5H2O → CuSO4 + 5H2O(g)
... 1) An atom (or molecule) in its elemental state has an oxidation number of 0. 2) An atom in a monatomic ion (Na+, Cl-) has an oxidation number identical to its charge. 3a) Hydrogen has an oxidation number of +1, unless it is combined with a metal, in which case it has an oxidation number of –1. 3b) ...
... 1) An atom (or molecule) in its elemental state has an oxidation number of 0. 2) An atom in a monatomic ion (Na+, Cl-) has an oxidation number identical to its charge. 3a) Hydrogen has an oxidation number of +1, unless it is combined with a metal, in which case it has an oxidation number of –1. 3b) ...
4/3 Lecture Slides
... It is desired to separate the following two compounds: CH3(CH2)3OH and CH3(CH2)3NH2. The two compounds have similar KOW values (around 11) but the second compound is basic. What can be done to separate the two? It is desired to transfer butanol (left compound in #2) from water to an organic phase. W ...
... It is desired to separate the following two compounds: CH3(CH2)3OH and CH3(CH2)3NH2. The two compounds have similar KOW values (around 11) but the second compound is basic. What can be done to separate the two? It is desired to transfer butanol (left compound in #2) from water to an organic phase. W ...
UNITS OF CONCENTRATION
... takes into account the actual number of reacting species per mole of reagent (i.e., protons in the case of acid/base reactions or electrons in the case of redox reactions). For acids, an equivalent is defined as one mole of protons. The equivalent amount of any acid is the amount of acid that delive ...
... takes into account the actual number of reacting species per mole of reagent (i.e., protons in the case of acid/base reactions or electrons in the case of redox reactions). For acids, an equivalent is defined as one mole of protons. The equivalent amount of any acid is the amount of acid that delive ...
Lecture 2: Introduction to Proteins
... PRACTICE PROBLEMS (Work these without looking at the answers, which are on the last page.) pH/pK/buffer review & practice problems, page 2 of 4 ...
... PRACTICE PROBLEMS (Work these without looking at the answers, which are on the last page.) pH/pK/buffer review & practice problems, page 2 of 4 ...
oxidation and reduction
... During a redox reaction, the oxidant becomes reduced and the reductant becomes oxidised. e) Complete the following table by inserting the formulae of the species to which the given oxidants are reduced, and any colour change, precipitate formation or evolution of gas which is observed. ...
... During a redox reaction, the oxidant becomes reduced and the reductant becomes oxidised. e) Complete the following table by inserting the formulae of the species to which the given oxidants are reduced, and any colour change, precipitate formation or evolution of gas which is observed. ...
Chapter 4 Student Notes
... The double arrow means that the reaction is significant in both directions. It indicates that there is a balance between the forward and reverse reactions. This balance produces a state of chemical equilibrium. ...
... The double arrow means that the reaction is significant in both directions. It indicates that there is a balance between the forward and reverse reactions. This balance produces a state of chemical equilibrium. ...
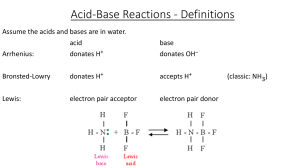
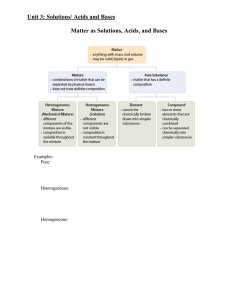
Outline for Unit 1 Solutions, Acid/Base, and Gases
... 3. Temperature – at higher temp kinetic energy of the solvent is higher so more collisions of solvent molecules with solute 4. Particle size – smaller particles dissolve faster since there is more surface area available to solvent 5. Pressure (partial pressure) – only affects gas in liquids – solubi ...
... 3. Temperature – at higher temp kinetic energy of the solvent is higher so more collisions of solvent molecules with solute 4. Particle size – smaller particles dissolve faster since there is more surface area available to solvent 5. Pressure (partial pressure) – only affects gas in liquids – solubi ...
Chemistry
... 11. _____(T/F) A one molar solution of sodium fluoride (NaF) would lower the vapor pressure of water to the same extent that a one molar solution of magnesium chloride (MgCl2). 12. _____(T/F) Elevation of the vapor pressure due to the increase in the number of nonvolatile solute particles will not a ...
... 11. _____(T/F) A one molar solution of sodium fluoride (NaF) would lower the vapor pressure of water to the same extent that a one molar solution of magnesium chloride (MgCl2). 12. _____(T/F) Elevation of the vapor pressure due to the increase in the number of nonvolatile solute particles will not a ...
Equilibrium chemistry
Equilibrium chemistry is a concerned with systems in chemical equilibrium. The unifying principle is that the free energy of a system at equilibrium is the minimum possible, so that the slope of the free energy with respect to the reaction coordinate is zero. This principle, applied to mixtures at equilibrium provides a definition of an equilibrium constant. Applications include acid-base, host-guest, metal-complex, solubility, partition, chromatography and redox equilibria.