Unit 13 Worksheet Answers
... They each cause more collisions so the reaction can happen faster. The temperature also causes the collisions to happen with more energy so there are more effective collisions. 4) It has been found that rates are more rapid at the beginning of a reaction than toward the end, assuming the temperature ...
... They each cause more collisions so the reaction can happen faster. The temperature also causes the collisions to happen with more energy so there are more effective collisions. 4) It has been found that rates are more rapid at the beginning of a reaction than toward the end, assuming the temperature ...
Chapter 5 – Chemical Reactions
... reaction will be synthesis. Two metals will not combine chemically Noble gases will not combine Write the symbol for the more positive element first and then use the criss-cross method to determine the formula. ...
... reaction will be synthesis. Two metals will not combine chemically Noble gases will not combine Write the symbol for the more positive element first and then use the criss-cross method to determine the formula. ...
Unit 5 Study Guide
... Unit 5 Study Guide: Chemical Reactions 1. What are the 7 diatomic molecules? ...
... Unit 5 Study Guide: Chemical Reactions 1. What are the 7 diatomic molecules? ...
snc 2do unit: chemistry unit test review questions
... c) What type of reaction is this? 5. Identify the type of reaction, and write a balanced chemical equation for: A) zinc + iron (III) nitrate -------> ________ + ______________ B) potassium + oxygen ------> _________________ C) magnesium carbonate -----> magnesium oxide + carbon dioxide D) __________ ...
... c) What type of reaction is this? 5. Identify the type of reaction, and write a balanced chemical equation for: A) zinc + iron (III) nitrate -------> ________ + ______________ B) potassium + oxygen ------> _________________ C) magnesium carbonate -----> magnesium oxide + carbon dioxide D) __________ ...
by Maillard Reaction
... synthesized using the Maillard reaction of 18F-FDG with biological amines, under different reaction conditions. Respective amines N-allyl-2-aminomethylpyrroactionlidine (NAP) and 2-(4′-aminophenyl)-6hydroxybenzothiazole (PIB precursor) were mixed with FDG to provide fluorodeoxyglycosylamines, FDGNAP ...
... synthesized using the Maillard reaction of 18F-FDG with biological amines, under different reaction conditions. Respective amines N-allyl-2-aminomethylpyrroactionlidine (NAP) and 2-(4′-aminophenyl)-6hydroxybenzothiazole (PIB precursor) were mixed with FDG to provide fluorodeoxyglycosylamines, FDGNAP ...
Sample Paper - Army Public School Jammu Cantt
... -amino acids have relatively higher melting points than the corresponding halo acids. Explain. ...
... -amino acids have relatively higher melting points than the corresponding halo acids. Explain. ...
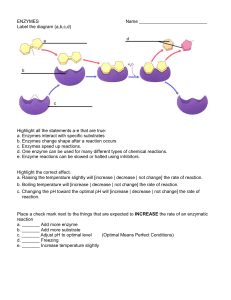
ENZYMES
... a. _______ Add more enzyme b. _______ Add more substrate c. _______ Adjust pH to optimal level (Optimal Means Perfect Conditions) d. _______ Freezing e. _______ Increase temperature slightly ...
... a. _______ Add more enzyme b. _______ Add more substrate c. _______ Adjust pH to optimal level (Optimal Means Perfect Conditions) d. _______ Freezing e. _______ Increase temperature slightly ...
Section 2-4 “Chemical Reactions and Enzymes”
... Products – Elements or compounds produced by a chemical reaction ...
... Products – Elements or compounds produced by a chemical reaction ...
Chemistry 2nd Semester Final Exam Review Chemical Bonds Give
... 45. How many calories are needed to raise 450. grams of water from 21.0 oC to 85.5oC? 46. How many grams of water can be heated 46.0oC by 34.8 kJ? Reaction Rates 47. Define reaction rate. 48. What are the units for reaction rate? 49. Describe what happens to the concentration of reactants during a c ...
... 45. How many calories are needed to raise 450. grams of water from 21.0 oC to 85.5oC? 46. How many grams of water can be heated 46.0oC by 34.8 kJ? Reaction Rates 47. Define reaction rate. 48. What are the units for reaction rate? 49. Describe what happens to the concentration of reactants during a c ...
2nd Semester Final Review
... 45. How many calories are needed to raise 450. grams of water from 21.0 oC to 85.5oC? 46. How many grams of water can be heated 46.0oC by 34.8 kJ? Reaction Rates 47. Define reaction rate. 48. What are the units for reaction rate? 49. Describe what happens to the concentration of reactants during a c ...
