document
... __________20. The number of atoms on both sides of an equation must be equal for each element. Part C: For each of the following compounds, identify the number of atoms of each element. ...
... __________20. The number of atoms on both sides of an equation must be equal for each element. Part C: For each of the following compounds, identify the number of atoms of each element. ...
synthesis reaction
... Any process in which an element loses electrons during a chemical reaction is called an oxidation. Oxygen is not necessary for an element to go through oxidation. This is a broad term for losing electrons. Sodium (Na) atoms go through oxidation to become ions: Na Na+ + 1e-. Everything in group ...
... Any process in which an element loses electrons during a chemical reaction is called an oxidation. Oxygen is not necessary for an element to go through oxidation. This is a broad term for losing electrons. Sodium (Na) atoms go through oxidation to become ions: Na Na+ + 1e-. Everything in group ...
Chemistry: The Molecular Nature of Matter and Change
... 3. Effect of temperature change on rates 4. Energy of activation; the role of catalysts 5. The relationship between the rate-determining step and a mechanism E. Thermodynamics 1. State functions 2. First law: change in enthalpy; heat of formation; heat of reaction; Hess's law; heats of vaporization ...
... 3. Effect of temperature change on rates 4. Energy of activation; the role of catalysts 5. The relationship between the rate-determining step and a mechanism E. Thermodynamics 1. State functions 2. First law: change in enthalpy; heat of formation; heat of reaction; Hess's law; heats of vaporization ...
The only sure evidence that a chemical reaction has occured is
... 3. A shorter, easier way to show chemical reactions, using symbols instead of words, is called a _____. 4. The substances on the left of the arrow in a chemical equation are the substances you start with called ______. 5. Give an example of a change that is NOT a chemical reaction? 6. How many atoms ...
... 3. A shorter, easier way to show chemical reactions, using symbols instead of words, is called a _____. 4. The substances on the left of the arrow in a chemical equation are the substances you start with called ______. 5. Give an example of a change that is NOT a chemical reaction? 6. How many atoms ...
Exam 2 Fall 2005 Chemsitry 1211
... This exam is twenty five questions long. Each question is worth 4 points. Please read through all of the questions first and ask about anything you do not understand. You will have one hour and 15 minutes to complete this exam. Exams will be picked up at the end of the class period. No late exams wi ...
... This exam is twenty five questions long. Each question is worth 4 points. Please read through all of the questions first and ask about anything you do not understand. You will have one hour and 15 minutes to complete this exam. Exams will be picked up at the end of the class period. No late exams wi ...
Ch. 2 The Chemistry of Life
... - ____________ that _________ energy will not occur without a source of _________ - _____________ need to carry out _____________ that require _________ in order to stay ________ - ____________ release the energy needed to ________, breathe, __________, & even __________ through chemical reactions - ...
... - ____________ that _________ energy will not occur without a source of _________ - _____________ need to carry out _____________ that require _________ in order to stay ________ - ____________ release the energy needed to ________, breathe, __________, & even __________ through chemical reactions - ...
Exam 3 Answer Key
... Which of the following statements are true? A. In Bohr’s atomic theory, when an electron moves from one energy level to another energy level more distant from the nucleus, energy is emitted. B. The principal quantum number determines the size and the shape of the orbitals. C. Mendeleev assembled the ...
... Which of the following statements are true? A. In Bohr’s atomic theory, when an electron moves from one energy level to another energy level more distant from the nucleus, energy is emitted. B. The principal quantum number determines the size and the shape of the orbitals. C. Mendeleev assembled the ...
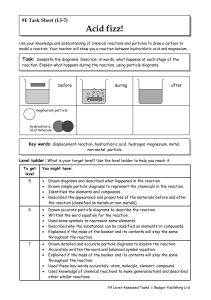
Year 9 Homework Task 9E-5 Reactions 5-7
... Level ladder: What is your target level? Use the level ladder to help you reach it: To get level ...
... Level ladder: What is your target level? Use the level ladder to help you reach it: To get level ...
Equilibrium 4 Noteform - IndustrialProcesses
... 2. How can the rate be maximized? (Think about the factors that affect the rate of a chemical reaction.) ...
... 2. How can the rate be maximized? (Think about the factors that affect the rate of a chemical reaction.) ...
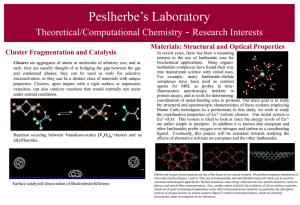
Cluster Fragmentation and Catalysis
... interest in the use of lanthanide ions for biochemical applications. Many organolanthanide complexes have found their way into mainstream science with varied uses. For example, many lanthanide-chelate complexes have been used as contrast agents for MRI, as probes in timefluorescence spectroscopy, ma ...
... interest in the use of lanthanide ions for biochemical applications. Many organolanthanide complexes have found their way into mainstream science with varied uses. For example, many lanthanide-chelate complexes have been used as contrast agents for MRI, as probes in timefluorescence spectroscopy, ma ...
