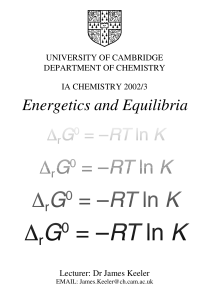Are diglycolamide ligands hard or soft Lewis bases?
... Pearson’s concept of Hard/Soft Acids/Bases (HSAB) in coordination chemistry – recapitulation Chemical hardness/softness of ligand molecules (L) can be considered in terms of the amount of electron density donated by the ligand (Lewis base) to the central metal ion (Lewis acid) in the complex. Hard ...
... Pearson’s concept of Hard/Soft Acids/Bases (HSAB) in coordination chemistry – recapitulation Chemical hardness/softness of ligand molecules (L) can be considered in terms of the amount of electron density donated by the ligand (Lewis base) to the central metal ion (Lewis acid) in the complex. Hard ...
Determination of the diffusion coefficient of sucrose in water and its
... of a concentration, chemical, or potential energy gradient the probability of motion in any one direction is equal to the probability of motion in exactly the opposite direction.[1] In this experiment, the directed displacement of molecules in solution will be considered. The driving force for this ...
... of a concentration, chemical, or potential energy gradient the probability of motion in any one direction is equal to the probability of motion in exactly the opposite direction.[1] In this experiment, the directed displacement of molecules in solution will be considered. The driving force for this ...
- Catalyst
... • Recall, a properly balanced redox reaction means both mass and charge are conserved. • Oftentimes the solvent (in this course, we will only consider water) will be explicitly involved in the redox reaction. • For example, consider the following reaction: CuS(s) + NO3-(aq) ...
... • Recall, a properly balanced redox reaction means both mass and charge are conserved. • Oftentimes the solvent (in this course, we will only consider water) will be explicitly involved in the redox reaction. • For example, consider the following reaction: CuS(s) + NO3-(aq) ...
Title Pressure effect on the eda
... Assumingthe K and s remained unchangedat high pressure, the relative increase in optical density would be about the square of the relative density of solvent since the EDA-complexdepends onh~upon the concentration; of two components..-1sshownin Fig. 5, the increase in the optical density with pressu ...
... Assumingthe K and s remained unchangedat high pressure, the relative increase in optical density would be about the square of the relative density of solvent since the EDA-complexdepends onh~upon the concentration; of two components..-1sshownin Fig. 5, the increase in the optical density with pressu ...
Insertion of SO2 into the Metal−Carbon Bonds of Rhodium and
... (Cp*Rh(PMe3)(Cl)2) was a stable species, unable to bind the free methane sulfinic acid. In the second case (HOTf, HBF4), the inability to form a strong bond between the metal and the labile counterion prevented the release of free sulfinic acid. A third case can be imagined corresponding to an inter ...
... (Cp*Rh(PMe3)(Cl)2) was a stable species, unable to bind the free methane sulfinic acid. In the second case (HOTf, HBF4), the inability to form a strong bond between the metal and the labile counterion prevented the release of free sulfinic acid. A third case can be imagined corresponding to an inter ...
CLASSIFICATION OF MATTER
... In heterogeneous mixtures the distribution of the particles is not uniform; in consequence, the composition is not the same at all points. For example: the mixture of sulphur and iron filings. ...
... In heterogeneous mixtures the distribution of the particles is not uniform; in consequence, the composition is not the same at all points. For example: the mixture of sulphur and iron filings. ...
Energetics and Equilibria
... In the Michaelmas Term course Introduction to Energetics and Kinetics we saw that some processes could be classed as natural or spontaneous. Such processes take place on their own without any intervention from us. The reverse of such processes do not happen spontaneously, but we can force them to ha ...
... In the Michaelmas Term course Introduction to Energetics and Kinetics we saw that some processes could be classed as natural or spontaneous. Such processes take place on their own without any intervention from us. The reverse of such processes do not happen spontaneously, but we can force them to ha ...
PREPARATORY PROBLEMS
... applied to macrosystems. To illustrate this idea, E. Schrödinger proposed the following mental experiment. Consider the Geiger counter which detects the entering electrons. The counter is connected to a device which breaks the glass with the poison when the particle enters the counter. Near the glas ...
... applied to macrosystems. To illustrate this idea, E. Schrödinger proposed the following mental experiment. Consider the Geiger counter which detects the entering electrons. The counter is connected to a device which breaks the glass with the poison when the particle enters the counter. Near the glas ...
Stage 2 Chemistry Intended Student Learning 2014
... This topic deals with some of the underlying principles of chemistry (‘elemental chemistry’) and then considers the chemistry of the environment. The elemental chemistry component of the topic focuses on the periodic table and the concept of electronegativity; together these underlie most of the oth ...
... This topic deals with some of the underlying principles of chemistry (‘elemental chemistry’) and then considers the chemistry of the environment. The elemental chemistry component of the topic focuses on the periodic table and the concept of electronegativity; together these underlie most of the oth ...
Catalysis and Catalyst
... Acidity of the Catalyst Vs. Acid Sites It is possible to conclude that: the acid strength of a site will increase when there is a decrease in the number of Al atoms in the Next Nearest Neighbor position of the Al atom. ...
... Acidity of the Catalyst Vs. Acid Sites It is possible to conclude that: the acid strength of a site will increase when there is a decrease in the number of Al atoms in the Next Nearest Neighbor position of the Al atom. ...
aq - Moodle@FCT
... The volume of NaOH solution is given in the problem. Therefore, we need to find the number of moles of NaOH to solve for molarity. From the preceding equation for the reaction between KHP and NaOH shown in the text we see that 1 mole of KHP neutralizes 1 mole of NaOH. How many moles of KHP are conta ...
... The volume of NaOH solution is given in the problem. Therefore, we need to find the number of moles of NaOH to solve for molarity. From the preceding equation for the reaction between KHP and NaOH shown in the text we see that 1 mole of KHP neutralizes 1 mole of NaOH. How many moles of KHP are conta ...
Sources of uncertainty of thermodynamic and reaction
... There is a hierachy of approximations in routine methods 1. one solves the nonrelativistic Schrödinger equation for the electrons + atomic nuclei system 2. Born-Oppenheimer approximation: electrons and nuclei treated separately a. solve the electron Schrödinger equation for electrons at fixed nuclea ...
... There is a hierachy of approximations in routine methods 1. one solves the nonrelativistic Schrödinger equation for the electrons + atomic nuclei system 2. Born-Oppenheimer approximation: electrons and nuclei treated separately a. solve the electron Schrödinger equation for electrons at fixed nuclea ...
Chemistry 2000 Lecture 19: Organic acids
... If we repeat the above calculation at a number of different pH values and plot the results, we obtain distribution curves for the acid and its conjugate base. ...
... If we repeat the above calculation at a number of different pH values and plot the results, we obtain distribution curves for the acid and its conjugate base. ...
Equilibrium chemistry
Equilibrium chemistry is a concerned with systems in chemical equilibrium. The unifying principle is that the free energy of a system at equilibrium is the minimum possible, so that the slope of the free energy with respect to the reaction coordinate is zero. This principle, applied to mixtures at equilibrium provides a definition of an equilibrium constant. Applications include acid-base, host-guest, metal-complex, solubility, partition, chromatography and redox equilibria.