the rate of a chemical reaction due to the participation of an additional substance called a catalyst. With a catalyst, reactions occur faster and require less activation energy. Because catalysts are not consumed in the catalyzed reaction, they can continue to catalyze the reaction of further quantities of reactant. Often only tiny amounts are required.