Chemistry I Final Review
... CUMULATIVE QUIZ #2 Nuclear: 13. Write the nuclear equation for the: a. alpha decay of Uranium-238 ...
... CUMULATIVE QUIZ #2 Nuclear: 13. Write the nuclear equation for the: a. alpha decay of Uranium-238 ...
Lecture 8
... - Large activation energies arise in reactions where covalent bonds must be broken before new ones are formed, or where atoms must move through solids. - Reactions involving free radicals, or ions in solution, often have small (sometimes zero) activation energies. ...
... - Large activation energies arise in reactions where covalent bonds must be broken before new ones are formed, or where atoms must move through solids. - Reactions involving free radicals, or ions in solution, often have small (sometimes zero) activation energies. ...
Test 4
... 2. Define the following terms: Spontaneous process A process that will occur without input of energy from a external source. Second law of thermodynamics In any spontaneous process the entropy of the universe always increases. Positional disorder Randomness that comes from the number of different ar ...
... 2. Define the following terms: Spontaneous process A process that will occur without input of energy from a external source. Second law of thermodynamics In any spontaneous process the entropy of the universe always increases. Positional disorder Randomness that comes from the number of different ar ...
File - Ingolstadt Academy
... Density (definition and equation) Dimensional analysis Instruments that measure mass, volume, pressure, etc. (lab stuff!) The Scientific Method Atomic Structure: ...
... Density (definition and equation) Dimensional analysis Instruments that measure mass, volume, pressure, etc. (lab stuff!) The Scientific Method Atomic Structure: ...
CHM 101 - Academic Computer Center
... Cold packs, whose temperatures are lowered when ammonium nitrate dissolves in water, are carried by athletic trainers when transporting ice is not possible. Which of the following is true of this reaction? A. H < 0, process is exothermic B. H > 0, process is exothermic C. H < 0, process is endoth ...
... Cold packs, whose temperatures are lowered when ammonium nitrate dissolves in water, are carried by athletic trainers when transporting ice is not possible. Which of the following is true of this reaction? A. H < 0, process is exothermic B. H > 0, process is exothermic C. H < 0, process is endoth ...
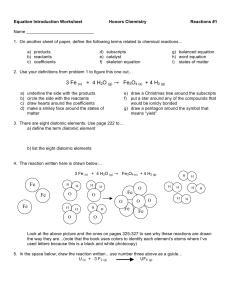
Equation Intro Worksheet 1213
... Look at the above picture and the ones on pages 325-327 to see why these reactions are drawn the way they are…(note that the book uses colors to identify each element’s atoms where I’ve used letters because this is a black and white photocopy) 5. In the space below, draw the reaction written…use num ...
... Look at the above picture and the ones on pages 325-327 to see why these reactions are drawn the way they are…(note that the book uses colors to identify each element’s atoms where I’ve used letters because this is a black and white photocopy) 5. In the space below, draw the reaction written…use num ...
What are reactions?
... 1. Hydrogen and carbon dioxide are __________. If they are formed in a reaction you will see __________. This can be a sign that a chemical __________ has happened. 2. Other signs of a chemical reaction might be an increase in temperature if _____ is released or a change in ________. 3. Physical cha ...
... 1. Hydrogen and carbon dioxide are __________. If they are formed in a reaction you will see __________. This can be a sign that a chemical __________ has happened. 2. Other signs of a chemical reaction might be an increase in temperature if _____ is released or a change in ________. 3. Physical cha ...
What are reactions? - UTLNET Secure Site
... 1. Hydrogen and carbon dioxide are __________. If they are formed in a reaction you will see __________. This can be a sign that a chemical __________ has happened. 2. Other signs of a chemical reaction might be an increase in temperature if _____ is released or a change in ________. 3. Physical cha ...
... 1. Hydrogen and carbon dioxide are __________. If they are formed in a reaction you will see __________. This can be a sign that a chemical __________ has happened. 2. Other signs of a chemical reaction might be an increase in temperature if _____ is released or a change in ________. 3. Physical cha ...
General Chemistry - Review for final exam: (Make sure you bring
... 71. In the above reaction, NaCl + F2 NaF + Cl2, F is more or less reactive than Cl? 72. In the activity series of metals are the more reactive metals found on the top or the bottom of the chart? 73. What conditions in the reactants must be present in order for a double-replacement to take place? 7 ...
... 71. In the above reaction, NaCl + F2 NaF + Cl2, F is more or less reactive than Cl? 72. In the activity series of metals are the more reactive metals found on the top or the bottom of the chart? 73. What conditions in the reactants must be present in order for a double-replacement to take place? 7 ...
ConcepTest On Simple Redox Reactions
... Comment to Instructor: Correct answer is 3. HCl. Since the oxidation number of H is decreasing from +1 to 0, it is undergoing reduction. Zn is being oxidized, and HCl is the “agent” that is causing the Zn to be oxidized. #4 indicates that the student is thinking that the Zn+2in ZnCl2 is undergoing r ...
