Dielectric and thermodynamic response of a
... induced in the solvent by a reflecting boundary, but it necessitates the introduction of a cutoff, described below, which is applied to the reaction field forces on solvent molecules approaching the surface of the spherical cavity. A series of molecular dynamics simulations of liquid water, as well ...
... induced in the solvent by a reflecting boundary, but it necessitates the introduction of a cutoff, described below, which is applied to the reaction field forces on solvent molecules approaching the surface of the spherical cavity. A series of molecular dynamics simulations of liquid water, as well ...
1 Acids and Bases
... be present in the solution. Some substances that are placed in water may become involved with either the hydrogen or hydroxide ions and alter the equilibrium state. However, as long as the temperature is kept constant at 25◦ C, the equilibrium will shift to maintain the equilibrium constant, Kw , at ...
... be present in the solution. Some substances that are placed in water may become involved with either the hydrogen or hydroxide ions and alter the equilibrium state. However, as long as the temperature is kept constant at 25◦ C, the equilibrium will shift to maintain the equilibrium constant, Kw , at ...
Activity C14: Rate of a Chemical Reaction 1
... to use a Colorimeter to measure the formation of the solid sulfur generated. The solid sulfur will block the light in the Colorimeter and the amount of blockage is directly proportional to the amount of sulfur in suspension. The rate of this chemical reaction is given by the equation: Rate = k [thio ...
... to use a Colorimeter to measure the formation of the solid sulfur generated. The solid sulfur will block the light in the Colorimeter and the amount of blockage is directly proportional to the amount of sulfur in suspension. The rate of this chemical reaction is given by the equation: Rate = k [thio ...
Η - Knockhardy
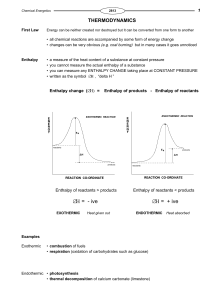
... Standard Enthalpy Changes • enthalpy values vary according to the conditions - so standard conditions are needed • a substance will then be in its standard state ... Pressure:- 100 kPa (1 atmosphere) ...
... Standard Enthalpy Changes • enthalpy values vary according to the conditions - so standard conditions are needed • a substance will then be in its standard state ... Pressure:- 100 kPa (1 atmosphere) ...
الشريحة 1
... themselves on the surface of the NaCl crystals. The +ve end of H2O dipole is oriented toward the Clions, and the –ve end of the H2O dipole is oriented toward the Na+ ions. The ion-dipole attractions between the ions and H2O molecules are strong enough to pull the ions from their positions in the cry ...
... themselves on the surface of the NaCl crystals. The +ve end of H2O dipole is oriented toward the Clions, and the –ve end of the H2O dipole is oriented toward the Na+ ions. The ion-dipole attractions between the ions and H2O molecules are strong enough to pull the ions from their positions in the cry ...
fulltext (9)
... the alkalic CMCTS solutions (pH = 12.4) at least for 6 months. However, black precipitation can be observed in the acidic solution (pH 0.7 and pH 2.2) within 24 h, indicating that pH 12.4 is an ideal condition for synthesizing and preserving AgNPs in the CMCTS solutions. We speculated that the chang ...
... the alkalic CMCTS solutions (pH = 12.4) at least for 6 months. However, black precipitation can be observed in the acidic solution (pH 0.7 and pH 2.2) within 24 h, indicating that pH 12.4 is an ideal condition for synthesizing and preserving AgNPs in the CMCTS solutions. We speculated that the chang ...
A Quantitative Theory of Negative Adsorption of Nonelectrolytes
... interface. We have analyzed this phenomenon from the point of view that the solute molecules are repelled from the interface because of the existence of a repulsive van der Waals force. The theoretical treatment employs the Lifshitz theory of forces, together with the thermodynamic theory of interfa ...
... interface. We have analyzed this phenomenon from the point of view that the solute molecules are repelled from the interface because of the existence of a repulsive van der Waals force. The theoretical treatment employs the Lifshitz theory of forces, together with the thermodynamic theory of interfa ...
Water - UFMG
... as many as four neighboring water molecules. In liquid water at room temperature and atmospheric pressure, however, water molecules are disorganized and in continuous motion, so that each molecule forms hydrogen bonds with an average of only 3.4 other molecules. In ice, on the other hand, each water ...
... as many as four neighboring water molecules. In liquid water at room temperature and atmospheric pressure, however, water molecules are disorganized and in continuous motion, so that each molecule forms hydrogen bonds with an average of only 3.4 other molecules. In ice, on the other hand, each water ...
Part II - American Chemical Society
... score on Part II. Testing materials, scratch paper, and the “Blue Book” should be made available to the student only during the examination period. All testing materials including scratch paper should be turned in and kept secure until April 27, 2003, after which tests can be returned to students an ...
... score on Part II. Testing materials, scratch paper, and the “Blue Book” should be made available to the student only during the examination period. All testing materials including scratch paper should be turned in and kept secure until April 27, 2003, after which tests can be returned to students an ...
Chapter 4 Aqueous Reactions and Solution Stoichiometry
... • Homogeneous mixtures of two or more pure substances. • The solvent is present in greatest abundance. • All other substances are solutes. ...
... • Homogeneous mixtures of two or more pure substances. • The solvent is present in greatest abundance. • All other substances are solutes. ...
RLE-TR-059-047069 - DSpace@MIT - Massachusetts Institute of
... information is still obtained by making the rigid rotor approximation. In the case of OCS the rigid rotor approximation is not a bad one, since it is the shift in frequency of the absorption due to an isotopic substitution upon which the interatomic distances are dependent. This may be seen roughly ...
... information is still obtained by making the rigid rotor approximation. In the case of OCS the rigid rotor approximation is not a bad one, since it is the shift in frequency of the absorption due to an isotopic substitution upon which the interatomic distances are dependent. This may be seen roughly ...
2009
... c. Based on the proper thermochemical data calculate enthalpies of elemental parallel reactions of chlorine-induced formation of 1- and 2-propyl radicals (ΔHI, ΔHII), as well as analogous reactions with bromine (ΔHIII, ΔHIV). Compare results of calculations. What is the difference of enthalpies of p ...
... c. Based on the proper thermochemical data calculate enthalpies of elemental parallel reactions of chlorine-induced formation of 1- and 2-propyl radicals (ΔHI, ΔHII), as well as analogous reactions with bromine (ΔHIII, ΔHIV). Compare results of calculations. What is the difference of enthalpies of p ...
Energetics of the primary electron transfer reaction revealed by
... obtained by continuum generation. They interrogate the absorbance changes as a function of time delay tD. Parallel polarizations of the exciting and probing pulses are used. The sample concentration was adjusted to yield a transmission Tx 10% at I= 865 nm. At room temperature, non-adiabatic ET theor ...
... obtained by continuum generation. They interrogate the absorbance changes as a function of time delay tD. Parallel polarizations of the exciting and probing pulses are used. The sample concentration was adjusted to yield a transmission Tx 10% at I= 865 nm. At room temperature, non-adiabatic ET theor ...
Equilibrium chemistry
Equilibrium chemistry is a concerned with systems in chemical equilibrium. The unifying principle is that the free energy of a system at equilibrium is the minimum possible, so that the slope of the free energy with respect to the reaction coordinate is zero. This principle, applied to mixtures at equilibrium provides a definition of an equilibrium constant. Applications include acid-base, host-guest, metal-complex, solubility, partition, chromatography and redox equilibria.