... 45. How many calories are needed to raise 450. grams of water from 21.0 oC to 85.5oC? 46. How many grams of water can be heated 46.0oC by 34.8 kJ? Reaction Rates 47. Define reaction rate. 48. What are the units for reaction rate? 49. Describe what happens to the concentration of reactants during a c ...
South Pasadena • AP Chemistry
... The chemical elements are the building blocks of matter, which can be understood in terms of arrangements of atoms. Molecules & elements Chemical analysis The mole Electron configuration Periodicity Quantum mechanical model Atomic models Mass spectrometry Light & matter Conservat ...
... The chemical elements are the building blocks of matter, which can be understood in terms of arrangements of atoms. Molecules & elements Chemical analysis The mole Electron configuration Periodicity Quantum mechanical model Atomic models Mass spectrometry Light & matter Conservat ...
Chapter 4
... Solve stoichiometry problems when either the reactants or the products are species in solution and concentration and volume data are given. ...
... Solve stoichiometry problems when either the reactants or the products are species in solution and concentration and volume data are given. ...
03. The Theoretic bases of bioenergetics
... A = p · Z, where Z is the collision rate and p is a steric factor. Z turns out to be only weakly dependant on temperature. Thus the frequency factor is a constant, specific for each reaction. ...
... A = p · Z, where Z is the collision rate and p is a steric factor. Z turns out to be only weakly dependant on temperature. Thus the frequency factor is a constant, specific for each reaction. ...
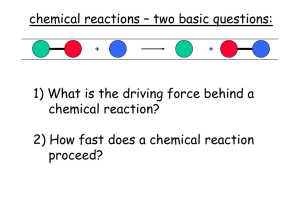
Chemical Reactions
... What is a chemical reaction? • A chemical reaction is the process by which the atoms of one or more substances are rearranged to form different substances. ...
... What is a chemical reaction? • A chemical reaction is the process by which the atoms of one or more substances are rearranged to form different substances. ...
Slide 1 - Mrs. Reed Science Classes
... After calculating the amount of reactant B required to completely react with A, then comparing that amount with the amount of B available, one can determine the a. limiting reactant. b. rate of the reaction. c. energy released in the reaction. d. pathway of the reaction. ...
... After calculating the amount of reactant B required to completely react with A, then comparing that amount with the amount of B available, one can determine the a. limiting reactant. b. rate of the reaction. c. energy released in the reaction. d. pathway of the reaction. ...
Standard 4 notes
... Conservation of Mass—Atoms are not created or destroyed in chemical reactions. They just change partners. If we could mass the reactants in a sealed, airtight container and make them react without opening the container, we should find that the total mass before the reaction is the same as the total ...
... Conservation of Mass—Atoms are not created or destroyed in chemical reactions. They just change partners. If we could mass the reactants in a sealed, airtight container and make them react without opening the container, we should find that the total mass before the reaction is the same as the total ...
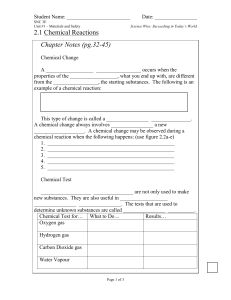
Chemical Reactions
... The ___________ of which a new substances forms is called the ___________ of __________________. Different chemical substances will produce _______________ at _________________ rates. Factor that affects rate of reaction Temperature ...
... The ___________ of which a new substances forms is called the ___________ of __________________. Different chemical substances will produce _______________ at _________________ rates. Factor that affects rate of reaction Temperature ...
Name________________ Hour____ Chapter 11 Review 1. Name
... 2 atoms of solid aluminum react with 6 molecules of liquid water to produce 3 molecules of hydrogen gas and 2 formula units of solid aluminum hydroxide. 4. Write in symbols: 2 formula units of solid lead (IV) oxide decomposes in the presence of heat to produce 2 formula units of solid lead (II) oxid ...
... 2 atoms of solid aluminum react with 6 molecules of liquid water to produce 3 molecules of hydrogen gas and 2 formula units of solid aluminum hydroxide. 4. Write in symbols: 2 formula units of solid lead (IV) oxide decomposes in the presence of heat to produce 2 formula units of solid lead (II) oxid ...
Catalysis

Catalysis is the increase in the rate of a chemical reaction due to the participation of an additional substance called a catalyst. With a catalyst, reactions occur faster and require less activation energy. Because catalysts are not consumed in the catalyzed reaction, they can continue to catalyze the reaction of further quantities of reactant. Often only tiny amounts are required.