... Comment to Instructor: Correct answer is 3. HCl. Since the oxidation number of H is decreasing from +1 to 0, it is undergoing reduction. Zn is being oxidized, and HCl is the “agent” that is causing the Zn to be oxidized. #4 indicates that the student is thinking that the Zn+2in ZnCl2 is undergoing r ...
Chapter 19 part 1
... • Electrochemical processes • Oxidation-reduction processes, which involve electron transfers from one substance to another • Energy released by a spontaneous chemical reaction is converted into electricity (e.g. battery) • Electrical energy can be used to force a non-spontaneous reaction to occur ( ...
... • Electrochemical processes • Oxidation-reduction processes, which involve electron transfers from one substance to another • Energy released by a spontaneous chemical reaction is converted into electricity (e.g. battery) • Electrical energy can be used to force a non-spontaneous reaction to occur ( ...
1. What are micelles? Give two examples of micellar systems. Sol. A
... energetically preferred orientation has the magnetic moment aligned parallel with the applied field (spin +1/2) and is often given the notation , whereas the higher energy anti-parallel orientation (spin -1/2) is referred to as . The rotational axis of the spinning nucleus cannot be orientated exact ...
... energetically preferred orientation has the magnetic moment aligned parallel with the applied field (spin +1/2) and is often given the notation , whereas the higher energy anti-parallel orientation (spin -1/2) is referred to as . The rotational axis of the spinning nucleus cannot be orientated exact ...
This `practice exam`
... 30. Which of the following types of experiments demonstrate that an electron has the properties of a particle? a) nuclear fission b) electron diffraction c) light emission from atomic gases d) mass spectroscopy e) photoelectric effect 31. Which of the following sets of quantum numbers refers to a 4p ...
... 30. Which of the following types of experiments demonstrate that an electron has the properties of a particle? a) nuclear fission b) electron diffraction c) light emission from atomic gases d) mass spectroscopy e) photoelectric effect 31. Which of the following sets of quantum numbers refers to a 4p ...
1 Lecture 11. Redox Chemistry Many elements in the periodic table
... Steps for relating half-reaction voltages and activities from the Nernst Equation (4 or 5): Write a balanced half-reaction (see below rules in assigning oxidation numbers). Determine DGr° (from tabulated DGf° values, using molar coefficients and DGf° of e- = 0) Determine Eho from DGr°, or a given va ...
... Steps for relating half-reaction voltages and activities from the Nernst Equation (4 or 5): Write a balanced half-reaction (see below rules in assigning oxidation numbers). Determine DGr° (from tabulated DGf° values, using molar coefficients and DGf° of e- = 0) Determine Eho from DGr°, or a given va ...
Electronic Spectroscopy of Transition Metal Ions
... in order to understand the spectroscopy of d ions with more than one d electron we must take the effect of e- - e- repulsion into account (we have ignored this so far) ...
... in order to understand the spectroscopy of d ions with more than one d electron we must take the effect of e- - e- repulsion into account (we have ignored this so far) ...
Photoredox catalysis
_Schematic.png?width=300)
Photoredox catalysis is a branch of catalysis that harnesses the energy of visible light to accelerate a chemical reaction via a single-electron transfer. This area is named as a combination of ""photo-"" referring to light and redox, a condensed expression for the chemical processes of reduction and oxidation. In particular, photoredox catalysis employs small quantities of a light-sensitive compound that, when excited by light, can mediate the transfer of electrons between chemical compounds that otherwise would not react. Photoredox catalysts are generally drawn from three classes of materials: transition-metal complexes, organic dyes and semiconductors. While each class of materials has advantages, soluble transition-metal complexes are used most often.Study of this branch of catalysis led to the development of new methods to accomplish known and new chemical transformations. One attraction to the area is that photoredox catalysts are often less toxic than other reagents often used to generate free radicals, such as organotin reagents. Furthermore, while photoredox catalysts generate potent redox agents while exposed to light, they are innocuous under ordinary conditions Thus transition-metal complex photoredox catalysts are in some ways more attractive than stoichiometric redox agents such as quinones. The properties of photoredox catalysts can be modified by changing ligands and the metal, reflecting the somewhat modular nature of the catalyst.While photoredox catalysis has most often been applied to generate known reactive intermediates in a novel way, the study of this mode of catalysis led to the discovery of new organic reactions, such as the first direct functionalization of the β-arylation of saturated aldehydes. Although the D3-symmetric transition-metal complexes used in many photoredox-catalyzed reactions are chiral, the use of enantioenriched photoredox catalysts led to low levels of enantioselectivity in a photoredox-catalyzed aryl-aryl coupling reaction, suggesting that the chiral nature of these catalysts is not yet a highly effective means of transmitting stereochemical information in photoredox reactions. However, while synthetically useful levels of enantioselectivity have not been achieved using chiral photoredox catalysts alone, optically-active products have been obtained through the synergistic combination of photoredox catalysis with chiral organocatalysts such as secondary amines and Brønsted acids.