Reactions
... 1. Every chemical compound has a formula which cannot be altered. 2. A chemical reaction must account for every atom that is used. This is an application of the Law of Conservation of Matter which states that in a chemical reaction atoms are neither created nor destroyed. ...
... 1. Every chemical compound has a formula which cannot be altered. 2. A chemical reaction must account for every atom that is used. This is an application of the Law of Conservation of Matter which states that in a chemical reaction atoms are neither created nor destroyed. ...
pure liquid-vapour equilibrium - Theoretical and Computational
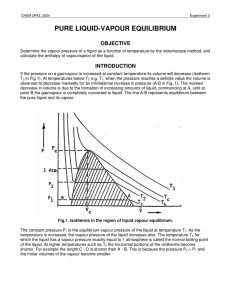
... Part of the shaded area, up to the normal boiling point, Tb, of the liquid, is the subject of this experiment in which the vapour pressure dependence on temperature will be investigated. This dependence can be related to the enthalpy of vapourisation Hvap in the following way. For equilibrium betwee ...
... Part of the shaded area, up to the normal boiling point, Tb, of the liquid, is the subject of this experiment in which the vapour pressure dependence on temperature will be investigated. This dependence can be related to the enthalpy of vapourisation Hvap in the following way. For equilibrium betwee ...
Document
... change in the amount of component A with all other parameters held constant. It is essentially the free energy increase (or decrease) associated with adding a little of A to the system. ...
... change in the amount of component A with all other parameters held constant. It is essentially the free energy increase (or decrease) associated with adding a little of A to the system. ...
Document
... Standard enthalpy of formation of a compound, Hof, is the enthalpy change for the formation of 1 mol of compound with all substances in their standard ...
... Standard enthalpy of formation of a compound, Hof, is the enthalpy change for the formation of 1 mol of compound with all substances in their standard ...
Measuring Rates
... The integrated rate law for a chemical reaction expresses how the concentration of a relevant reacting species changes as a function of time. Thus, it can be used to predict the time it will take for a reactant or product to reach a given concentration, or to predict such concentration at a selected ...
... The integrated rate law for a chemical reaction expresses how the concentration of a relevant reacting species changes as a function of time. Thus, it can be used to predict the time it will take for a reactant or product to reach a given concentration, or to predict such concentration at a selected ...
1 Fundamentals of Chemical Kinetics
... Chemical kinetics is the quantitative study of chemical systems that are changing with time. (Thermodynamics, another of the major branches of physical chemistry, applies to systems at equilibrium—those that do not change with time.) In this course, we will restrict our attention to systems that are ...
... Chemical kinetics is the quantitative study of chemical systems that are changing with time. (Thermodynamics, another of the major branches of physical chemistry, applies to systems at equilibrium—those that do not change with time.) In this course, we will restrict our attention to systems that are ...
AP® Chemistry
... Labs: Selecting Indicators for Acid-Base Titrations (Vonderbrink #16) (SP 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 7) Guided Inquiry Lab: Analysis by Redox Titration (Jennifer Cook Miller – Moline HS) (SP 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7) ...
... Labs: Selecting Indicators for Acid-Base Titrations (Vonderbrink #16) (SP 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 7) Guided Inquiry Lab: Analysis by Redox Titration (Jennifer Cook Miller – Moline HS) (SP 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7) ...
Kinetic Study of the Reaction of Diborane with Phosphine*
... reaction of the borine "radical" with one of the reactants. The apparent activation energy of each reaction included contributions from various elementary steps. While the heat of dissociation of diborane could not be estimated from the temperature coefficient of these rate studies, an upper limit f ...
... reaction of the borine "radical" with one of the reactants. The apparent activation energy of each reaction included contributions from various elementary steps. While the heat of dissociation of diborane could not be estimated from the temperature coefficient of these rate studies, an upper limit f ...
WJEC CBAC AS/A LEVEL GCE in Chemistry REVISION AID UNIT 1
... All radioactive radiation is potentially harmful. High energy alpha and beta particles can damage cells and DNA, as can the highly penetrating gamma rays. Changes in DNA can cause mutations of genes with unfortunate genetic effects and the production of cancer causing cells. Leukaemia is a common il ...
... All radioactive radiation is potentially harmful. High energy alpha and beta particles can damage cells and DNA, as can the highly penetrating gamma rays. Changes in DNA can cause mutations of genes with unfortunate genetic effects and the production of cancer causing cells. Leukaemia is a common il ...
Equilibrium chemistry
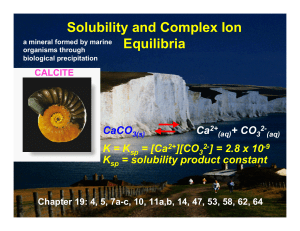
Equilibrium chemistry is a concerned with systems in chemical equilibrium. The unifying principle is that the free energy of a system at equilibrium is the minimum possible, so that the slope of the free energy with respect to the reaction coordinate is zero. This principle, applied to mixtures at equilibrium provides a definition of an equilibrium constant. Applications include acid-base, host-guest, metal-complex, solubility, partition, chromatography and redox equilibria.